Dado un vector de vectores arr[] , la tarea es imprimir los elementos de arr[] en el orden diagonalmente ascendente como se ilustra a continuación.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr[][] = {{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}}
Salida: 1 4 2 7 5 3 8 6 9
Explicación:
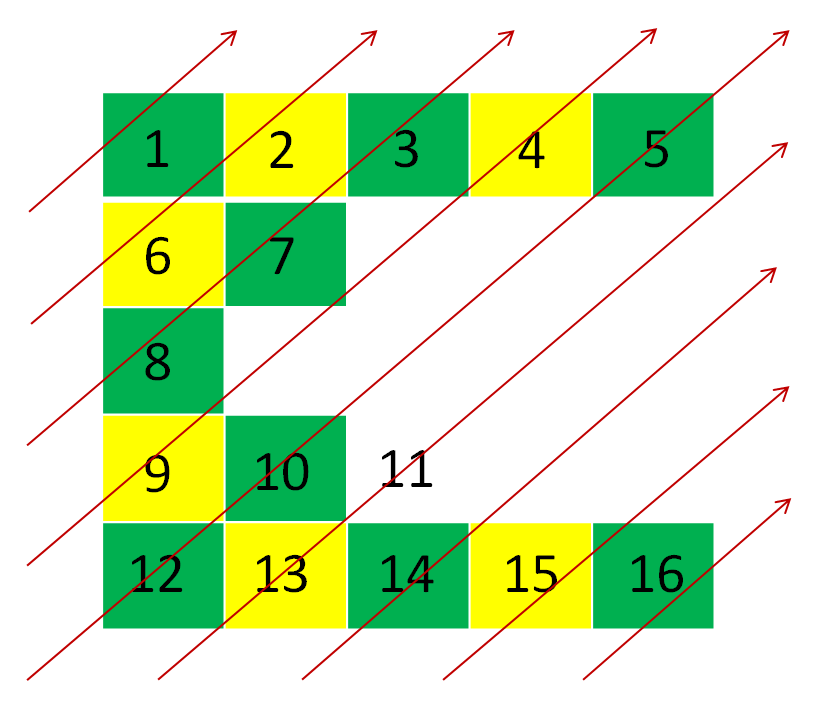
A continuación se muestra la ilustración de cómo se imprime el orden diagonalmente hacia arriba:Entrada: arr[][] = {{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, {6, 7}, {8}, {9, 10, 11}, {12, 13, 14, 15, 16} }
Salida: 1 6 28 7 3 9 4 12 10 5 13 11 14 15 16
Explicación:
A continuación se muestra la ilustración de cómo se imprime el orden en diagonal hacia arriba:
Enfoque: La idea se basa en la observación de que todos los elementos en una determinada diagonal ascendente tienen una suma igual a (índice de fila + índice de columna) . Siga los pasos para resolver el problema:
- Inicialice un vector de vectores v para almacenar los elementos en el formato deseado.
- Itere sobre la array arr[][] usando las variables i y j y para cada i y j empuje arr[i][j] a v[i + j] .
- Después de los pasos anteriores, invierta cada fila en la v .
- Ahora, imprima todos los elementos almacenados en v en forma de fila para obtener el resultado deseado.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to traverse the matrix
// diagonally upwards
void printDiagonalTraversal(
vector<vector<int> >& nums)
{
// Stores the maximum size of vector
// from all row of matrix nums[][]
int max_size = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (max_size < nums[i].size()) {
max_size = nums[i].size();
}
}
// Store elements in desired order
vector<vector<int> > v(2 * max_size - 1);
// Store every element on the basis
// of sum of index (i + j)
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0;
j < nums[i].size(); j++) {
v[i + j].push_back(nums[i][j]);
}
}
// Print the stored result
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
// Reverse all sublist
reverse(v[i].begin(), v[i].end());
for (int j = 0; j < v[i].size(); j++)
cout << v[i][j] << " ";
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Given vector of vectors arr
vector<vector<int> > arr
= { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 }, { 7, 8, 9 } };
// Function Call
printDiagonalTraversal(arr);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Function to traverse the matrix
// diagonally upwards
static void printDiagonalTraversal(int[][] nums)
{
// Stores the maximum size of vector
// from all row of matrix nums[][]
int max_size = nums[0].length;
// Store elements in desired order
ArrayList<
ArrayList<Integer>> v = new ArrayList<
ArrayList<Integer>>();
for(int i = 0; i < 2 * max_size - 1; i++)
{
v.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
// Store every element on the basis
// of sum of index (i + j)
for(int i = 0; i < nums[0].length; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < nums[0].length; j++)
{
v.get(i + j).add(nums[i][j]);
}
}
// Print the stored result
for(int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
// Print in reverse order
for(int j = v.get(i).size() - 1;
j >= 0; j--)
{
System.out.print(v.get(i).get(j) + " ");
}
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given vector of vectors arr
int[][] arr = { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 } };
// Function Call
printDiagonalTraversal(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach # Function to traverse the matrix # diagonally upwards def printDiagonalTraversal(nums): # Stores the maximum size of vector # from all row of matrix nums[][] max_size = len(nums) for i in range(len(nums)): if (max_size < len(nums[i])): max_size = len(nums[i]) # Store elements in desired order v = [[] for i in range(2 * max_size - 1)] # Store every element on the basis # of sum of index (i + j) for i in range(len(nums)): for j in range(len(nums[i])): v[i + j].append(nums[i][j]) # Print the stored result for i in range(len(v)): # Reverse all sublist v[i] = v[i][::-1] for j in range(len(v[i])): print(v[i][j], end = " ") # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': # Given vector of vectors arr arr = [ [ 1, 2, 3 ], [ 4, 5, 6 ], [ 7, 8, 9 ] ] # Function Call printDiagonalTraversal(arr) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Function to traverse the matrix
// diagonally upwards
static void printDiagonalTraversal(int[,] nums)
{
// Stores the maximum size of vector
// from all row of matrix nums[][]
int max_size = nums.GetLength(0);
// Store elements in desired order
List<List<int>> v = new List<List<int>>();
for(int i = 0; i < 2 * max_size - 1; i++)
{
v.Add(new List<int>());
}
// Store every element on the basis
// of sum of index (i + j)
for(int i = 0; i < nums.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < nums.GetLength(0); j++)
{
v[i + j].Add(nums[i, j]);
}
}
// Print the stored result
for(int i = 0; i < v.Count; i++)
{
// print in reverse order
for(int j = v[i].Count - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
Console.Write(v[i][j] + " ");
}
}
}
// Driver Code
static void Main()
{
// Given vector of vectors arr
int[,] arr = { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 } };
// Function Call
printDiagonalTraversal(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for the above approach
// Function to traverse the matrix
// diagonally upwards
function printDiagonalTraversal(nums)
{
// Stores the maximum size of vector
// from all row of matrix nums[][]
let max_size = nums[0].length;
// Store elements in desired order
let v = [];
for(let i = 0; i < 2 * max_size - 1; i++)
{
v.push([]);
}
// Store every element on the basis
// of sum of index (i + j)
for(let i = 0; i < nums[0].length; i++)
{
for(let j = 0; j < nums[0].length; j++)
{
v[i + j].push(nums[i][j]);
}
}
// Print the stored result
for(let i = 0; i < v.length; i++)
{
// Print in reverse order
for(let j = v[i].length - 1;
j >= 0; j--)
{
document.write(v[i][j] + " ");
}
}
}
// Driver Code
// Given vector of vectors arr
let arr = [ [ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 4, 5, 6 ],
[ 7, 8, 9 ] ];
// Function Call
printDiagonalTraversal(arr);
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
1 4 2 7 5 3 8 6 9
Complejidad temporal: O(N*M), donde N es el tamaño de la array dada y M es el tamaño máximo de cualquier fila de la array.
Espacio auxiliar: O(N*M)
Enfoque alternativo: el problema anterior también se puede resolver utilizando queue . Siga los pasos para resolver el problema:
- Inicialice una cola Q e inserte el índice de la primera celda de arr[][] , es decir, (0, 0) .
- Inicialice un vector v para almacenar los elementos en el formato deseado.
- Mientras q no esté vacío, haga lo siguiente:
- Coloca el elemento al frente de la cola y empújalo en v .
- Empuje el índice de la celda actual justo debajo de él, solo si la celda actual es la primera en su fila.
- Empuje el índice de su celda vecina derecha si existe.
- Después de los pasos anteriores, imprima todos los elementos almacenados en v .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to traverse the matrix
// diagonally upwards
void printDiagonalTraversal(
vector<vector<int> >& nums)
{
// Store the number of rows
int m = nums.size();
// Initialize queue
queue<pair<int, int> > q;
// Push the index of first element
// i.e., (0, 0)
q.push({ 0, 0 });
while (!q.empty()) {
// Get the front element
pair<int, int> p = q.front();
// Pop the element at the front
q.pop();
cout << nums[p.first][p.second]
<< " ";
// Insert the element below
// if the current element is
// in first column
if (p.second == 0
&& p.first + 1 < m) {
q.push({ p.first + 1,
p.second });
}
// Insert the right neighbour
// if it exists
if (p.second + 1 < nums[p.first].size())
q.push({ p.first,
p.second + 1 });
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given vector of vectors arr
vector<vector<int> > arr
= { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 }, { 7, 8, 9 } };
// Function call
printDiagonalTraversal(arr);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class pair
{
int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Function to traverse the matrix
// diagonally upwards
static void printDiagonalTraversal(
int [][]nums)
{
// Store the number of rows
int m = nums.length;
// Initialize queue
Queue<pair> q = new LinkedList<>();
// Push the index of first element
// i.e., (0, 0)
q.add(new pair( 0, 0 ));
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// Get the front element
pair p = q.peek();
// Pop the element at the front
q.remove();
System.out.print(nums[p.first][p.second]
+ " ");
// Insert the element below
// if the current element is
// in first column
if (p.second == 0
&& p.first + 1 < m) {
q.add(new pair( p.first + 1,
p.second ));
}
// Insert the right neighbour
// if it exists
if (p.second + 1 < nums[p.first].length)
q.add(new pair( p.first,
p.second + 1 ));
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given vector of vectors arr
int[][] arr
= { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 }, { 7, 8, 9 } };
// Function call
printDiagonalTraversal(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach # Function to traverse the matrix # diagonally upwards def printDiagonalTraversal(nums): # Store the number of rows m = len(nums) # Initialize queue q = [] # Push the index of first element # i.e., (0, 0) q.append([ 0, 0 ]) while (len(q) != 0): # Get the front element p = q[0] # Pop the element at the front q.pop(0); print(nums[p[0]][p[1]], end = " ") # Insert the element below # if the current element is # in first column if (p[1] == 0 and p[0] + 1 < m): q.append([ p[0]+ 1, p[1] ]); # Insert the right neighbour # if it exists if (p[1] + 1 < len(nums[p[0]])): q.append([ p[0], p[1] + 1 ]); # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": # Given vector of vectors arr arr = [[ 1, 2, 3 ], [ 4, 5, 6 ] ,[ 7, 8, 9 ]] # Function call printDiagonalTraversal(arr); # This code is contributed by chitranayal
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
class pair
{
public int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Function to traverse the matrix
// diagonally upwards
static void printDiagonalTraversal(
int [,]nums)
{
// Store the number of rows
int m = nums.GetLength(0);
// Initialize queue
Queue<pair> q = new Queue<pair>();
// Push the index of first element
// i.e., (0, 0)
q.Enqueue(new pair(0, 0));
while (q.Count != 0)
{
// Get the front element
pair p = q.Peek();
// Pop the element at the front
q.Dequeue();
Console.Write(nums[p.first,p.second]
+ " ");
// Insert the element below
// if the current element is
// in first column
if (p.second == 0
&& p.first + 1 < m)
{
q.Enqueue(new pair( p.first + 1,
p.second ));
}
// Insert the right neighbour
// if it exists
if (p.second + 1 < nums.GetLength(1))
q.Enqueue(new pair( p.first,
p.second + 1 ));
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Given vector of vectors arr
int[,] arr
= { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 }, { 7, 8, 9 } };
// Function call
printDiagonalTraversal(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for the above approach
class pair
{
constructor(first,second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Function to traverse the matrix
// diagonally upwards
function printDiagonalTraversal(nums)
{
// Store the number of rows
let m = nums.length;
// Initialize queue
let q = [];
// Push the index of first element
// i.e., (0, 0)
q.push(new pair( 0, 0 ));
while (q.length!=0) {
// Get the front element
let p = q[0];
// Pop the element at the front
q.shift();
document.write(nums[p.first][p.second]
+ " ");
// Insert the element below
// if the current element is
// in first column
if (p.second == 0
&& p.first + 1 < m) {
q.push(new pair( p.first + 1,
p.second ));
}
// Insert the right neighbour
// if it exists
if (p.second + 1 < nums[p.first].length)
q.push(new pair( p.first,
p.second + 1 ));
}
}
// Driver Code
// Given vector of vectors arr
let arr=[[ 1, 2, 3 ], [ 4, 5, 6 ], [ 7, 8, 9] ];
// Function call
printDiagonalTraversal(arr);
// This code is contributed by rag2127
</script>
1 4 2 7 5 3 8 6 9
Complejidad temporal: O(N*M), donde N es el tamaño de la array dada y M es el tamaño máximo de cualquier fila de la array.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por Rohit_prasad y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA