Dado un árbol binario , la tarea es imprimir la ruta más larga desde el Node raíz hasta el Node hoja. Si hay varias respuestas, imprima cualquiera de ellas.
Ejemplos:
Input:
4
/ \
3 6
/ \
5 7
Output:
4 -> 6 -> 7
Explanation:
Longest paths from root to leaf
are (4 -> 6 -> 5)
and (4 -> 6 -> 7).
Print any of them.
Input:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
\
6
Output:
1 -> 2 -> 5 -> 6
Enfoque ingenuo: la idea es generar todas las rutas posibles desde el Node raíz hasta todos los Nodes hoja, realizar un seguimiento de la ruta con la longitud máxima y, finalmente, imprimir la ruta más larga.
Complejidad temporal: O(N 2 )
Enfoque Eficiente: La idea es usar Recursion para resolver este problema de manera eficiente. La idea principal es obtener recursivamente la ruta más larga desde el subárbol izquierdo y el subárbol derecho y luego agregar el Node actual a uno que tenga una longitud mayor y será la ruta más larga desde el Node actual hasta la hoja. Comenzando con el Node raíz, siga los pasos a continuación para cada Node llamado recursivamente.
- Si el Node raíz es nulo, no existe una ruta, devuelva un vector vacío.
- Obtenga la ruta más larga desde el subárbol derecho en un vector derecho vectorial al atravesar recursivamente la raíz -> derecha.
- De manera similar, obtenga la ruta más larga desde el subárbol izquierdo en un vector izquierdo atravesando recursivamente raíz -> izquierda.
- Compare la longitud de rightvect y leftvect y agregue el Node actual al más largo de los dos y devuelva ese vector.
Siguiendo los pasos anteriores, el vector obtenido al final del recorrido del árbol es el camino más largo posible. Imprime el vector al revés como el camino más largo desde la raíz hasta la hoja.
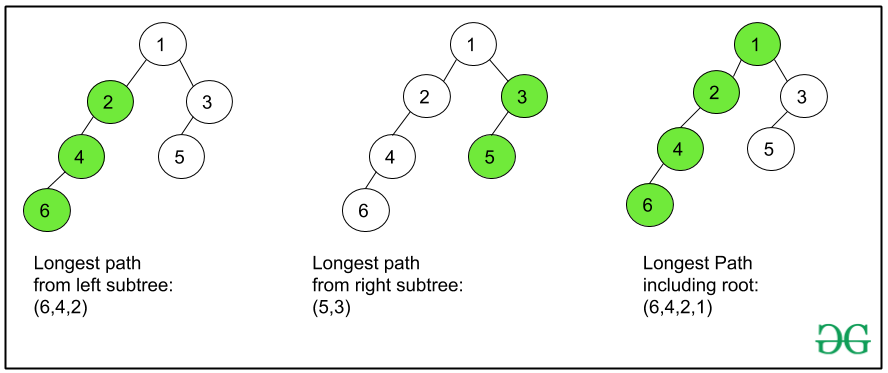
Mire esta imagen para comprender cómo se utilizan las rutas más largas desde los Nodes del subárbol izquierdo y derecho para obtener la ruta más larga desde el Node actual:
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ Program to print Longest Path
// from root to leaf in a Binary tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Tree node Structure
struct Node {
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
struct Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
// Function to find and return the
// longest path
vector<int> longestPath(Node* root)
{
// If root is null means there
// is no binary tree so
// return a empty vector
if (root == NULL) {
vector<int> temp
= {};
return temp;
}
// Recursive call on root->right
vector<int> rightvect
= longestPath(root->right);
// Recursive call on root->left
vector<int> leftvect
= longestPath(root->left);
// Compare the size of the two vectors
// and insert current node accordingly
if (leftvect.size() > rightvect.size())
leftvect.push_back(root->data);
else
rightvect.push_back(root->data);
// Return the appropriate vector
return (leftvect.size() > rightvect.size()
? leftvect
: rightvect);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
struct Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->left->right->right = newNode(6);
vector<int> output = longestPath(root);
int n = output.size();
cout << output[n - 1];
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << " -> " << output[i];
}
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to print Longest Path
// from root to leaf in a Binary tree
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
class GFG{
// Binary tree node
static class Node
{
Node left;
Node right;
int data;
};
// Function to create a new
// Binary node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to find and return the
// longest path
public static ArrayList<Integer> longestPath(Node root)
{
// If root is null means there
// is no binary tree so
// return a empty vector
if(root == null)
{
ArrayList<Integer> output = new ArrayList<>();
return output;
}
// Recursive call on root.right
ArrayList<Integer> right = longestPath(root.right);
// Recursive call on root.left
ArrayList<Integer> left = longestPath(root.left);
// Compare the size of the two ArrayList
// and insert current node accordingly
if(right.size() < left.size())
{
left.add(root.data);
}
else
{
right.add(root.data);
}
// Return the appropriate ArrayList
return (left.size() >
right.size() ? left :right);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.left.right.right = newNode(6);
ArrayList<Integer> output = longestPath(root);
int n = output.size();
System.out.print(output.get(n - 1));
for(int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
System.out.print(" -> " + output.get(i));
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by HamreetSingh
Python3
# Python3 program to print longest path
# from root to leaf in a Binary tree
# Tree node Structure
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to find and return the
# longest path
def longestPath(root):
# If root is null means there
# is no binary tree so
# return a empty vector
if (root == None):
return []
# Recursive call on root.right
rightvect = longestPath(root.right)
# Recursive call on root.left
leftvect = longestPath(root.left)
# Compare the size of the two vectors
# and insert current node accordingly
if (len(leftvect) > len(rightvect)):
leftvect.append(root.data)
else:
rightvect.append(root.data)
# Return the appropriate vector
if len(leftvect) > len(rightvect):
return leftvect
return rightvect
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.left.right.right = Node(6)
output = longestPath(root)
n = len(output)
print(output[n - 1], end = "")
for i in range(n - 2, -1, -1):
print(" ->", output[i], end = "")
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# program to print
// longest Path from
// root to leaf in a
// Binary tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Binary tree node
class Node
{
public Node left;
public Node right;
public int data;
};
// Function to create a new
// Binary node
static Node newNode(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to find and
// return the longest path
static List<int> longestPath(Node root)
{
// If root is null means there
// is no binary tree so
// return a empty vector
if(root == null)
{
List<int> output = new List<int>();
return output;
}
// Recursive call on root.right
List<int> right = longestPath(root.right);
// Recursive call on root.left
List<int> left = longestPath(root.left);
// Compare the size of the two List
// and insert current node accordingly
if(right.Count < left.Count)
{
left.Add(root.data);
}
else
{
right.Add(root.data);
}
// Return the appropriate List
return (left.Count >
right.Count ?
left :right);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.left = newNode(4);
root.left.right = newNode(5);
root.left.right.right = newNode(6);
List<int> output = longestPath(root);
int n = output.Count;
Console.Write(output[n - 1]);
for(int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
Console.Write(" -> " + output[i]);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to print Longest Path
// from root to leaf in a Binary tree
// Binary tree node
class Node
{
// Function to create a new
// Binary node
constructor(data)
{
this.data = data;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
// Function to find and return the
// longest path
function longestPath(root)
{
// If root is null means there
// is no binary tree so
// return a empty vector
if (root == null)
{
let output = [];
return output;
}
// Recursive call on root.right
let right = longestPath(root.right);
// Recursive call on root.left
let left = longestPath(root.left);
// Compare the size of the two ArrayList
// and insert current node accordingly
if (right.length < left.length)
{
left.push(root.data);
}
else
{
right.push(root.data);
}
// Return the appropriate ArrayList
return (left.length >
right.length ? left :right);
}
// Driver code
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.left.right.right = new Node(6);
let output = longestPath(root);
let n = output.length;
document.write(output[n - 1]);
for(let i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
document.write(" -> " + output[i]);
}
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
1 -> 2 -> 5 -> 6
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por mansibhardwaj009 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA