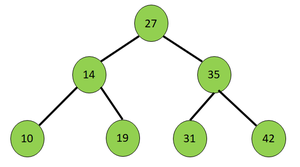
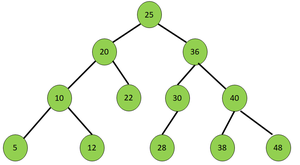
Dado un árbol de búsqueda binario , la tarea es imprimir los Nodes del BST en el siguiente orden:
- Si el BST contiene niveles numerados del 1 al N , el orden de impresión es el nivel 1 , el nivel N , el nivel 2 , el nivel N – 1 , y así sucesivamente.
- Los Nodes de orden de nivel superior ( 1, 2 , …) se imprimen de izquierda a derecha, mientras que los Nodes de orden de nivel inferior ( N , N-1 , …) se imprimen de derecha a izquierda.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: Salida: 27 42 31 19 10 14 35 Explicación: Nivel 1 de izquierda a derecha: 27 Nivel 3 de derecha a izquierda: 42 31 19 10 Nivel 2 de izquierda a derecha: 14 35
Planteamiento: Para resolver el problema, la idea es almacenar los Nodes de BST en orden ascendente y descendente de niveles y valores de Node e imprimir todos los Nodes del mismo nivel alternativamente entre orden ascendente y descendente. Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Inicialice un Min Heap y un Max Heap para almacenar los Nodes en orden ascendente y descendente de niveles y valores de Node, respectivamente.
- Realice un recorrido de orden de nivel en el BST dado para almacenar los Nodes en las respectivas colas de prioridad .
- Imprima todos los Nodes de cada nivel uno por uno desde Min Heap seguido por Max Heap alternativamente.
- Si se encuentra que algún nivel en Min Heap o Max Heap ya está impreso, salte al siguiente nivel.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Structure of a BST node
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
// Utility function to create a new BST node
struct node* newnode(int d)
{
struct node* temp
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
temp->data = d;
return temp;
}
// Function to print the nodes of a
// BST in Top Level Order and Reversed
// Bottom Level Order alternatively
void printBST(node* root)
{
// Stores the nodes in descending order
// of the level and node values
priority_queue<pair<int, int> > great;
// Stores the nodes in ascending order
// of the level and node values
priority_queue<pair<int, int>,
vector<pair<int, int> >,
greater<pair<int, int> > >
small;
// Initialize a stack for
// level order traversal
stack<pair<node*, int> > st;
// Push the root of BST
// into the stack
st.push({ root, 1 });
// Perform Level Order Traversal
while (!st.empty()) {
// Extract and pop the node
// from the current level
node* curr = st.top().first;
// Stores level of current node
int level = st.top().second;
st.pop();
// Store in the priority queues
great.push({ level, curr->data });
small.push({ level, curr->data });
// Traverse left subtree
if (curr->left)
st.push({ curr->left, level + 1 });
// Traverse right subtree
if (curr->right)
st.push({ curr->right, level + 1 });
}
// Stores the levels that are printed
unordered_set<int> levelsprinted;
// Print the nodes in the required manner
while (!small.empty() && !great.empty()) {
// Store the top level of traversal
int toplevel = small.top().first;
// If the level is already printed
if (levelsprinted.find(toplevel)
!= levelsprinted.end())
break;
// Otherwise
else
levelsprinted.insert(toplevel);
// Print nodes of same level
while (!small.empty()
&& small.top().first == toplevel) {
cout << small.top().second << " ";
small.pop();
}
// Store the bottom level of traversal
int bottomlevel = great.top().first;
// If the level is already printed
if (levelsprinted.find(bottomlevel)
!= levelsprinted.end()) {
break;
}
else {
levelsprinted.insert(bottomlevel);
}
// Print the nodes of same level
while (!great.empty()
&& great.top().first == bottomlevel) {
cout << great.top().second << " ";
great.pop();
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
/*
Given BST
25
/ \
20 36
/ \ / \
10 22 30 40
/ \ / / \
5 12 28 38 48
*/
// Creating the BST
node* root = newnode(25);
root->left = newnode(20);
root->right = newnode(36);
root->left->left = newnode(10);
root->left->right = newnode(22);
root->left->left->left = newnode(5);
root->left->left->right = newnode(12);
root->right->left = newnode(30);
root->right->right = newnode(40);
root->right->left->left = newnode(28);
root->right->right->left = newnode(38);
root->right->right->right = newnode(48);
// Function Call
printBST(root);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Structure of a BST node
static class node {
int data;
node left;
node right;
}
//Structure of pair (used in PriorityQueue)
static class pair{
int x,y;
pair(int xx, int yy){
this.x=xx;
this.y=yy;
}
}
//Structure of pair (used in Stack)
static class StackPair{
node n;
int x;
StackPair(node nn, int xx){
this.n=nn;
this.x=xx;
}
}
// Utility function to create a new BST node
static node newnode(int d)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
temp.data = d;
return temp;
}
//Custom Comparator for pair class to sort
//elements in increasing order
static class IncreasingOrder implements Comparator<pair>{
public int compare(pair p1, pair p2){
if(p1.x>p2.x){
return 1;
}else{
if(p1.x<p2.x){
return -1;
}else{
if(p1.y>p2.y){
return 1;
}else{
if(p1.y<p2.y){
return -1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
}
}
}
}
// Custom Comparator for pair class to sort
// elements in decreasing order
static class DecreasingOrder implements Comparator<pair>{
public int compare(pair p1, pair p2){
if(p1.x>p2.x){
return -1;
}else{
if(p1.x<p2.x){
return 1;
}else{
if(p1.y>p2.y){
return -1;
}else{
if(p1.y<p2.y){
return 1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
}
}
}
}
// Function to print the nodes of a
// BST in Top Level Order and Reversed
// Bottom Level Order alternatively
static void printBST(node root)
{
// Stores the nodes in descending order
// of the level and node values
PriorityQueue<pair> great = new PriorityQueue<>(new DecreasingOrder());
// Stores the nodes in ascending order
// of the level and node values
PriorityQueue<pair> small = new PriorityQueue<>(new IncreasingOrder());
// Initialize a stack for
// level order traversal
Stack<StackPair> st = new Stack<>();
// Push the root of BST
// into the stack
st.push(new StackPair(root,1));
// Perform Level Order Traversal
while (!st.isEmpty()) {
// Extract and pop the node
// from the current level
StackPair sp = st.pop();
node curr = sp.n;
// Stores level of current node
int level = sp.x;
// Store in the priority queues
great.add(new pair(level,curr.data));
small.add(new pair(level,curr.data));
// Traverse left subtree
if (curr.left!=null)
st.push(new StackPair(curr.left,level+1));
// Traverse right subtree
if (curr.right!=null)
st.push(new StackPair(curr.right,level+1));
}
// Stores the levels that are printed
HashSet<Integer> levelsprinted = new HashSet<>();
// Print the nodes in the required manner
while (!small.isEmpty() && !great.isEmpty()) {
// Store the top level of traversal
int toplevel = small.peek().x;
// If the level is already printed
if (levelsprinted.contains(toplevel))
break;
// Otherwise
else
levelsprinted.add(toplevel);
// Print nodes of same level
while (!small.isEmpty() && small.peek().x == toplevel) {
System.out.print(small.poll().y + " ");
}
// Store the bottom level of traversal
int bottomlevel = great.peek().x;
// If the level is already printed
if (levelsprinted.contains(bottomlevel)) {
break;
}
else {
levelsprinted.add(bottomlevel);
}
// Print the nodes of same level
while (!great.isEmpty() && great.peek().x == bottomlevel) {
System.out.print(great.poll().y + " ");
}
}
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
/*
Given BST
25
/ \
20 36
/ \ / \
10 22 30 40
/ \ / / \
5 12 28 38 48
*/
// Creating the BST
node root = newnode(25);
root.left = newnode(20);
root.right = newnode(36);
root.left.left = newnode(10);
root.left.right = newnode(22);
root.left.left.left = newnode(5);
root.left.left.right = newnode(12);
root.right.left = newnode(30);
root.right.right = newnode(40);
root.right.left.left = newnode(28);
root.right.right.left = newnode(38);
root.right.right.right = newnode(48);
// Function Call
printBST(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shruti456rawal
25 48 38 28 12 5 20 36 40 30 22 10
Complejidad de tiempo: O(V log(V)), donde V denota el número de vértices en el espacio auxiliar del árbol binario dado : O(V)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por sunilkannur98 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA