En cálculo matemático, la forma expandida de una función periódica “f(x)” en términos de una suma infinita de cosenos y senos se denomina serie de Fourier. Hace uso de las relaciones de ortogonalidad de las funciones coseno y seno. En otras palabras, la serie de Fourier también se puede definir como una forma de representar cualquier función periódica “f(x)” como una suma de funciones coseno y seno (posiblemente infinitas).
Para una función periódica “f(x)”, la serie de Fourier de “f(x)” en el Rango de [ c, c+2 l ] viene dada por:
(En general, l =π) ![]()
Aquí:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Aquí, a n & b n se denominan coeficientes de seno y coseno de Fourier, respectivamente.
Nota: Si en la fórmula anterior de la Serie de Fourier, en lugar de Infinito, usamos la suma de n=1 a n=k, entonces la llamamos serie de Fourier de f(x) hasta armónicos ‘k’.
Las funciones de MATLAB utilizadas en el código son:
- disp(“txt”): este método muestra el mensaje-“txt” al usuario.
- entrada («txt»): este método muestra el mensaje-«txt» y espera a que el usuario ingrese un valor y presione la tecla Retorno.
- int(y,x 1 ,x 2 ): este método calcula la integral definida de ‘y’ de x 1 a x 2 .
- vpa(f,4): este método evalúa cada elemento de ‘f’ en al menos 4 dígitos significativos.
- ezplot(y,[x 1 ,x 2 ]): este método traza ‘y’ en el intervalo especificado [x 1 ,x 2 ].
- title(‘GFG’): Este método agrega el título-“GFG” especificado a una gráfica.
- legend(A,B,…): este método crea una leyenda con etiquetas descriptivas para cada línea trazada.
- strcat(A,B): este método concatena horizontalmente el texto en sus argumentos de entrada.
- char(f): este método convierte la array de entrada ‘f’ en una array de caracteres.
Ejemplo:
Matlab
% MATLAB code for Implementation of
% Fourier Series up to 'n' Harmonics in MATLAB:
clear all
clc
disp("Implementation of Fourier Series
up to 'n' Harmonics in MATLAB | GeeksforGeeks")
syms x
f=input("Enter the function of x, whose fourier series is to be found:");
I=input("Enter the limits of Integration [a , b] :");
k=input("Enter the number of Harmonics:");
% Lower limit of Integration
a=I(1);
% Upper limit of Integration
b=I(2);
l=(b-a)/2;
a0=(1/l)*(int(f,a,b));
Fx=a0/2;
% Calculating the nth Harmonic
for n=1:k
%To creates a new figure window
% using default property values
figure;
an(n)=(1/l)*(int(f*cos(n*pi*x/l),a,b));
bn(n)=(1/l)*(int(f*sin(n*pi*x/l),a,b));
Fx=Fx+((an(n))*cos(n*pi*x/l))+((bn(n))*sin(n*pi*x/l));
% To evaluate Each element of
% Fx to at least 4-Significant digits
Fx=vpa(Fx,4);
% To plot the curve Fx (Fourier series upto
% nth Harmonic) in the given interval [a,b]
ezplot(Fx,[a,b]);
% To add a second line plot (Given Function/f) without deleting
% the existing line plot (Fourier series upto nth Harmonic/Fx)
hold on;
ezplot(f,[a,b]);
% To plot the curve f (Given Function)
% in the given interval [a,b]
title(["The Fourier series upto ", num2str(n)," Harmonics is:"]);
% To create a legend with descriptive labels
% for both of the plotted lines (f & Fx)
legend("Fourier series","Given Function");
% To set the hold state to off
hold off;
end
disp(strcat('The Fourier series upto ', num2str(n),' Harmonics is:',char(Fx)))
Producción:
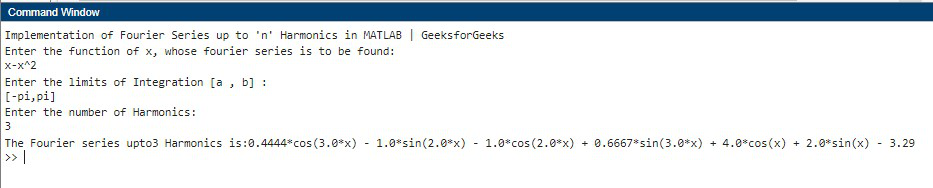
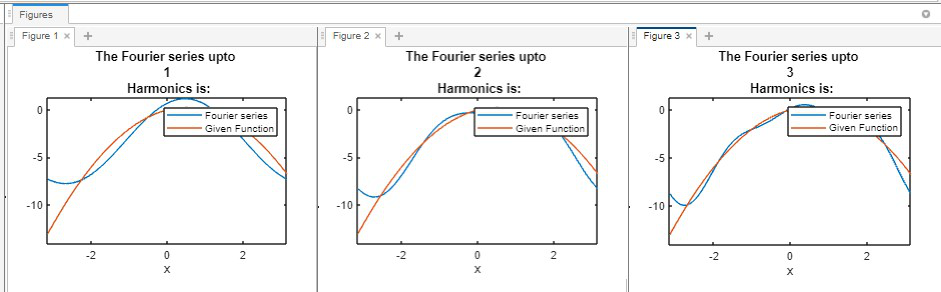
Input: For a functionin the Range= [ -π, π ], Fourier Series of f(x) up to '3' Harmonics is:
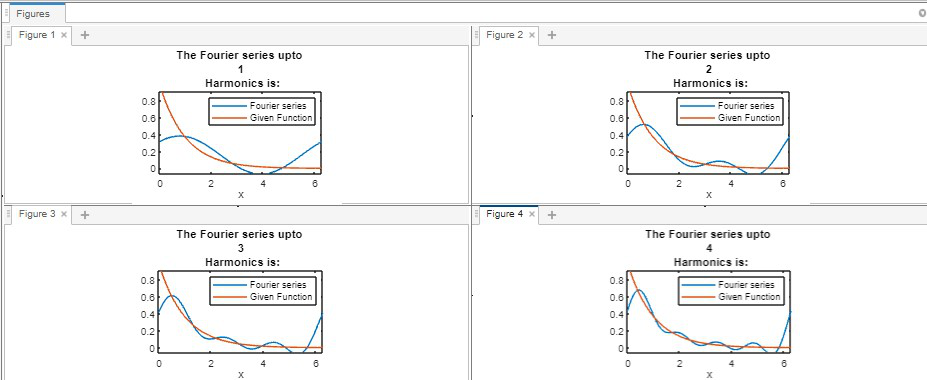
Input: For a function f(x)=e-x in the Range= [ 0, 2π ],
Fourier Series of f(x) up to '4' Harmonics is:

Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por kothavvsaakash y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA