Dada una lista enlazada individualmente, escriba una función para intercambiar elementos por pares.
Entrada: 1->2->3->4->5->6->NULO
Salida: 2->1->4->3->6->5->NULOEntrada: 1->2->3->4->5->NULO
Salida: 2->1->4->3->5->NULOEntrada: 1->NULO
Salida: 1->NULOPor ejemplo, si la lista enlazada es 1->2->3->4->5 entonces la función debería cambiarla a 2->1->4->3->5, y si la lista enlazada es entonces el la función debería cambiarlo a.
MÉTODO 1 (Iterativo)
Comience desde el Node principal y recorra la lista. Al atravesar los datos de intercambio de cada Node con los datos de su siguiente Node.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to pairwise swap elements// in a given linked list#include <bits/stdc++.h>usingnamespacestd;/* A linked list node */classNode {public:intdata;Node* next;};/* Function to pairwise swap elementsof a linked list */voidpairWiseSwap(Node* head){Node* temp = head;/* Traverse further only ifthere are at-least two nodes left */while(temp != NULL && temp->next != NULL) {/* Swap data of node withits next node's data */swap(temp->data,temp->next->data);/* Move temp by 2 for the next pair */temp = temp->next->next;}}/* Function to add a node at thebeginning of Linked List */voidpush(Node** head_ref,intnew_data){/* allocate node */Node* new_node =newNode();/* put in the data */new_node->data = new_data;/* link the old list off the new node */new_node->next = (*head_ref);/* move the head to pointto the new node */(*head_ref) = new_node;}/* Function to print nodesin a given linked list */voidprintList(Node* node){while(node != NULL) {cout << node->data <<" ";node = node->next;}}// Driver Codeintmain(){Node* start = NULL;/* The constructed linked list is:1->2->3->4->5 */push(&start, 5);push(&start, 4);push(&start, 3);push(&start, 2);push(&start, 1);cout <<"Linked list "<<"before calling pairWiseSwap()\n";printList(start);pairWiseSwap(start);cout <<"\nLinked list "<<"after calling pairWiseSwap()\n";printList(start);return0;}// This code is contributed// by rathbhupendraC
/* C program to pairwise swap elements in a given linked list */#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>/* A linked list node */structNode {intdata;structNode* next;};/*Function to swap two integers at addresses a and b */voidswap(int* a,int* b);/* Function to pairwise swap elements of a linked list */voidpairWiseSwap(structNode* head){structNode* temp = head;/* Traverse further only if there are at-least two nodes left */while(temp != NULL && temp->next != NULL) {/* Swap data of node with its next node's data */swap(&temp->data, &temp->next->data);/* Move temp by 2 for the next pair */temp = temp->next->next;}}/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS *//* Function to swap two integers */voidswap(int* a,int* b){inttemp;temp = *a;*a = *b;*b = temp;}/* Function to add a node at the beginning of Linked List */voidpush(structNode** head_ref,intnew_data){/* allocate node */structNode* new_node = (structNode*)malloc(sizeof(structNode));/* put in the data */new_node->data = new_data;/* link the old list off the new node */new_node->next = (*head_ref);/* move the head to point to the new node */(*head_ref) = new_node;}/* Function to print nodes in a given linked list */voidprintList(structNode* node){while(node != NULL) {printf("%d ", node->data);node = node->next;}}/* Driver program to test above function */intmain(){structNode* start = NULL;/* The constructed linked list is:1->2->3->4->5 */push(&start, 5);push(&start, 4);push(&start, 3);push(&start, 2);push(&start, 1);printf("Linked list before calling pairWiseSwap()\n");printList(start);pairWiseSwap(start);printf("\nLinked list after calling pairWiseSwap()\n");printList(start);return0;}Java
// Java program to pairwise swap elements of a linked listclassLinkedList {Node head;// head of list/* Linked list Node*/classNode {intdata;Node next;Node(intd){data = d;next =null;}}voidpairWiseSwap(){Node temp = head;/* Traverse only till there are atleast 2 nodes left */while(temp !=null&& temp.next !=null) {/* Swap the data */intk = temp.data;temp.data = temp.next.data;temp.next.data = k;temp = temp.next.next;}}/* Utility functions *//* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */publicvoidpush(intnew_data){/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &Put in the data*/Node new_node =newNode(new_data);/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */new_node.next = head;/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */head = new_node;}/* Function to print linked list */voidprintList(){Node temp = head;while(temp !=null) {System.out.print(temp.data +" ");temp = temp.next;}System.out.println();}/* Driver program to test above functions */publicstaticvoidmain(String args[]){LinkedList llist =newLinkedList();/* Created Linked List 1->2->3->4->5 */llist.push(5);llist.push(4);llist.push(3);llist.push(2);llist.push(1);System.out.println("Linked List before calling pairWiseSwap() ");llist.printList();llist.pairWiseSwap();System.out.println("Linked List after calling pairWiseSwap() ");llist.printList();}}/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */Python
# Python program to swap the elements of linked list pairwise# Node classclassNode:# Constructor to initialize the node objectdef__init__(self, data):self.data=dataself.next=NoneclassLinkedList:# Function to initialize headdef__init__(self):self.head=None# Function to pairwise swap elements of a linked listdefpairwiseSwap(self):temp=self.head# There are no nodes in linked listiftempisNone:return# Traverse furthethr only if there are at least two# leftwhile(tempandtemp.next):# If both nodes are same,# no need to swap dataif(temp.data !=temp.next.data):# Swap data of node with its next node's datatemp.data, temp.next.data=temp.next.data, temp.data# Move temp by 2 to the next pairtemp=temp.next.next# Function to insert a new node at the beginningdefpush(self, new_data):new_node=Node(new_data)new_node.next=self.headself.head=new_node# Utility function to print the linked LinkedListdefprintList(self):temp=self.headwhile(temp):temp.data,temp=temp.next# Driver programllist=LinkedList()llist.push(5)llist.push(4)llist.push(3)llist.push(2)llist.push(1)"Linked list before calling pairWiseSwap() "llist.printList()llist.pairwiseSwap()"\nLinked list after calling pairWiseSwap()"llist.printList()# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// C# program to pairwise swap elements of a linked listusingSystem;classLinkedList {Node head;// head of list/* Linked list Node*/publicclassNode {publicintdata;publicNode next;publicNode(intd){data = d;next =null;}}voidpairWiseSwap(){Node temp = head;/* Traverse only till there are atleast 2 nodes left */while(temp !=null&& temp.next !=null) {/* Swap the data */intk = temp.data;temp.data = temp.next.data;temp.next.data = k;temp = temp.next.next;}}/* Utility functions *//* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */publicvoidpush(intnew_data){/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &Put in the data*/Node new_node =newNode(new_data);/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */new_node.next = head;/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */head = new_node;}/* Function to print linked list */voidprintList(){Node temp = head;while(temp !=null) {Console.Write(temp.data +" ");temp = temp.next;}Console.WriteLine();}/* Driver program to test above functions */publicstaticvoidMain(String[] args){LinkedList llist =newLinkedList();/* Created Linked List 1->2->3->4->5 */llist.push(5);llist.push(4);llist.push(3);llist.push(2);llist.push(1);Console.WriteLine("Linked List before calling pairWiseSwap() ");llist.printList();llist.pairWiseSwap();Console.WriteLine("Linked List after calling pairWiseSwap() ");llist.printList();}}// This code is contributed by Arnab KunduJavaScript
<script>// JavaScript program to pairwise swap// elements of a linked listvarhead;// head of list/* Linked list Node */class Node {constructor(val) {this.data = val;this.next =null;}}functionpairWiseSwap() {vartemp = head;/* Traverse only till there areatleast 2 nodes left */while(temp !=null&& temp.next !=null) {/* Swap the data */vark = temp.data;temp.data = temp.next.data;temp.next.data = k;temp = temp.next.next;}}/* Utility functions *//* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */functionpush(new_data) {/** 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data*/varnew_node =newNode(new_data);/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */new_node.next = head;/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */head = new_node;}/* Function to print linked list */functionprintList() {vartemp = head;while(temp !=null) {document.write(temp.data +" ");temp = temp.next;}document.write("<br/>");}/* Driver program to test above functions *//* Created Linked List 1->2->3->4->5 */push(5);push(4);push(3);push(2);push(1);document.write("Linked List before calling pairWiseSwap() <br/>");printList();pairWiseSwap();document.write("Linked List after calling pairWiseSwap()<br/> ");printList();// This code is contributed by todaysgaurav</script>ProducciónLinked list before calling pairWiseSwap() 1 2 3 4 5 Linked list after calling pairWiseSwap() 2 1 4 3 5Complejidad del tiempo: O(N)
A medida que recorremos la lista enlazada solo una vez.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Como espacio adicional constante se utiliza.
MÉTODO 2 (Recursivo)
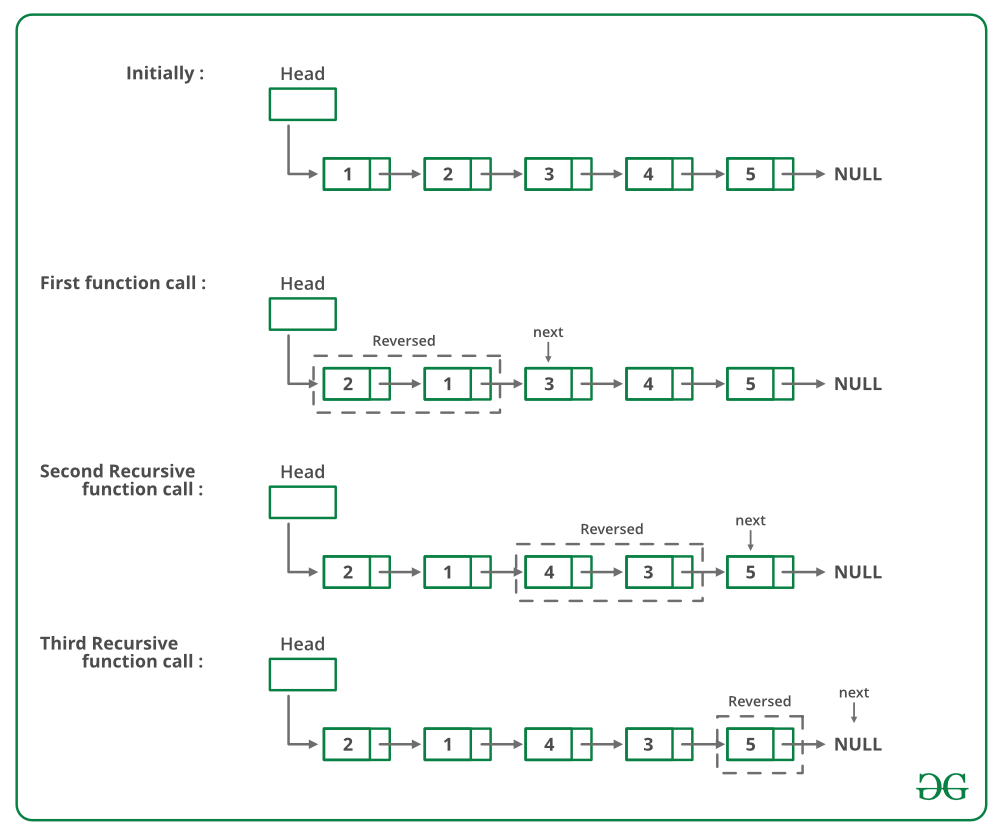
Si hay 2 o más de 2 Nodes en la lista enlazada, intercambie los dos primeros Nodes y llame recursivamente al resto de la lista.La imagen de abajo es una ejecución en seco del enfoque anterior:
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
/* Recursive function to pairwise swap elementsof a linked list */voidpairWiseSwap(node* head){/* There must be at-least two nodes in the list */if(head != NULL && head->next != NULL) {/* Swap the node's data with data of next node */swap(head->data, head->next->data);/* Call pairWiseSwap() for rest of the list */pairWiseSwap(head->next->next);}}// The code is contributed by Gautam goel (gautamgoel962)C
/* Recursive function to pairwise swap elementsof a linked list */voidpairWiseSwap(structnode* head){/* There must be at-least two nodes in the list */if(head != NULL && head->next != NULL) {/* Swap the node's data with data of next node */swap(head->data, head->next->data);/* Call pairWiseSwap() for rest of the list */pairWiseSwap(head->next->next);}}Java
/* Recursive function to pairwise swap elementsof a linked list */staticvoidpairWiseSwap(node head){/* There must be at-least two nodes in the list */if(head !=null&& head.next !=null) {/* Swap the node's data with data of next node */swap(head.data, head.next.data);/* Call pairWiseSwap() for rest of the list */pairWiseSwap(head.next.next);}}// This code contributed by aashish1995Python3
# Recursive function to pairwise swap elements of a linked listdefpairWiseSwap(head):# There must be at-least two nodes in the listif(head !=Noneandhead.next!=None):# Swap the node's data with data of next nodeswap(head.data, head.next.data);# Call pairWiseSwap() for rest of the listpairWiseSwap(head.next.next);# This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswalC#
/* Recursive function to pairwise swap elementsof a linked list */staticvoidpairWiseSwap(node head){/* There must be at-least two nodes in the list */if(head !=null&& head.next !=null) {/* Swap the node's data with data of next node */swap(head.data, head.next.data);/* Call pairWiseSwap() for rest of the list */pairWiseSwap(head.next.next);}}// This code contributed by aashish1995JavaScript
<script>/* Recursive function to pairwise swap elementsof a linked list */functionpairWiseSwap(head){/* There must be at-least two nodes in the list */if(head !=null&& head.next !=null) {/* Swap the node's data with data of next node */swap(head.data, head.next.data);/* Call pairWiseSwap() for rest of the list */pairWiseSwap(head.next.next);}}// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155</script>Complejidad temporal: O(n)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Como es una función recursiva de cola, la pila de llamadas de función no se construiría y, por lo tanto, no se usará espacio adicional.
La solución provista aquí intercambia datos de Nodes. Si los datos contienen muchos campos (por ejemplo, una lista enlazada de Objetos de Estudiante), la operación de intercambio será costosa. Consulte el siguiente artículo para obtener una mejor solución que funcione bien para todo tipo de listas vinculadas
Intercambiar Nodes por parejas cambiando enlaces
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algún error en el código/algoritmo anterior, o encuentre otras formas de resolver el mismo problema.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA