Dada una lista enlazada, imprima el reverso usando una función recursiva. Por ejemplo, si la lista enlazada dada es 1->2->3->4, entonces la salida debería ser 4->3->2->1.
Tenga en cuenta que la pregunta es solo sobre la impresión del reverso. Para invertir la lista en sí, vea este
Nivel de dificultad: Novato
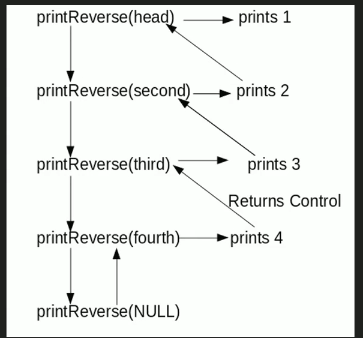
Algoritmo
printReverse(head) 1. call print reverse for head->next 2. print head->data
Implementación:
C++
// C++ program to print reverse of a linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
/* Function to reverse the linked list */
void printReverse(Node* head)
{
// Base case
if (head == NULL)
return;
// print the list after head node
printReverse(head->next);
// After everything else is printed, print head
cout << head->data << " ";
}
/*UTILITY FUNCTIONS*/
/* Push a node to linked list. Note that this function
changes the head */
void push(Node** head_ref, char new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
// Let us create linked list 1->2->3->4
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
printReverse(head);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
// C program to print reverse of a linked list
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
/* Link list node */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* Function to reverse the linked list */
void printReverse(struct Node* head)
{
// Base case
if (head == NULL)
return;
// print the list after head node
printReverse(head->next);
// After everything else is printed, print head
printf("%d ", head->data);
}
/*UTILITY FUNCTIONS*/
/* Push a node to linked list. Note that this function
changes the head */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, char new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
// Let us create linked list 1->2->3->4
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
printReverse(head);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to print reverse of a linked list
class LinkedList
{
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d) {data = d; next = null; }
}
/* Function to print reverse of linked list */
void printReverse(Node head)
{
if (head == null) return;
// print list of head node
printReverse(head.next);
// After everything else is printed
System.out.print(head.data+" ");
}
/* Utility Functions */
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/*Driver function to test the above methods*/
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Let us create linked list 1->2->3->4
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(4);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
llist.printReverse(llist.head);
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */
Python3
# Python3 program to print reverse # of a linked list # Node class class Node: # Constructor to initialize # the node object def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None class LinkedList: # Function to initialize head def __init__(self): self.head = None # Recursive function to print # linked list in reverse order def printrev(self, temp): if temp: self.printrev(temp.next) print(temp.data, end = ' ') else: return # Function to insert a new node # at the beginning def push(self, new_data): new_node = Node(new_data) new_node.next = self.head self.head = new_node # Driver code llist = LinkedList() llist.push(4) llist.push(3) llist.push(2) llist.push(1) llist.printrev(llist.head) # This code is contributed by Vinay Kumar(vinaykumar71)
C#
// C# program to print reverse of a linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList
{
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d; next = null;
}
}
/* Function to print reverse of linked list */
void printReverse(Node head)
{
if (head == null) return;
// print list of head node
printReverse(head.next);
// After everything else is printed
Console.Write(head.data + " ");
}
/* Utility Functions */
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/*Driver function to test the above methods*/
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// Let us create linked list 1->2->3->4
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(4);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
llist.printReverse(llist.head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to print reverse of a linked list
var head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node */
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
/* Function to print reverse of linked list */
function printReverse( head) {
if (head == null)
return;
// print list of head node
printReverse(head.next);
// After everything else is printed
document.write(head.data + " ");
}
/* Utility Functions */
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
function push(new_data) {
/*
* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data
*/
new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/* Driver function to test the above methods */
// Let us create linked list 1->2->3->4
push(4);
push(3);
push(2);
push(1);
printReverse(head);
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
4 3 2 1
Complejidad de tiempo: O(n)
Espacio auxiliar: O (n) para el espacio de pila desde que se usa la recursividad
Otro enfoque:
También podemos realizar la misma acción usando una pila usando un método iterativo.
Algoritmo:
Store the values of the linked list in a stack. Keep removing the elements from the stack and print them.
Implementación:
C++
// C++ program to print reverse of a linked list using iterative method
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
/* Function to print the reverse of the linked list using iterative method */
void printReverse(Node* head)
{
stack<int> st;
Node *curr = head;
while(curr!=NULL)
{
st.push(curr->data);
curr = curr->next;
}
while(st.empty()==false)
{
cout << st.top()<<" -> ";
st.pop();
}
}
/*UTILITY FUNCTIONS*/
/* function to print the elements of the linked list*/
void printList(Node *head)
{
Node *curr = head;
while(curr!=NULL)
{
cout << curr->data << " -> ";
curr = curr->next;
}
cout<<"\n";
}
/* Push a node to linked list. Note that this function
changes the head */
void push(Node** head_ref, char new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
// Let us create linked list 1->2->3->4
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
printList(head);
printReverse(head);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403)
Java
// Java program to print reverse of a linked list using iterative method
import java.util.*;
class LinkedList
{
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d) {data = d; next = null; }
}
/* Function to print reverse of linked list */
void printReverse(Node head)
{
Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<Integer>();
Node curr = head;
while(curr!=null)
{
st.push(curr.data);
curr = curr.next;
}
while(st.isEmpty()==false)
{
System.out.print(st.peek() + " -> ");
st.pop();
}
}
/* Utility Functions */
/* function to print the elements of the linked list*/
void printList(Node head)
{
Node curr = head;
while(curr!=null)
{
System.out.print(curr.data + " -> ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/*Driver function to test the above methods*/
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Let us create linked list 1->2->3->4
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(4);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
llist.printList(llist.head);
llist.printReverse(llist.head);
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403) */
Python3
# Python3 program to print reverse # of a linked list using iterative method # Node class class Node: # Constructor to initialize # the node object def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None class LinkedList: # Function to initialize head def __init__(self): self.head = None # Recursive function to print # linked list in reverse order using iterative method def printrev(self, curr): stack = [] while curr: stack.append(curr) curr = curr.next while len(stack): print(stack.pop().data,"->" , end = ' ') print() #Function to print the linked list def printlist(self,curr): while curr: print(curr.data,"->" , end = ' ') curr = curr.next print() # Function to insert a new node # at the beginning def push(self, new_data): new_node = Node(new_data) new_node.next = self.head self.head = new_node # Driver code llist = LinkedList() llist.push(4) llist.push(3) llist.push(2) llist.push(1) llist.printlist(llist.head) llist.printrev(llist.head) # This code is contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403)
C#
// C# program to print reverse of a linked list
using System;
using System.Collections;
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Function to print reverse of linked list */
void printReverse(Node head)
{
Stack st = new Stack();
Node curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
st.Push(curr.data);
curr = curr.next;
}
while (st.Count != 0) {
Console.Write(st.Peek() + " -> ");
st.Pop();
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
/* Utility Functions */
/* A function to print the elements of the list*/
void printList(Node head)
{
Node curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
Console.Write(curr.data + " -> ");
curr = curr.next;
}
Console.Write("\n");
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/*Driver function to test the above methods*/
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Let us create linked list 1->2->3->4
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.push(4);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
llist.printList(llist.head);
llist.printReverse(llist.head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403)
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to print reverse of a linked list using iterative method
var head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node */
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
/* Function to print reverse of linked list using iterative method */
function printReverse( head) {
var st = new Stack();
var curr = this.head;
while(curr != null)
{
st.push(curr.data);
curr = curr.next;
}
while(st.idEmpty())
{
document.write(head.data + " -> ");
st.pop();
}
}
/* Utility Functions */
/* function to print the elements of the linked list*/
void printList( head)
{
var curr = this.head;
while(curr!=null)
{
document.write(curr.data + " -> ");
curr = curr.next;
}
document.write("\n");
}
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
function push(new_data) {
/*
* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data
*/
new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/* Driver function to test the above methods */
// Let us create linked list 1->2->3->4
push(4);
push(3);
push(2);
push(1);
printList(head);
printReverse(head);
// This code contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403)
</script>
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 ->
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N)
Como estamos atravesando la lista enlazada solo una vez.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(N)
El espacio adicional se utiliza para almacenar los elementos en la pila.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
