Dados los pesos y valores de n artículos, coloque estos artículos en una mochila de capacidad W para obtener el valor total máximo en la mochila. En otras palabras, dadas dos arrays de enteros, val[0..n-1] y wt[0..n-1] representan valores y pesos asociados con n elementos respectivamente. También, dado un número entero W que representa la capacidad de la mochila, encuentre los artículos tales que la suma de los pesos de esos artículos de un subconjunto dado sea menor o igual a W. No puede romper un artículo, elegir el artículo completo o no. elegirlo (propiedad 0-1).
Requisito previo: 0/1
Ejemplos de mochila:
Input : val[] = {60, 100, 120};
wt[] = {10, 20, 30};
W = 50;
Output : 220 //maximum value that can be obtained
30 20 //weights 20 and 30 are included.
Input : val[] = {40, 100, 50, 60};
wt[] = {20, 10, 40, 30};
W = 60;
Output : 200
30 20 10
Enfoque:
Sea val[] = {1, 4, 5, 7}, wt[] = {1, 3, 4, 5}
W = 7.
La tabla de mochila 2d se verá así:
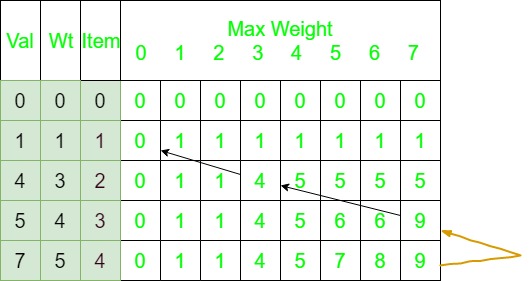
Comience retrocediendo desde K[n][W]. Aquí K[n][W] es 9.
Dado que este valor proviene de la parte superior (que se muestra con una flecha gris), el elemento de esta fila no está incluido. Ir verticalmente hacia arriba en la mesa sin incluir esto en la mochila. Ahora, este valor K[n-1][W], que es 9, no viene de la parte superior, lo que significa que el artículo en esta fila está incluido y sube verticalmente y luego a la izquierda por el peso del artículo incluido (mostrado en negro flecha). Continuando con este proceso incluir pesos 3 y 4 con valor total 9 en la mochila.
C++
// CPP code for Dynamic Programming based
// solution for 0-1 Knapsack problem
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// A utility function that returns maximum of two integers
int max(int a, int b) { return (a > b) ? a : b; }
// Prints the items which are put in a knapsack of capacity W
void printknapSack(int W, int wt[], int val[], int n)
{
int i, w;
int K[n + 1][W + 1];
// Build table K[][] in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (w = 0; w <= W; w++) {
if (i == 0 || w == 0)
K[i][w] = 0;
else if (wt[i - 1] <= w)
K[i][w] = max(val[i - 1] +
K[i - 1][w - wt[i - 1]], K[i - 1][w]);
else
K[i][w] = K[i - 1][w];
}
}
// stores the result of Knapsack
int res = K[n][W];
cout<< res << endl;
w = W;
for (i = n; i > 0 && res > 0; i--) {
// either the result comes from the top
// (K[i-1][w]) or from (val[i-1] + K[i-1]
// [w-wt[i-1]]) as in Knapsack table. If
// it comes from the latter one/ it means
// the item is included.
if (res == K[i - 1][w])
continue;
else {
// This item is included.
cout<<" "<<wt[i - 1] ;
// Since this weight is included its
// value is deducted
res = res - val[i - 1];
w = w - wt[i - 1];
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int val[] = { 60, 100, 120 };
int wt[] = { 10, 20, 30 };
int W = 50;
int n = sizeof(val) / sizeof(val[0]);
printknapSack(W, wt, val, n);
return 0;
}
// this code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
C
// CPP code for Dynamic Programming based
// solution for 0-1 Knapsack problem
#include <stdio.h>
// A utility function that returns maximum of two integers
int max(int a, int b) { return (a > b) ? a : b; }
// Prints the items which are put in a knapsack of capacity W
void printknapSack(int W, int wt[], int val[], int n)
{
int i, w;
int K[n + 1][W + 1];
// Build table K[][] in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (w = 0; w <= W; w++) {
if (i == 0 || w == 0)
K[i][w] = 0;
else if (wt[i - 1] <= w)
K[i][w] = max(val[i - 1] +
K[i - 1][w - wt[i - 1]], K[i - 1][w]);
else
K[i][w] = K[i - 1][w];
}
}
// stores the result of Knapsack
int res = K[n][W];
printf("%d\n", res);
w = W;
for (i = n; i > 0 && res > 0; i--) {
// either the result comes from the top
// (K[i-1][w]) or from (val[i-1] + K[i-1]
// [w-wt[i-1]]) as in Knapsack table. If
// it comes from the latter one/ it means
// the item is included.
if (res == K[i - 1][w])
continue;
else {
// This item is included.
printf("%d ", wt[i - 1]);
// Since this weight is included its
// value is deducted
res = res - val[i - 1];
w = w - wt[i - 1];
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int val[] = { 60, 100, 120 };
int wt[] = { 10, 20, 30 };
int W = 50;
int n = sizeof(val) / sizeof(val[0]);
printknapSack(W, wt, val, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java code for Dynamic Programming based
// solution for 0-1 Knapsack problem
class GFG {
// A utility function that returns
// maximum of two integers
static int max(int a, int b)
{
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
// Prints the items which are put
// in a knapsack of capacity W
static void printknapSack(int W, int wt[],
int val[], int n)
{
int i, w;
int K[][] = new int[n + 1][W + 1];
// Build table K[][] in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (w = 0; w <= W; w++) {
if (i == 0 || w == 0)
K[i][w] = 0;
else if (wt[i - 1] <= w)
K[i][w] = Math.max(val[i - 1] +
K[i - 1][w - wt[i - 1]], K[i - 1][w]);
else
K[i][w] = K[i - 1][w];
}
}
// stores the result of Knapsack
int res = K[n][W];
System.out.println(res);
w = W;
for (i = n; i > 0 && res > 0; i--) {
// either the result comes from the top
// (K[i-1][w]) or from (val[i-1] + K[i-1]
// [w-wt[i-1]]) as in Knapsack table. If
// it comes from the latter one/ it means
// the item is included.
if (res == K[i - 1][w])
continue;
else {
// This item is included.
System.out.print(wt[i - 1] + " ");
// Since this weight is included its
// value is deducted
res = res - val[i - 1];
w = w - wt[i - 1];
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String arg[])
{
int val[] = { 60, 100, 120 };
int wt[] = { 10, 20, 30 };
int W = 50;
int n = val.length;
printknapSack(W, wt, val, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Anant Agarwal.
Python3
# Python3 code for Dynamic Programming # based solution for 0-1 Knapsack problem # Prints the items which are put in a # knapsack of capacity W def printknapSack(W, wt, val, n): K = [[0 for w in range(W + 1)] for i in range(n + 1)] # Build table K[][] in bottom # up manner for i in range(n + 1): for w in range(W + 1): if i == 0 or w == 0: K[i][w] = 0 elif wt[i - 1] <= w: K[i][w] = max(val[i - 1] + K[i - 1][w - wt[i - 1]], K[i - 1][w]) else: K[i][w] = K[i - 1][w] # stores the result of Knapsack res = K[n][W] print(res) w = W for i in range(n, 0, -1): if res <= 0: break # either the result comes from the # top (K[i-1][w]) or from (val[i-1] # + K[i-1] [w-wt[i-1]]) as in Knapsack # table. If it comes from the latter # one/ it means the item is included. if res == K[i - 1][w]: continue else: # This item is included. print(wt[i - 1]) # Since this weight is included # its value is deducted res = res - val[i - 1] w = w - wt[i - 1] # Driver code val = [ 60, 100, 120 ] wt = [ 10, 20, 30 ] W = 50 n = len(val) printknapSack(W, wt, val, n) # This code is contributed by Aryan Garg.
C#
// C# code for Dynamic Programming based
// solution for 0-1 Knapsack problem
using System ;
class GFG {
// A utility function that returns
// maximum of two integers
static int max(int a, int b)
{
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
// Prints the items which are put
// in a knapsack of capacity W
static void printknapSack(int W, int []wt,
int []val, int n)
{
int i, w;
int [,]K = new int[n + 1,W + 1];
// Build table K[][] in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (w = 0; w <= W; w++) {
if (i == 0 || w == 0)
K[i,w] = 0;
else if (wt[i - 1] <= w)
K[i,w] = Math.Max(val[i - 1] +
K[i - 1,w - wt[i - 1]], K[i - 1,w]);
else
K[i,w] = K[i - 1,w];
}
}
// stores the result of Knapsack
int res = K[n,W];
Console.WriteLine(res);
w = W;
for (i = n; i > 0 && res > 0; i--) {
// either the result comes from the top
// (K[i-1][w]) or from (val[i-1] + K[i-1]
// [w-wt[i-1]]) as in Knapsack table. If
// it comes from the latter one/ it means
// the item is included.
if (res == K[i - 1,w])
continue;
else {
// This item is included.
Console.Write(wt[i - 1] + " ");
// Since this weight is included its
// value is deducted
res = res - val[i - 1];
w = w - wt[i - 1];
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int []val = { 60, 100, 120 };
int []wt = { 10, 20, 30 };
int W = 50;
int n = val.Length;
printknapSack(W, wt, val, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Ryuga.
PHP
<?php
// PHP code for Dynamic Programming based
// solution for 0-1 Knapsack problem
// Prints the items which are kept in
// a knapsack of capacity W
function printknapSack($W, &$wt, &$val, $n)
{
$K = array_fill(0, $n + 1,
array_fill(0, $W + 1, NULL));
// Build table K[][] in bottom up manner
for ($i = 0; $i <= $n; $i++)
{
for ($w = 0; $w <= $W; $w++)
{
if ($i == 0 || $w == 0)
$K[$i][$w] = 0;
else if ($wt[$i - 1] <= $w)
$K[$i][$w] = max($val[$i - 1] +
$K[$i - 1][$w - $wt[$i - 1]],
$K[$i - 1][$w]);
else
$K[$i][$w] = $K[$i - 1][$w];
}
}
// stores the result of Knapsack
$res = $K[$n][$W];
echo $res . "\n";
$w = $W;
for ($i = $n; $i > 0 && $res > 0; $i--)
{
// either the result comes from the top
// (K[i-1][w]) or from (val[i-1] + K[i-1]
// [w-wt[i-1]]) as in Knapsack table. If
// it comes from the latter one/ it means
// the item is included.
if ($res == $K[$i - 1][$w])
continue;
else
{
// This item is included.
echo $wt[$i - 1] . " ";
// Since this weight is included
// its value is deducted
$res = $res - $val[$i - 1];
$w = $w - $wt[$i - 1];
}
}
}
// Driver code
$val = array(60, 100, 120);
$wt = array(10, 20, 30);
$W = 50;
$n = sizeof($val);
printknapSack($W, $wt, $val, $n);
// This code is contributed by ita_c
?>
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript code for Dynamic Programming based
// solution for 0-1 Knapsack problem
// A utility function that returns
// maximum of two integers
function max(a,b)
{
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
// Prints the items which are put
// in a knapsack of capacity W
function printknapSack(W,wt,val,n)
{
let i, w;
let K = new Array(n + 1);
for( i=0;i<K.length;i++)
{
K[i]=new Array(W+1);
for(let j=0;j<W+1;j++)
{
K[i][j]=0;
}
}
// Build table K[][] in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (w = 0; w <= W; w++) {
if (i == 0 || w == 0)
K[i][w] = 0;
else if (wt[i - 1] <= w)
K[i][w] = Math.max(val[i - 1] +
K[i - 1][w - wt[i - 1]],
K[i - 1][w]);
else
K[i][w] = K[i - 1][w];
}
}
// stores the result of Knapsack
let res = K[n][W];
document.write(res+"<br>");
w = W;
for (i = n; i > 0 && res > 0; i--)
{
// either the result comes from the top
// (K[i-1][w]) or from (val[i-1] + K[i-1]
// [w-wt[i-1]]) as in Knapsack table. If
// it comes from the latter one/ it means
// the item is included.
if (res == K[i - 1][w])
continue;
else {
// This item is included.
document.write(wt[i - 1] + " ");
// Since this weight is included its
// value is deducted
res = res - val[i - 1];
w = w - wt[i - 1];
}
}
}
let val=[60, 100, 120 ];
let wt=[10, 20, 30 ];
let W = 50;
let n = val.length;
printknapSack(W, wt, val, n);
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
220 30 20
Complejidad temporal: O(n*W)
Complejidad del espacio: O(n*W)