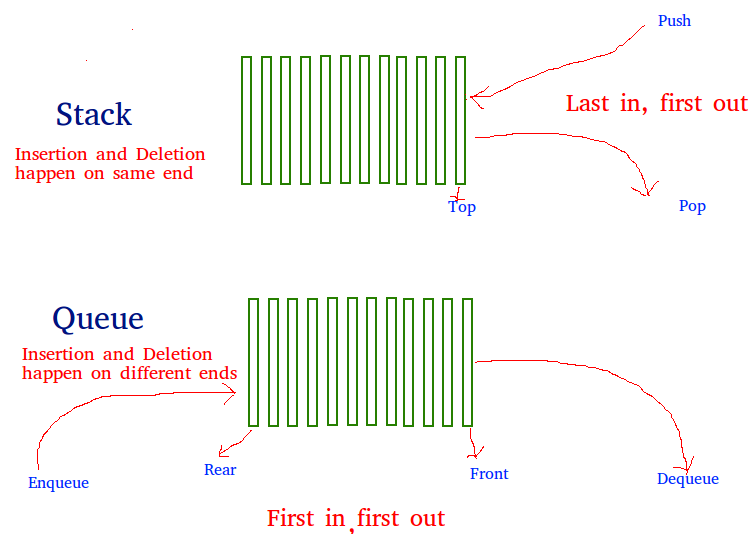
Se nos proporciona una estructura de datos de cola que admite operaciones estándar como enqueue() y dequeue(). Necesitamos implementar una estructura de datos Stack usando solo instancias de Queue y operaciones de cola permitidas en las instancias.
C++
/* Program to implement a stack using
two queue */
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Stack {
// Two inbuilt queues
queue<int> q1, q2;
public:
void push(int x)
{
// Push x first in empty q2
q2.push(x);
// Push all the remaining
// elements in q1 to q2.
while (!q1.empty()) {
q2.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
// swap the names of two queues
queue<int> q = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = q;
}
void pop()
{
// if no elements are there in q1
if (q1.empty())
return;
q1.pop();
}
int top()
{
if (q1.empty())
return -1;
return q1.front();
}
int size()
{
return q1.size();
}
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
Stack s;
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
cout << "current size: " << s.size()
<< endl;
cout << s.top() << endl;
s.pop();
cout << s.top() << endl;
s.pop();
cout << s.top() << endl;
cout << "current size: " << s.size()
<< endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Chhavi
Java
/* Java Program to implement a stack using
two queue */
import java.util.*;
class GfG {
static class Stack {
// Two inbuilt queues
static Queue<Integer> q1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
static Queue<Integer> q2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
// To maintain current number of
// elements
static int curr_size;
static void push(int x)
{
// Push x first in empty q2
q2.add(x);
// Push all the remaining
// elements in q1 to q2.
while (!q1.isEmpty()) {
q2.add(q1.peek());
q1.remove();
}
// swap the names of two queues
Queue<Integer> q = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = q;
}
static void pop()
{
// if no elements are there in q1
if (q1.isEmpty())
return;
q1.remove();
}
static int top()
{
if (q1.isEmpty())
return -1;
return q1.peek();
}
static int size()
{
return q1.size();
}
}
// driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Stack s = new Stack();
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
System.out.println("current size: " + s.size());
System.out.println(s.top());
s.pop();
System.out.println(s.top());
s.pop();
System.out.println(s.top());
System.out.println("current size: " + s.size());
}
}
// This code is contributed by Prerna
Python3
# Program to implement a stack using
# two queue
from _collections import deque
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
# Two inbuilt queues
self.q1 = deque()
self.q2 = deque()
def push(self, x):
# Push x first in empty q2
self.q2.append(x)
# Push all the remaining
# elements in q1 to q2.
while (self.q1):
self.q2.append(self.q1.popleft())
# swap the names of two queues
self.q1, self.q2 = self.q2, self.q1
def pop(self):
# if no elements are there in q1
if self.q1:
self.q1.popleft()
def top(self):
if (self.q1):
return self.q1[0]
return None
def size(self):
return len(self.q1)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = Stack()
s.push(1)
s.push(2)
s.push(3)
print("current size: ", s.size())
print(s.top())
s.pop()
print(s.top())
s.pop()
print(s.top())
print("current size: ", s.size())
# This code is contributed by PranchalK
C#
/* C# Program to implement a stack using
two queue */
using System;
using System.Collections;
class GfG {
public class Stack {
// Two inbuilt queues
public Queue q1 = new Queue();
public Queue q2 = new Queue();
public void push(int x)
{
// Push x first in empty q2
q2.Enqueue(x);
// Push all the remaining
// elements in q1 to q2.
while (q1.Count > 0) {
q2.Enqueue(q1.Peek());
q1.Dequeue();
}
// swap the names of two queues
Queue q = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = q;
}
public void pop()
{
// if no elements are there in q1
if (q1.Count == 0)
return;
q1.Dequeue();
}
public int top()
{
if (q1.Count == 0)
return -1;
return (int)q1.Peek();
}
public int size()
{
return q1.Count;
}
};
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Stack s = new Stack();
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
Console.WriteLine("current size: " + s.size());
Console.WriteLine(s.top());
s.pop();
Console.WriteLine(s.top());
s.pop();
Console.WriteLine(s.top());
Console.WriteLine("current size: " + s.size());
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
C++
/* Program to implement a stack
using two queue */
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Stack {
queue<int> q1, q2;
public:
void pop()
{
if (q1.empty())
return;
// Leave one element in q1 and
// push others in q2.
while (q1.size() != 1) {
q2.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
// Pop the only left element
// from q1
q1.pop();
// swap the names of two queues
queue<int> q = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = q;
}
void push(int x)
{
q1.push(x);
}
int top()
{
if (q1.empty())
return -1;
while (q1.size() != 1) {
q2.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
// last pushed element
int temp = q1.front();
// to empty the auxiliary queue after
// last operation
q1.pop();
// push last element to q2
q2.push(temp);
// swap the two queues names
queue<int> q = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = q;
return temp;
}
int size()
{
return q1.size();
}
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
Stack s;
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
s.push(4);
cout << "current size: " << s.size()
<< endl;
cout << s.top() << endl;
s.pop();
cout << s.top() << endl;
s.pop();
cout << s.top() << endl;
cout << "current size: " << s.size()
<< endl;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Chhavi
Java
/* Java Program to implement a stack
using two queue */
import java.util.*;
class Stack {
Queue<Integer> q1 = new LinkedList<>(), q2 = new LinkedList<>();
void remove()
{
if (q1.isEmpty())
return;
// Leave one element in q1 and
// push others in q2.
while (q1.size() != 1) {
q2.add(q1.peek());
q1.remove();
}
// Pop the only left element
// from q1
q1.remove();
// swap the names of two queues
Queue<Integer> q = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = q;
}
void add(int x)
{
q1.add(x);
}
int top()
{
if (q1.isEmpty())
return -1;
while (q1.size() != 1) {
q2.add(q1.peek());
q1.remove();
}
// last pushed element
int temp = q1.peek();
// to empty the auxiliary queue after
// last operation
q1.remove();
// push last element to q2
q2.add(temp);
// swap the two queues names
Queue<Integer> q = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = q;
return temp;
}
int size()
{
return q1.size();
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Stack s = new Stack();
s.add(1);
s.add(2);
s.add(3);
s.add(4);
System.out.println("current size: " + s.size());
System.out.println(s.top());
s.remove();
System.out.println(s.top());
s.remove();
System.out.println(s.top());
System.out.println("current size: " + s.size());
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi Singh
Python3
# Program to implement a stack using
# two queue
from _collections import deque
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
# Two inbuilt queues
self.q1 = deque()
self.q2 = deque()
def push(self, x):
self.q1.append(x)
def pop(self):
# if no elements are there in q1
if (not self.q1):
return
# Leave one element in q1 and push others in q2
while(len(self.q1) != 1):
self.q2.append(self.q1.popleft())
# swap the names of two queues
self.q1, self.q2 = self.q2, self.q1
def top(self):
# if no elements are there in q1
if (not self.q1):
return
# Leave one element in q1 and push others in q2
while(len(self.q1) != 1):
self.q2.append(self.q1.popleft())
# Pop the only left element from q1 to q2
top = self.q1[0]
self.q2.append(self.q1.popleft())
# swap the names of two queues
self.q1, self.q2 = self.q2, self.q1
return top
def size(self):
return len(self.q1)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = Stack()
s.push(1)
s.push(2)
s.push(3)
s.push(4)
print("current size: ", s.size())
print(s.top())
s.pop()
print(s.top())
s.pop()
print(s.top())
print("current size: ", s.size())
# This code is contributed by jainlovely450
C#
using System;
using System.Collections;
class GfG {
public class Stack {
public Queue q1 = new Queue();
public Queue q2 = new Queue();
// Just enqueue the new element to q1
public void Push(int x) => q1.Enqueue(x);
// move all elements from q1 to q2 except the rear
// of q1. Store the rear of q1 swap q1 and q2 return
// the stored result
public int Pop()
{
if (q1.Count == 0)
return -1;
while (q1.Count > 1) {
q2.Enqueue(q1.Dequeue());
}
int res = (int)q1.Dequeue();
Queue temp = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = temp;
return res;
}
public int Size() => q1.Count;
public int Top()
{
if (q1.Count == 0)
return -1;
while (q1.Count > 1) {
q2.Enqueue(q1.Dequeue());
}
int res = (int)q1.Dequeue();
q2.Enqueue(res);
Queue temp = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = temp;
return res;
}
};
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Stack s = new Stack();
s.Push(1);
s.Push(2);
s.Push(3);
s.Push(4);
Console.WriteLine("Size of Stack: " + s.Size());
Console.WriteLine(s.Top());
s.Pop();
Console.WriteLine(s.Top());
s.Pop();
Console.WriteLine(s.Top());
Console.WriteLine("Size of Stack: " + s.Size());
}
}
// Submitted by Sakti Prasad
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Stack Class that acts as a queue
class Stack {
queue<int> q;
public:
void push(int data);
void pop();
int top();
bool empty();
};
// Push operation
void Stack::push(int data)
{
// Get previous size of queue
int s = q.size();
// Push the current element
q.push(data);
// Pop all the previous elements and put them after
// current element
for (int i = 0; i < s; i++) {
// Add the front element again
q.push(q.front());
// Delete front element
q.pop();
}
}
// Removes the top element
void Stack::pop()
{
if (q.empty())
cout << "No elements\n";
else
q.pop();
}
// Returns top of stack
int Stack::top() { return (q.empty()) ? -1 : q.front(); }
// Returns true if Stack is empty else false
bool Stack::empty() { return (q.empty()); }
int main()
{
Stack st;
st.push(40);
st.push(50);
st.push(70);
cout << st.top() << "\n";
st.pop();
cout << st.top() << "\n";
st.pop();
cout << st.top() << "\n";
st.push(80);
st.push(90);
st.push(100);
cout << st.top() << "\n";
st.pop();
cout << st.top() << "\n";
st.pop();
cout << st.top() << "\n";
return 0;
}
Python3
from _collections import deque
# Stack Class that acts as a queue
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.q = deque()
# Push operation
def push(self,data):
# Get previous size of queue
s = len(self.q)
# Push the current element
self.q.append(data)
# Pop all the previous elements and put them after
# current element
for i in range(s):
self.q.append(self.q.popleft())
# Removes the top element
def pop(self):
if (not self.q):
print("No elements")
else:
self.q.popleft()
# Returns top of stack
def top(self):
if (not self.q):
return
return self.q[0]
if __name__ == '__main__':
st = Stack()
st.push(40)
st.push(50)
st.push(70)
print(st.top())
st.pop()
print(st.top())
st.pop()
print(st.top())
st.push(80)
st.push(90)
st.push(100)
print(st.top())
st.pop()
print(st.top())
st.pop()
print(st.top())
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA