Dado un gráfico dirigido G N Nodes y E Edges que consta de Nodes valorados [0, N – 1] y una array 2D Edges[][2] de tipo { u , v } que denota un borde dirigido entre los vértices u y v . La tarea es encontrar los Nodes que no forman parte de ningún ciclo en el gráfico G dado .
Ejemplos:
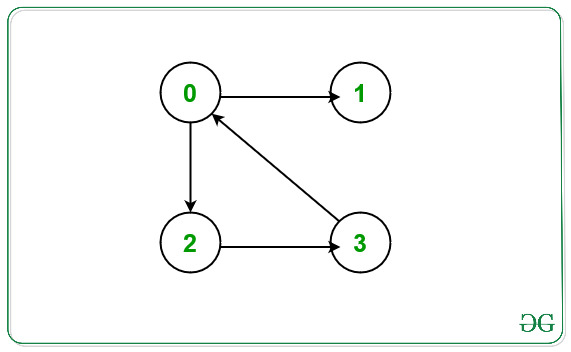
Entrada: N = 4, E = 4, Edges[][2] = { {0, 2}, {0, 1}, {2, 3}, {3, 0} }
Salida: 1
Explicación:
Del gráfico anterior existe un ciclo entre los Nodes 0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 0. El
Node que no ocurre en ningún ciclo es 1.
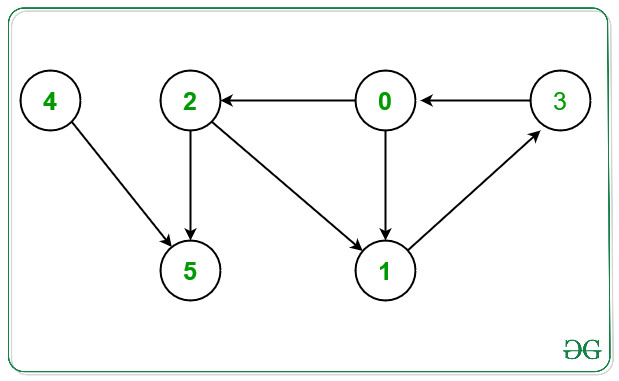
Por lo tanto, imprima 1.Entrada: N = 6, E = 7, Bordes[][2] = { {0, 1}, {0, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 1}, {2, 5}, {3 , 0}, {4, 5}}
Salida: 4 5
Explicación:
Del gráfico anterior existe un ciclo entre los Nodes:
1) 0 -> 1 -> 3 -> 0.
2) 0 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3 -> 0.
Nodes que no ocurren en ningún ciclo son 4 y 5.
Por lo tanto, imprima 4 y 5.
Enfoque ingenuo: el enfoque más simple es detectar un ciclo en un gráfico dirigido para cada Node en el gráfico dado e imprimir solo aquellos Nodes que no forman parte de ningún ciclo en el gráfico dado.
Complejidad temporal: O(V * (V + E)), donde V es el número de vértices y E es el número de aristas.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(V)
Enfoque eficiente: para optimizar el enfoque anterior, la idea es almacenar el Node intermedio como un Node de ciclo visitado siempre que haya un ciclo en el gráfico dado. Para implementar esta parte, use una array auxiliar cyclePart[] que almacenará el Node de ciclo intermedio mientras realiza el DFS Traversal . A continuación se muestran los pasos:
- Inicialice una array auxiliar CyclePart[] de tamaño N , de modo que si CyclePart[i] = 0 , entonces el i -ésimo Node no existe en ningún ciclo.
- Inicialice una array auxiliar recStack[] de tamaño N , de modo que almacene el Node visitado en la pila de recurrencia marcando ese Node como verdadero .
- Realice el DFS Traversal en el gráfico dado para cada Node no visitado y haga lo siguiente:
- Ahora encuentre un ciclo en el gráfico dado, cada vez que encuentre un ciclo, marque el Node en CyclePart[] como verdadero ya que este Node es parte del ciclo.
- Si se visita algún Node en la llamada recursiva y recStack[node] también es verdadero, entonces ese Node es parte del ciclo, luego marque ese Node como verdadero .
- Después de realizar el DFS Traversal , recorra la array CyclePart[] e imprima todos los Nodes que están marcados como falsos , ya que estos Nodes no forman parte de ningún ciclo.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Graph {
// No. of vertices
int V;
// Stores the Adjacency List
list<int>* adj;
bool printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
int v, bool visited[], bool* rs,
bool* cyclePart);
public:
// Constructor
Graph(int V);
// Member Functions
void addEdge(int v, int w);
void printNodesNotInCycle();
};
// Function to initialize the graph
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list<int>[V];
}
// Function that adds directed edges
// between node v with node w
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w);
}
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
// and return true if current node v
// formes cycle
bool Graph::printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
int v, bool visited[],
bool* recStack, bool* cyclePart)
{
// If node v is unvisited
if (visited[v] == false) {
// Mark the current node as
// visited and part of
// recursion stack
visited[v] = true;
recStack[v] = true;
// Traverse the Adjacency
// List of current node v
for (auto& child : adj[v]) {
// If child node is unvisited
if (!visited[child]
&& printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
child, visited,
recStack, cyclePart)) {
// If child node is a part
// of cycle node
cyclePart[child] = 1;
return true;
}
// If child node is visited
else if (recStack[child]) {
cyclePart[child] = 1;
return true;
}
}
}
// Remove vertex from recursion stack
recStack[v] = false;
return false;
}
// Function that print the nodes for
// the given directed graph that are
// not present in any cycle
void Graph::printNodesNotInCycle()
{
// Stores the visited node
bool* visited = new bool[V];
// Stores nodes in recursion stack
bool* recStack = new bool[V];
// Stores the nodes that are
// part of any cycle
bool* cyclePart = new bool[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
recStack[i] = false;
cyclePart[i] = false;
}
// Traverse each node
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
// If current node is unvisited
if (!visited[i]) {
// Perform DFS Traversal
if (printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
i, visited, recStack,
cyclePart)) {
// Mark as cycle node
// if it return true
cyclePart[i] = 1;
}
}
}
// Traverse the cyclePart[]
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
// If node i is not a part
// of any cycle
if (cyclePart[i] == 0) {
cout << i << " ";
}
}
}
// Function that print the nodes for
// the given directed graph that are
// not present in any cycle
void solve(int N, int E,
int Edges[][2])
{
// Initialize the graph g
Graph g(N);
// Create a directed Graph
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
g.addEdge(Edges[i][0],
Edges[i][1]);
}
// Function Call
g.printNodesNotInCycle();
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Number of nodes
int N = 6;
// Given Edges
int E = 7;
int Edges[][2] = { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 },
{ 1, 3 }, { 2, 1 },
{ 2, 5 }, { 3, 0 },
{ 4, 5 } };
// Function Call
solve(N, E, Edges);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for above approach
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
class GFG
{
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj;
static int V;
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
// and return true if current node v
// formes cycle
static boolean printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
int v, boolean visited[],
boolean[] recStack, boolean[] cyclePart)
{
// If node v is unvisited
if (visited[v] == false)
{
// Mark the current node as
// visited and part of
// recursion stack
visited[v] = true;
recStack[v] = true;
// Traverse the Adjacency
// List of current node v
for (Integer child : adj.get(v))
{
// If child node is unvisited
if (!visited[child]
&& printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
child, visited,
recStack, cyclePart))
{
// If child node is a part
// of cycle node
cyclePart[child] = true;
return true;
}
// If child node is visited
else if (recStack[child])
{
cyclePart[child] = true;
return true;
}
}
}
// Remove vertex from recursion stack
recStack[v] = false;
return false;
}
static void printNodesNotInCycle()
{
// Stores the visited node
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
// Stores nodes in recursion stack
boolean[] recStack = new boolean[V];
// Stores the nodes that are
// part of any cycle
boolean[] cyclePart = new boolean[V];
// Traverse each node
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// If current node is unvisited
if (!visited[i])
{
// Perform DFS Traversal
if (printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
i, visited, recStack,
cyclePart)) {
// Mark as cycle node
// if it return true
cyclePart[i] = true;
}
}
}
// Traverse the cyclePart[]
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// If node i is not a part
// of any cycle
if (!cyclePart[i])
{
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
}
// Function that print the nodes for
// the given directed graph that are
// not present in any cycle
static void solve(int N, int E,
int Edges[][])
{
adj = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
// Create a directed Graph
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
adj.get(Edges[i][0]).add(Edges[i][1]);
}
// Function Call
printNodesNotInCycle();
}
// Driver function
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// Given Number of nodes
V = 6;
// Given Edges
int E = 7;
int Edges[][] = { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 },
{ 1, 3 }, { 2, 1 },
{ 2, 5 }, { 3, 0 },
{ 4, 5 } };
// Function Call
solve(V, E, Edges);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach class Graph: # Function to initialize the graph def __init__(self, V): self.V = V self.adj = [[] for i in range(self.V)] # Function that adds directed edges # between node v with node w def addEdge(self, v, w): self.adj[v].append(w); # Function to perform DFS Traversal # and return True if current node v # formes cycle def printNodesNotInCycleUtil(self, v, visited,recStack, cyclePart): # If node v is unvisited if (visited[v] == False): # Mark the current node as # visited and part of # recursion stack visited[v] = True; recStack[v] = True; # Traverse the Adjacency # List of current node v for child in self.adj[v]: # If child node is unvisited if (not visited[child] and self.printNodesNotInCycleUtil(child, visited,recStack, cyclePart)): # If child node is a part # of cycle node cyclePart[child] = 1; return True; # If child node is visited elif (recStack[child]): cyclePart[child] = 1; return True; # Remove vertex from recursion stack recStack[v] = False; return False; # Function that print the nodes for # the given directed graph that are # not present in any cycle def printNodesNotInCycle(self): # Stores the visited node visited = [False for i in range(self.V)]; # Stores nodes in recursion stack recStack = [False for i in range(self.V)]; # Stores the nodes that are # part of any cycle cyclePart = [False for i in range(self.V)] # Traverse each node for i in range(self.V): # If current node is unvisited if (not visited[i]): # Perform DFS Traversal if(self.printNodesNotInCycleUtil( i, visited, recStack, cyclePart)): # Mark as cycle node # if it return True cyclePart[i] = 1; # Traverse the cyclePart[] for i in range(self.V): # If node i is not a part # of any cycle if (cyclePart[i] == 0) : print(i,end=' ') # Function that print the nodes for # the given directed graph that are # not present in any cycle def solve( N, E, Edges): # Initialize the graph g g = Graph(N); # Create a directed Graph for i in range(E): g.addEdge(Edges[i][0], Edges[i][1]); # Function Call g.printNodesNotInCycle(); # Driver Code if __name__=='__main__': # Given Number of nodes N = 6; # Given Edges E = 7; Edges = [ [ 0, 1 ], [ 0, 2 ], [ 1, 3 ], [ 2, 1 ], [ 2, 5 ], [ 3, 0 ], [ 4, 5 ] ]; # Function Call solve(N, E, Edges); # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C#
// C# program for above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG
{
static List<List<int>> adj;
static int V;
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
// and return true if current node v
// formes cycle
static bool printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
int v, bool []visited,
bool[] recStack, bool[] cyclePart)
{
// If node v is unvisited
if (visited[v] == false)
{
// Mark the current node as
// visited and part of
// recursion stack
visited[v] = true;
recStack[v] = true;
// Traverse the Adjacency
// List of current node v
foreach (int child in adj[v])
{
// If child node is unvisited
if (!visited[child]
&& printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
child, visited,
recStack, cyclePart))
{
// If child node is a part
// of cycle node
cyclePart[child] = true;
return true;
}
// If child node is visited
else if (recStack[child])
{
cyclePart[child] = true;
return true;
}
}
}
// Remove vertex from recursion stack
recStack[v] = false;
return false;
}
static void printNodesNotInCycle()
{
// Stores the visited node
bool[] visited = new bool[V];
// Stores nodes in recursion stack
bool[] recStack = new bool[V];
// Stores the nodes that are
// part of any cycle
bool[] cyclePart = new bool[V];
// Traverse each node
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// If current node is unvisited
if (!visited[i])
{
// Perform DFS Traversal
if (printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
i, visited, recStack,
cyclePart)) {
// Mark as cycle node
// if it return true
cyclePart[i] = true;
}
}
}
// Traverse the cyclePart[]
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// If node i is not a part
// of any cycle
if (!cyclePart[i])
{
Console.Write(i+" ");
}
}
}
// Function that print the nodes for
// the given directed graph that are
// not present in any cycle
static void solve(int N, int E,
int [,]Edges)
{
adj = new List<List<int>>();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
adj.Add(new List<int>());
// Create a directed Graph
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
adj[Edges[i,0]].Add(Edges[i,1]);
}
// Function Call
printNodesNotInCycle();
}
// Driver function
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Given Number of nodes
V = 6;
// Given Edges
int E = 7;
int [,]Edges = { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 },
{ 1, 3 }, { 2, 1 },
{ 2, 5 }, { 3, 0 },
{ 4, 5 } };
// Function Call
solve(V, E, Edges);
}
}
// This code contributed by shikhasingrajput
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program for the above approach
class Graph{
// Function to initialize the graph
constructor(V){
this.V = V
this.adj = new Array(V).fill(0).map(()=>[])
}
// Function that adds directed edges
// between node v with node w
addEdge(v, w){
this.adj[v].push(w);
}
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
// and return true if current node v
// formes cycle
printNodesNotInCycleUtil(v, visited,recStack, cyclePart){
// If node v is unvisited
if (visited[v] == false){
// Mark the current node as
// visited and part of
// recursion stack
visited[v] = true;
recStack[v] = true;
// Traverse the Adjacency
// List of current node v
for(let child of this.adj[v]){
// If child node is unvisited
if (visited[child] == false && this.printNodesNotInCycleUtil(child, visited,recStack, cyclePart)){
// If child node is a part
// of cycle node
cyclePart[child] = 1;
return true;
}
// If child node is visited
else if (recStack[child]){
cyclePart[child] = 1;
return true;
}
}
}
// Remove vertex from recursion stack
recStack[v] = false;
return false;
}
// Function that print the nodes for
// the given directed graph that are
// not present in any cycle
printNodesNotInCycle(){
// Stores the visited node
let visited = new Array(this.V).fill(false);
// Stores nodes in recursion stack
let recStack = new Array(this.V).fill(false);
// Stores the nodes that are
// part of any cycle
let cyclePart = new Array(this.V).fill(false)
// Traverse each node
for(let i=0;i<this.V;i++){
// If current node is unvisited
if (visited[i] == false){
// Perform DFS Traversal
if(this.printNodesNotInCycleUtil(
i, visited, recStack,
cyclePart))
// Mark as cycle node
// if it return true
cyclePart[i] = 1;
}
}
// Traverse the cyclePart[]
for(let i=0;i<this.V;i++){
// If node i is not a part
// of any cycle
if (cyclePart[i] == 0)
document.write(i,' ')
}
}
}
// Function that print the nodes for
// the given directed graph that are
// not present in any cycle
function solve(N, E, Edges){
// Initialize the graph g
let g = new Graph(N);
// Create a directed Graph
for(let i=0;i<E;i++){
g.addEdge(Edges[i][0],
Edges[i][1]);
}
// Function Call
g.printNodesNotInCycle();
}
// Driver Code
// Given Number of nodes
let N = 6;
// Given Edges
let E = 7;
let Edges = [ [ 0, 1 ], [ 0, 2 ],
[ 1, 3 ], [ 2, 1 ],
[ 2, 5 ], [ 3, 0 ],
[ 4, 5 ] ];
// Function Call
solve(N, E, Edges)
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
</script>
4 5
Complejidad Temporal: O(V + E)
Complejidad Espacial: O(V)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por pradyumanagarwal y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA