Dado un árbol binario, imprímalo verticalmente. El siguiente ejemplo ilustra el recorrido de orden vertical.
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
\ \
8 9
The output of print this tree vertically will be:
4
2
1 5 6
3 8
7
9
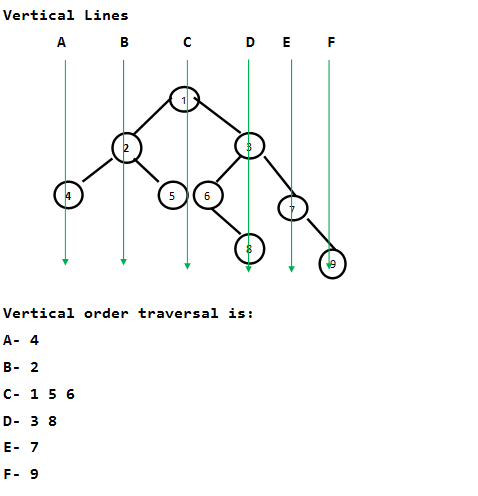
La idea es atravesar el árbol una vez y obtener la distancia horizontal mínima y máxima con respecto a la raíz. Para el árbol que se muestra arriba, la distancia mínima es -2 (para el Node con valor 4) y la distancia máxima es 3 (para el Node con valor 9).
Una vez que tenemos las distancias máxima y mínima desde la raíz, iteramos para cada línea vertical a la distancia mínima a máxima desde la raíz, y para cada línea vertical recorremos el árbol e imprimimos los Nodes que se encuentran en esa línea vertical.
Algoritmo:
// min --> Minimum horizontal distance from root
// max --> Maximum horizontal distance from root
// hd --> Horizontal distance of current node from root
findMinMax(tree, min, max, hd)
if tree is NULL then return;
if hd is less than min then
*min = hd;
else if hd is greater than max then
*max = hd;
findMinMax(tree->left, min, max, hd-1);
findMinMax(tree->right, min, max, hd+1);
printVerticalLine(tree, line_no, hd)
if tree is NULL then return;
if hd is equal to line_no, then
print(tree->data);
printVerticalLine(tree->left, line_no, hd-1);
printVerticalLine(tree->right, line_no, hd+1);
Implementación:
A continuación se muestra la implementación del algoritmo anterior.
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// A node of binary tree
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// A utility function to create a new Binary Tree node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to find min and max distances with respect
// to root.
void findMinMax(Node *node, int *min, int *max, int hd)
{
// Base case
if (node == NULL) return;
// Update min and max
if (hd < *min) *min = hd;
else if (hd > *max) *max = hd;
// Recur for left and right subtrees
findMinMax(node->left, min, max, hd-1);
findMinMax(node->right, min, max, hd+1);
}
// A utility function to print all nodes on a given line_no.
// hd is horizontal distance of current node with respect to root.
void printVerticalLine(Node *node, int line_no, int hd)
{
// Base case
if (node == NULL) return;
// If this node is on the given line number
if (hd == line_no)
cout << node->data << " ";
// Recur for left and right subtrees
printVerticalLine(node->left, line_no, hd-1);
printVerticalLine(node->right, line_no, hd+1);
}
// The main function that prints a given binary tree in
// vertical order
void verticalOrder(Node *root)
{
// Find min and max distances with resepect to root
int min = 0, max = 0;
findMinMax(root, &min, &max, 0);
// Iterate through all possible vertical lines starting
// from the leftmost line and print nodes line by line
for (int line_no = min; line_no <= max; line_no++)
{
printVerticalLine(root, line_no, 0);
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Create binary tree shown in above figure
Node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
root->right->left->right = newNode(8);
root->right->right->right = newNode(9);
cout << "Vertical order traversal is \n";
verticalOrder(root);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to print binary tree in reverse order
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class Values
{
int max, min;
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
Values val = new Values();
// A utility function to find min and max distances with respect
// to root.
void findMinMax(Node node, Values min, Values max, int hd)
{
// Base case
if (node == null)
return;
// Update min and max
if (hd < min.min)
min.min = hd;
else if (hd > max.max)
max.max = hd;
// Recur for left and right subtrees
findMinMax(node.left, min, max, hd - 1);
findMinMax(node.right, min, max, hd + 1);
}
// A utility function to print all nodes on a given line_no.
// hd is horizontal distance of current node with respect to root.
void printVerticalLine(Node node, int line_no, int hd)
{
// Base case
if (node == null)
return;
// If this node is on the given line number
if (hd == line_no)
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
// Recur for left and right subtrees
printVerticalLine(node.left, line_no, hd - 1);
printVerticalLine(node.right, line_no, hd + 1);
}
// The main function that prints a given binary tree in
// vertical order
void verticalOrder(Node node)
{
// Find min and max distances with resepect to root
findMinMax(node, val, val, 0);
// Iterate through all possible vertical lines starting
// from the leftmost line and print nodes line by line
for (int line_no = val.min; line_no <= val.max; line_no++)
{
printVerticalLine(node, line_no, 0);
System.out.println("");
}
}
// Driver program to test the above functions
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
/* Let us construct the tree shown in above diagram */
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(7);
tree.root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
tree.root.right.right.right = new Node(9);
System.out.println("vertical order traversal is :");
tree.verticalOrder(tree.root);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal
Python3
# Program to print binary tree in vertical order
# A binary tree
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# A utility function to find min and max distances with
# respect to root
def findMinMax(node, minimum, maximum, hd):
# Base Case
if node is None:
return
# Update min and max
if hd < minimum[0] :
minimum[0] = hd
elif hd > maximum[0]:
maximum[0] = hd
# Recur for left and right subtrees
findMinMax(node.left, minimum, maximum, hd-1)
findMinMax(node.right, minimum, maximum, hd+1)
# A utility function to print all nodes on a given line_no
# hd is horizontal distance of current node with respect to root
def printVerticalLine(node, line_no, hd):
# Base Case
if node is None:
return
# If this node is on the given line number
if hd == line_no:
print (node.data,end=" ")
# Recur for left and right subtrees
printVerticalLine(node.left, line_no, hd-1)
printVerticalLine(node.right, line_no, hd+1)
def verticalOrder(root):
# Find min and max distances with respect to root
minimum = [0]
maximum = [0]
findMinMax(root, minimum, maximum, 0)
# Iterate through all possible lines starting
# from the leftmost line and print nodes line by line
for line_no in range(minimum[0], maximum[0]+1):
printVerticalLine(root, line_no, 0)
print()
# Driver program to test above function
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
root.right.left.right = Node(8)
root.right.right.right = Node(9)
print ("Vertical order traversal is")
verticalOrder(root)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
C#
// C# program to print binary tree in reverse order
using System;
// A binary tree node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class Values
{
public int max, min;
}
public class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
Values val = new Values();
// A utility function to find min and
// max distances with respect to root.
void findMinMax(Node node, Values min,
Values max, int hd)
{
// Base case
if (node == null)
return;
// Update min and max
if (hd < min.min)
min.min = hd;
else if (hd > max.max)
max.max = hd;
// Recur for left and right subtrees
findMinMax(node.left, min, max, hd - 1);
findMinMax(node.right, min, max, hd + 1);
}
// A utility function to print
// all nodes on a given line_no.
// hd is horizontal distance of
// current node with respect to root.
void printVerticalLine(Node node,
int line_no, int hd)
{
// Base case
if (node == null)
return;
// If this node is on the given line number
if (hd == line_no)
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
// Recur for left and right subtrees
printVerticalLine(node.left, line_no, hd - 1);
printVerticalLine(node.right, line_no, hd + 1);
}
// The main function that prints
// a given binary tree in vertical order
void verticalOrder(Node node)
{
// Find min and max distances with resepect to root
findMinMax(node, val, val, 0);
// Iterate through all possible
// vertical lines starting from the
// leftmost line and print nodes line by line
for (int line_no = val.min; line_no <= val.max; line_no++)
{
printVerticalLine(node, line_no, 0);
Console.WriteLine("");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
/* Let us construct the tree
shown in above diagram */
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(7);
tree.root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
tree.root.right.right.right = new Node(9);
Console.WriteLine("vertical order traversal is :");
tree.verticalOrder(tree.root);
}
}
/* This code is contributed PrinciRaj1992 */
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to print binary tree
// in reverse order
class Node
{
constructor(item) {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.data = item;
}
}
let root, min = 0, max = 0;
// A utility function to find min and
// max distances with respect
// to root.
function findMinMax(node, hd)
{
// Base case
if (node == null)
return;
// Update min and max
if (hd < min)
min = hd;
else if (hd > max)
max = hd;
// Recur for left and right subtrees
findMinMax(node.left, hd - 1);
findMinMax(node.right, hd + 1);
}
// A utility function to print all nodes on a given line_no.
// hd is horizontal distance of
// current node with respect to root.
function printVerticalLine(node, line_no, hd)
{
// Base case
if (node == null)
return;
// If this node is on the given line number
if (hd == line_no)
document.write(node.data + " ");
// Recur for left and right subtrees
printVerticalLine(node.left, line_no, hd - 1);
printVerticalLine(node.right, line_no, hd + 1);
}
// The main function that prints a given binary tree in
// vertical order
function verticalOrder(node)
{
// Find min and max distances with resepect to root
findMinMax(node, 0);
// Iterate through all possible vertical lines starting
// from the leftmost line and print nodes line by line
for (let line_no = min; line_no <= max; line_no++)
{
printVerticalLine(node, line_no, 0);
document.write("</br>");
}
}
/* Let us construct the tree shown in above diagram */
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
root.right.right.right = new Node(9);
document.write("Vertical order traversal is :" + "</br>");
verticalOrder(root);
</script>
Vertical order traversal is 4 2 1 5 6 3 8 7 9
Complejidad de tiempo: la complejidad de tiempo del algoritmo anterior es O (w * n), donde w es el ancho del árbol binario y n es el número de Nodes en el árbol binario. En el peor de los casos, el valor de w puede ser O(n) (considere un árbol completo, por ejemplo) y la complejidad del tiempo puede convertirse en O(n 2 ).
Este problema se puede resolver de manera más eficiente utilizando la técnica discutida en esta publicación. Pronto discutiremos el algoritmo completo y la implementación de un método más eficiente.
Este artículo es una contribución de Shalki Agarwal . Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Método -2 – Método más optimizado: (Con MinHeaps)
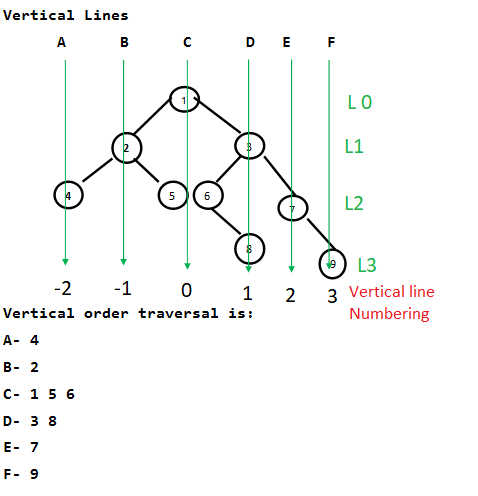
imagen hecha a sí mismo por Balakrishnan R
Algoritmo:
- Así que aquí necesitamos el recorrido de forma personalizada.
- Si numeramos las líneas verticales en dicha numeración según la imagen de arriba.
- Necesitamos el Recorrido en orden Ascendente de líneas verticales, SI EL MISMO Orden Ascendente de Nivel, SI EL MISMO Orden de Nivel Ordenamiento Traversal.
- Por lo tanto, necesitamos 4 parámetros = índice de línea vertical, índice de nivel, número de recorrido de orden de nivel (BFS), valor de Node.
- Numeración de índice vertical = comienza con 0 en la raíz.
- SI vas a la izquierda v=v-1
- SI vas a la derecha v = v+1 (Mira el diagrama para tener una idea más profunda de por qué es así)
- Índice de nivel = comienza con 0 en la raíz.
- Simplemente haga l = l+1, como izquierda o derecha, solo vamos hacia abajo.
- Entonces, con la modificación anterior, haga un recorrido de orden de nivel y almacene los Nodes abiertos en el MINHEAP.
- Luego simplemente salga de MINHEAP e imprímalo.
- Cuando vaya a la siguiente línea vertical, imprima una nueva línea según sea necesario.
NOTA:
- MinHeap, ¿por qué? Como necesitamos un orden Ascendente, lo mínimo primero en la parte superior.
- usamos pair<pair<int,int>,pair<int,int>> para almacenar los 4 parámetros {{ },{ }}
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define Nii pair<Node*, pair<int, int>>
#define ppi pair<pair<int,int>,pair<int,int>>
// A node of binary tree
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// A utility function to create a new Binary Tree node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
//Function to find the vertical order traversal of Binary Tree.
void verticalOrder(Node *root)
{
queue<Nii> qu; //node, vertical, level
priority_queue<ppi,vector<ppi>,greater<ppi>> minH;
//Vertical, Level, BFSNo, Val
int v = 0;
int l = 0;
qu.push({root,{v,l}});
//LEVEL order traversal
while(!qu.empty()){
int s = qu.size();
int i = 0;
while(i<s){
Node* node = qu.front().first;
v = qu.front().second.first;
l = qu.front().second.second;
//Vertical indx , Levelindx , BFSNo, Val - Insertion
minH.push({{v,l},{i,node->data}});
qu.pop();
if(node->left !=NULL) qu.push({node->left,{v-1,l+1}});
if(node->right !=NULL) qu.push({node->right,{v+1,l+1}});
i++;
}
}
while(!minH.empty()){
int vi = minH.top().first.first;
cout<< minH.top().second.second<<" ";
minH.pop();
if(vi!=minH.top().first.first) cout<<"\n";
}
}
int main()
{
// Create binary tree shown in above figure
Node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
root->right->left->right = newNode(8);
root->right->right->right = newNode(9);
cout << "Vertical order traversal is \n";
verticalOrder(root);
return 0;
}
//Code Done by Balakrishnan R (rbkraj000)
Vertical order traversal is 4 2 1 5 6 3 8 7 9
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N*LogN) Tiempo
Razón:
- El recorrido de orden de nivel normal (BFS) toma O (N).
- Pero aquí estamos presionando en MinHeap: solo empuje O (LogN).
- Entonces, en general O (N * LogN).
- También al salir de minHeap O(N*LogN).
Espacio Auxiliar: O(N)
Razón:
- La cola tendrá un máximo en el último nivel O(N/2) = O(N).
- El montón también almacena todos los Nodes en un punto, por lo que O(N).
N es el tamaño del árbol binario. (Nº total de Nodes)
Balakrishnan R (rbkraj000 – GFG ID) realiza la idea, el algoritmo y el código del Método 2 anterior . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA