La primera búsqueda en profundidad (DFS) se ha discutido en este artículo que utiliza la lista de adyacencia para la representación gráfica. En este artículo, se utilizará la array de adyacencia para representar el gráfico.
Representación de array de adyacencia: en la representación de array de adyacencia de un gráfico, la array mat[][] de tamaño n*n (donde n es el número de vértices) representará los bordes del gráfico donde mat[i][j] = 1 representa que hay una arista entre los vértices i y j mientras que mat[i][j] = 0 representa que no hay arista entre los vértices i y j .
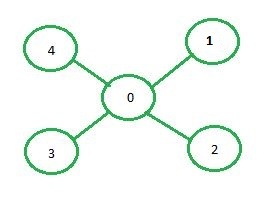
A continuación se muestra la representación de la array de adyacencia del gráfico que se muestra en la imagen de arriba:
0 1 2 3 4 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 2 1 0 0 0 0 3 1 0 0 0 0 4 1 0 0 0 0
Ejemplos:
Input: source = 0
Output: 0 1 3 2 Input: source = 0

Output: 0 1 2 3 4
Acercarse:
- Cree una array de tamaño n*n donde cada elemento sea 0 y represente que no hay borde en el gráfico.
- Ahora, para cada borde del gráfico entre los vértices i y j, establezca mat[i][j] = 1.
- Después de que se haya creado y llenado la array de adyacencia, llame a la función recursiva para la fuente, es decir, el vértice 0 que llamará recursivamente a la misma función para todos los vértices adyacentes.
- Además, mantenga una array para realizar un seguimiento de los vértices visitados, es decir, visited[i] = true representa que el vértice i ha sido visitado antes y no es necesario llamar a la función DFS para algún Node ya visitado.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// adjacency matrix
vector<vector<int> > adj;
// function to add edge to the graph
void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
adj[x][y] = 1;
adj[y][x] = 1;
}
// function to perform DFS on the graph
void dfs(int start, vector<bool>& visited)
{
// Print the current node
cout << start << " ";
// Set current node as visited
visited[start] = true;
// For every node of the graph
for (int i = 0; i < adj[start].size(); i++) {
// If some node is adjacent to the current node
// and it has not already been visited
if (adj[start][i] == 1 && (!visited[i])) {
dfs(i, visited);
}
}
}
int main()
{
// number of vertices
int v = 5;
// number of edges
int e = 4;
// adjacency matrix
adj = vector<vector<int> >(v, vector<int>(v, 0));
addEdge(0, 1);
addEdge(0, 2);
addEdge(0, 3);
addEdge(0, 4);
// Visited vector to so that
// a vertex is not visited more than once
// Initializing the vector to false as no
// vertex is visited at the beginning
vector<bool> visited(v, false);
// Perform DFS
dfs(0, visited);
}
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// adjacency matrix
static int[][] adj;
// function to add edge to the graph
static void addEdge(int x, int y)
{
adj[x][y] = 1;
adj[y][x] = 1;
}
// function to perform DFS on the graph
static void dfs(int start, boolean[] visited)
{
// Print the current node
System.out.print(start + " ");
// Set current node as visited
visited[start] = true;
// For every node of the graph
for (int i = 0; i < adj[start].length; i++) {
// If some node is adjacent to the current node
// and it has not already been visited
if (adj[start][i] == 1 && (!visited[i])) {
dfs(i, visited);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// number of vertices
int v = 5;
// number of edges
int e = 4;
// adjacency matrix
adj = new int[v][v];
addEdge(0, 1);
addEdge(0, 2);
addEdge(0, 3);
addEdge(0, 4);
// Visited vector to so that
// a vertex is not visited more than once
// Initializing the vector to false as no
// vertex is visited at the beginning
boolean[] visited = new boolean[v];
// Perform DFS
dfs(0, visited);
}
}
// This code is contributed by kdeepsingh2002
Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach class Graph: adj = [] # Function to fill empty adjacency matrix def __init__(self, v, e): self.v = v self.e = e Graph.adj = [[0 for i in range(v)] for j in range(v)] # Function to add an edge to the graph def addEdge(self, start, e): # Considering a bidirectional edge Graph.adj[start][e] = 1 Graph.adj[e][start] = 1 # Function to perform DFS on the graph def DFS(self, start, visited): # Print current node print(start, end = ' ') # Set current node as visited visited[start] = True # For every node of the graph for i in range(self.v): # If some node is adjacent to the # current node and it has not # already been visited if (Graph.adj[start][i] == 1 and (not visited[i])): self.DFS(i, visited) # Driver code v, e = 5, 4 # Create the graph G = Graph(v, e) G.addEdge(0, 1) G.addEdge(0, 2) G.addEdge(0, 3) G.addEdge(0, 4) # Visited vector to so that a vertex # is not visited more than once # Initializing the vector to false as no # vertex is visited at the beginning visited = [False] * v # Perform DFS G.DFS(0, visited); # This code is contributed by ng24_7
0 1 2 3 4
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por DeveshRattan y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA