requisito previo :
- Insertar Elemento Circular Lista Doblemente Vinculada .
- Convierta una array en una lista circular doblemente enlazada.
Dado el puntero de inicio que apunta al inicio de una Lista circular doblemente enlazada, un elemento y una posición . La tarea es insertar el elemento en la posición especificada en la lista circular doblemente enlazada dada.
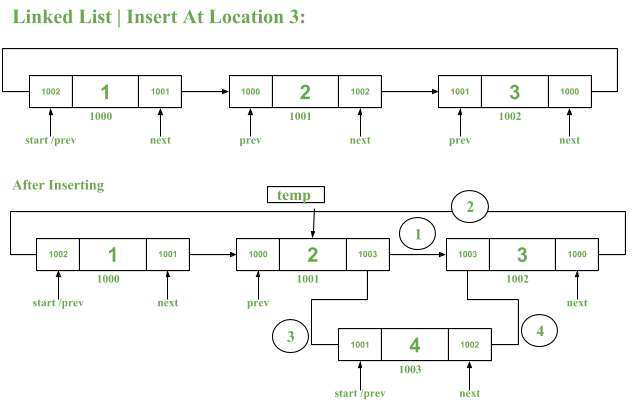
La idea es contar el número total de elementos en la lista. Compruebe si la ubicación especificada es válida o no, es decir, la ubicación está dentro del conteo.
Si la ubicación es válida:
- Crea un nuevo Node en la memoria.
- Recorra la lista usando un puntero temporal ( temp ) hasta el Node justo antes de la posición dada en la que se necesita insertar un nuevo Node.
- Inserte el nuevo Node realizando las siguientes operaciones:
- Asignar nuevoNode->siguiente = temporal->siguiente
- Asigne newNode->prev como temp->next
- Asignar temp->siguiente como newNode
- Asignar (temp->siguiente)->anterior como nuevoNode->siguiente
A continuación se muestra la implementación de la idea anterior:
C++
// CPP program to convert insert an element at a specific
// position in a circular doubly linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Doubly linked list node
struct node {
int data;
struct node* next;
struct node* prev;
};
// Utility function to create a node in memory
struct node* getNode()
{
return ((struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)));
}
// Function to display the list
int displayList(struct node* temp)
{
struct node* t = temp;
if (temp == NULL)
return 0;
else {
cout << "The list is: ";
while (temp->next != t) {
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << temp->data << endl;
return 1;
}
}
// Function to count number of
// elements in the list
int countList(struct node* start)
{
// Declare temp pointer to
// traverse the list
struct node* temp = start;
// Variable to store the count
int count = 0;
// Iterate the list and increment the count
while (temp->next != start) {
temp = temp->next;
count++;
}
// As the list is circular, increment the
// counter at last
count++;
return count;
}
// Function to insert a node at a given position
// in the circular doubly linked list
bool insertAtLocation(struct node* start, int data, int loc)
{
// Declare two pointers
struct node *temp, *newNode;
int i, count;
// Create a new node in memory
newNode = getNode();
// Point temp to start
temp = start;
// count of total elements in the list
count = countList(start);
// If list is empty or the position is
// not valid, return false
if (temp == NULL || count < loc)
return false;
else {
// Assign the data
newNode->data = data;
// Iterate till the loc
for (i = 1; i < loc - 1; i++) {
temp = temp->next;
}
// See in Image, circle 1
newNode->next = temp->next;
// See in Image, Circle 2
(temp->next)->prev = newNode;
// See in Image, Circle 3
temp->next = newNode;
// See in Image, Circle 4
newNode->prev = temp;
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Function to create circular doubly linked list
// from array elements
void createList(int arr[], int n, struct node** start)
{
// Declare newNode and temporary pointer
struct node *newNode, *temp;
int i;
// Iterate the loop until array length
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Create new node
newNode = getNode();
// Assign the array data
newNode->data = arr[i];
// If it is first element
// Put that node prev and next as start
// as it is circular
if (i == 0) {
*start = newNode;
newNode->prev = *start;
newNode->next = *start;
}
else {
// Find the last node
temp = (*start)->prev;
// Add the last node to make them
// in circular fashion
temp->next = newNode;
newNode->next = *start;
newNode->prev = temp;
temp = *start;
temp->prev = newNode;
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Array elements to create
// circular doubly linked list
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Start Pointer
struct node* start = NULL;
// Create the List
createList(arr, n, &start);
// Display the list before insertion
displayList(start);
// Inserting 8 at 3rd position
insertAtLocation(start, 8, 3);
// Display the list after insertion
displayList(start);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to convert insert
// an element at a specific position
// in a circular doubly linked listing,
// end and middle
class GFG
{
// Doubly linked list node
static class node
{
int data;
node next;
node prev;
};
// Utility function to create a node in memory
static node getNode()
{
return new node();
}
// Function to display the list
static int displayList( node temp)
{
node t = temp;
if (temp == null)
return 0;
else
{
System.out.println( "The list is: ");
while (temp.next != t)
{
System.out.print( temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println( temp.data );
return 1;
}
}
// Function to count number of
// elements in the list
static int countList( node start)
{
// Declare temp pointer to
// traverse the list
node temp = start;
// Variable to store the count
int count = 0;
// Iterate the list and
// increment the count
while (temp.next != start)
{
temp = temp.next;
count++;
}
// As the list is circular, increment
// the counter at last
count++;
return count;
}
// Function to insert a node at
// a given position in the
// circular doubly linked list
static node insertAtLocation( node start,
int data, int loc)
{
// Declare two pointers
node temp, newNode;
int i, count;
// Create a new node in memory
newNode = getNode();
// Point temp to start
temp = start;
// count of total elements in the list
count = countList(start);
// If list is empty or the position is
// not valid, return false
if (temp == null || count < loc)
return start;
else
{
// Assign the data
newNode.data = data;
// Iterate till the loc
for (i = 1; i < loc - 1; i++)
{
temp = temp.next;
}
// See in Image, circle 1
newNode.next = temp.next;
// See in Image, Circle 2
(temp.next).prev = newNode;
// See in Image, Circle 3
temp.next = newNode;
// See in Image, Circle 4
newNode.prev = temp;
return start;
}
}
// Function to create circular doubly
// linked list from array elements
static node createList(int arr[], int n, node start)
{
// Declare newNode and temporary pointer
node newNode, temp;
int i;
// Iterate the loop until array length
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Create new node
newNode = getNode();
// Assign the array data
newNode.data = arr[i];
// If it is first element
// Put that node prev and next as start
// as it is circular
if (i == 0)
{
start = newNode;
newNode.prev = start;
newNode.next = start;
}
else
{
// Find the last node
temp = (start).prev;
// Add the last node to make them
// in circular fashion
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.next = start;
newNode.prev = temp;
temp = start;
temp.prev = newNode;
}
}
return start;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Array elements to create
// circular doubly linked list
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
int n = arr.length;
// Start Pointer
node start = null;
// Create the List
start = createList(arr, n, start);
// Display the list before insertion
displayList(start);
// Inserting 8 at 3rd position
start = insertAtLocation(start, 8, 3);
// Display the list after insertion
displayList(start);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Python3
# Python3 program to insert an element
# at a specific position in a
# circular doubly linked list
# Node of the doubly linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.prev = None
self.next = None
# Utility function to create
# a node in memory
def getNode():
return (Node(0))
# Function to display the list
def displayList(temp):
t = temp
if (temp == None):
return 0
else :
print("The list is: ", end = " ")
while (temp.next != t):
print( temp.data, end = " ")
temp = temp.next
print(temp.data )
return 1
# Function to count number of
# elements in the list
def countList( start):
# Declare temp pointer to
# traverse the list
temp = start
# Variable to store the count
count = 0
# Iterate the list and increment the count
while (temp.next != start) :
temp = temp.next
count = count + 1
# As the list is circular, increment the
# counter at last
count = count + 1
return count
# Function to insert a node at a given position
# in the circular doubly linked list
def insertAtLocation(start, data, loc):
# Declare two pointers
temp = None
newNode = None
i = 0
count = 0
# Create a new node in memory
newNode = getNode()
# Point temp to start
temp = start
# count of total elements in the list
count = countList(start)
# If list is empty or the position is
# not valid, return False
if (temp == None or count < loc):
return start
else :
# Assign the data
newNode.data = data
# Iterate till the loc
i = 1;
while(i < loc - 1) :
temp = temp.next
i = i + 1
# See in Image, circle 1
newNode.next = temp.next
# See in Image, Circle 2
(temp.next).prev = newNode
# See in Image, Circle 3
temp.next = newNode
# See in Image, Circle 4
newNode.prev = temp
return start
return start
# Function to create circular
# doubly linked list from array elements
def createList(arr, n, start):
# Declare newNode and temporary pointer
newNode = None
temp = None
i = 0
# Iterate the loop until array length
while (i < n) :
# Create new node
newNode = getNode()
# Assign the array data
newNode.data = arr[i]
# If it is first element
# Put that node prev and next as start
# as it is circular
if (i == 0) :
start = newNode
newNode.prev = start
newNode.next = start
else :
# Find the last node
temp = (start).prev
# Add the last node to make them
# in circular fashion
temp.next = newNode
newNode.next = start
newNode.prev = temp
temp = start
temp.prev = newNode
i = i + 1;
return start
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Array elements to create
# circular doubly linked list
arr = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
n = len(arr)
# Start Pointer
start = None
# Create the List
start = createList(arr, n, start)
# Display the list before insertion
displayList(start)
# Inserting 8 at 3rd position
start = insertAtLocation(start, 8, 3)
# Display the list after insertion
displayList(start)
# This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
C#
// C# program to convert insert
// an element at a specific position
// in a circular doubly linked listing,
// end and middle
using System;
class GFG
{
// Doubly linked list node
public class node
{
public int data;
public node next;
public node prev;
};
// Utility function to create a node in memory
static node getNode()
{
return new node();
}
// Function to display the list
static int displayList( node temp)
{
node t = temp;
if (temp == null)
return 0;
else
{
Console.WriteLine( "The list is: ");
while (temp.next != t)
{
Console.Write( temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
Console.WriteLine( temp.data );
return 1;
}
}
// Function to count number of
// elements in the list
static int countList( node start)
{
// Declare temp pointer to
// traverse the list
node temp = start;
// Variable to store the count
int count = 0;
// Iterate the list and
// increment the count
while (temp.next != start)
{
temp = temp.next;
count++;
}
// As the list is circular, increment
// the counter at last
count++;
return count;
}
// Function to insert a node at
// a given position in the
// circular doubly linked list
static node insertAtLocation( node start,
int data, int loc)
{
// Declare two pointers
node temp, newNode;
int i, count;
// Create a new node in memory
newNode = getNode();
// Point temp to start
temp = start;
// count of total elements in the list
count = countList(start);
// If list is empty or the position is
// not valid, return false
if (temp == null || count < loc)
return start;
else
{
// Assign the data
newNode.data = data;
// Iterate till the loc
for (i = 1; i < loc - 1; i++)
{
temp = temp.next;
}
// See in Image, circle 1
newNode.next = temp.next;
// See in Image, Circle 2
(temp.next).prev = newNode;
// See in Image, Circle 3
temp.next = newNode;
// See in Image, Circle 4
newNode.prev = temp;
return start;
}
}
// Function to create circular doubly
// linked list from array elements
static node createList(int []arr, int n, node start)
{
// Declare newNode and temporary pointer
node newNode, temp;
int i;
// Iterate the loop until array length
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Create new node
newNode = getNode();
// Assign the array data
newNode.data = arr[i];
// If it is first element
// Put that node prev and next as start
// as it is circular
if (i == 0)
{
start = newNode;
newNode.prev = start;
newNode.next = start;
}
else
{
// Find the last node
temp = (start).prev;
// Add the last node to make them
// in circular fashion
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.next = start;
newNode.prev = temp;
temp = start;
temp.prev = newNode;
}
}
return start;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Array elements to create
// circular doubly linked list
int []arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
int n = arr.Length;
// Start Pointer
node start = null;
// Create the List
start = createList(arr, n, start);
// Display the list before insertion
displayList(start);
// Inserting 8 at 3rd position
start = insertAtLocation(start, 8, 3);
// Display the list after insertion
displayList(start);
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to convert insert
// an element at a specific position
// in a circular doubly linked listing,
// end and middle
// Doubly linked list node
class node {
constructor() {
this.data = 0;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
// Utility function to create a node in memory
function getNode() {
return new node();
}
// Function to display the list
function displayList(temp) {
var t = temp;
if (temp == null) return 0;
else {
document.write("The list is: ");
while (temp.next != t) {
document.write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
document.write(temp.data + "<br>");
return 1;
}
}
// Function to count number of
// elements in the list
function countList(start)
{
// Declare temp pointer to
// traverse the list
var temp = start;
// Variable to store the count
var count = 0;
// Iterate the list and
// increment the count
while (temp.next != start) {
temp = temp.next;
count++;
}
// As the list is circular, increment
// the counter at last
count++;
return count;
}
// Function to insert a node at
// a given position in the
// circular doubly linked list
function insertAtLocation(start, data, loc) {
// Declare two pointers
var temp, newNode;
var i, count;
// Create a new node in memory
newNode = getNode();
// Point temp to start
temp = start;
// count of total elements in the list
count = countList(start);
// If list is empty or the position is
// not valid, return false
if (temp == null || count < loc) return start;
else {
// Assign the data
newNode.data = data;
// Iterate till the loc
for (i = 1; i < loc - 1; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
// See in Image, circle 1
newNode.next = temp.next;
// See in Image, Circle 2
temp.next.prev = newNode;
// See in Image, Circle 3
temp.next = newNode;
// See in Image, Circle 4
newNode.prev = temp;
return start;
}
}
// Function to create circular doubly
// linked list from array elements
function createList(arr, n, start)
{
// Declare newNode and temporary pointer
var newNode, temp;
var i;
// Iterate the loop until array length
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Create new node
newNode = getNode();
// Assign the array data
newNode.data = arr[i];
// If it is first element
// Put that node prev and next as start
// as it is circular
if (i == 0)
{
start = newNode;
newNode.prev = start;
newNode.next = start;
}
else
{
// Find the last node
temp = start.prev;
// Add the last node to make them
// in circular fashion
temp.next = newNode;
newNode.next = start;
newNode.prev = temp;
temp = start;
temp.prev = newNode;
}
}
return start;
}
// Driver Code
// Array elements to create
// circular doubly linked list
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
var n = arr.length;
// Start Pointer
var start = null;
// Create the List
start = createList(arr, n, start);
// Display the list before insertion
displayList(start);
// Inserting 8 at 3rd position
start = insertAtLocation(start, 8, 3);
// Display the list after insertion
displayList(start);
// This code is contributed by rdtank.
</script>
The list is: 1 2 3 4 5 6 The list is: 1 2 8 3 4 5 6
Complejidad de tiempo: O(n) => para contar la lista ya que estamos usando un bucle para recorrer linealmente, O(n) => Insertar los elementos, ya que estamos usando un bucle para recorrer linealmente. Entonces, la complejidad total es O(n + n) = O(n). Donde n es el número de Nodes en la lista enlazada.
Espacio auxiliar: O(1), ya que no estamos utilizando ningún espacio adicional.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por bilal-hungund y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA