Prerrequisitos: Lista doblemente enlazada
Dada una lista doblemente enlazada , la tarea es intercambiar K -ésimo Node desde el principio con K -ésimo Node desde el final.
Nota: Tenga en cuenta que aquí se intercambian los Nodes y no los datos en los Nodes.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: DLL = 1 <-> 2 <-> 3 <-> 4 <-> 5 <-> 6, K = 3
Salida: 1 2 4 3 5 6
Explicación:
el tercer Node desde el principio (3) se intercambia con tercer Node desde la terminación (4).
Entrada: DLL = 1 <-> 2 <-> 3 <-> 4 <-> 5, K = 1
Salida: 5 2 3 4 1
Enfoque: La idea es atravesar al K -ésimo elemento desde el principio y al K -ésimo Node desde el final y cambiar los punteros anterior y siguiente. Sea K1 el K -ésimo Node desde el principio y K2 el K -ésimo Node desde el final. Después:
- El Node anterior a K2 debe cambiarse al Node anterior de K1 .
- El siguiente Node de K2 debe cambiarse al siguiente Node de K1 .
- El Node anterior a K1 debe cambiarse al Node anterior de K2 .
- El siguiente Node de K1 debe cambiarse al siguiente Node de K2 .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
public class GFG {
// Doubly Linked List implementation
private class Node {
private int data;
private Node next;
private Node previous;
public Node(int data, Node next,
Node previous)
{
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
this.previous = previous;
}
public int getData()
{
return data;
}
public void setData(int data)
{
this.data = data;
}
public Node getNext()
{
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next)
{
this.next = next;
}
public Node getPrevious()
{
return previous;
}
public void setPrevious(Node previous)
{
this.previous = previous;
}
}
private Node head;
private Node tail;
public GFG()
{
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
public Node getHead()
{
return head;
}
public void setHead(Node head)
{
this.head = head;
}
public Node getTail()
{
return tail;
}
public void setTail(Node tail)
{
this.tail = tail;
}
// Function to replace Kth node from
// beginning with Kth node from end
public void swapNode(Node headReference,
Node tailReference, int k)
{
// If K is 1, then the first node
// has to be swapped with the
// last node in the doubly linked list
if (k == 1) {
swapFirstAndLast(headReference,
tailReference);
return;
}
// If k is N, then the last node
// has to be swapped with the
// first node in the doubly linked list
int nodeCount = getCount(headReference);
if (k == nodeCount) {
swapFirstAndLast(headReference,
tailReference);
return;
}
// If the K<sup>th</sup> node from
// the beginning and K<sup>th</sup> node
// from the ending are same
if (2 * k - 1 == nodeCount) {
return;
}
// fNode represents K<sup>th</sup> node
// from the beginning
Node fNode = headReference;
for (int i = 1; i < k; i++) {
fNode = fNode.getNext();
}
Node fNodePrevious = fNode.getPrevious();
Node fNodeNext = fNode.getNext();
// sNode represents K<sup>th</sup> node
// from the ending
Node sNode = tailReference;
for (int i = 1; i < k; i++) {
sNode = sNode.getPrevious();
}
Node sNodePrevious = sNode.getPrevious();
Node sNodeNext = sNode.getNext();
// Checking if any of the pointers is null
// and interchanging the pointers
if (fNodePrevious != null && sNode != null) {
fNodePrevious.setNext(sNode);
sNode.setPrevious(fNodePrevious);
sNode.setNext(fNodeNext);
fNodeNext.setPrevious(sNode);
}
if (sNodePrevious != null && sNodeNext != null) {
sNodeNext.setPrevious(fNode);
fNode.setNext(sNodeNext);
sNodePrevious.setNext(fNode);
fNode.setPrevious(sNodePrevious);
}
}
// Function to swap the first and
// last node in the doubly linked list
private void swapFirstAndLast(
Node headReference,
Node tailReference)
{
Node headRef = headReference;
Node tailRef = tailReference;
headReference
= headReference.getNext();
tailReference
= tailReference.getPrevious();
tailReference.setNext(headRef);
headRef.setPrevious(tailReference);
headRef.setNext(null);
this.setTail(tailReference.getNext());
headReference.setPrevious(tailRef);
tailRef.setNext(headReference);
tailRef.setPrevious(null);
this.setHead(headReference
.getPrevious());
}
// Function to return the number of nodes
// in the linked list
private int getCount(Node headReference)
{
int nodeCount = 0;
while (headReference != null) {
nodeCount++;
headReference = headReference
.getNext();
}
return nodeCount;
}
// Function to print the Linked List
public void printList(Node headReference)
{
if (headReference == null) {
System.out.println(
"Doubly linked list is empty");
return;
}
else {
while (headReference != null) {
System.out.print(
headReference.getData()
+ " ");
headReference
= headReference.getNext();
}
}
}
// Function to insert a node at
// the end of the doubly linked list
public void push(int data)
{
Node newNode
= new Node(data, null, null);
if (head == null) {
head = tail = newNode;
}
else {
tail.setNext(newNode);
newNode.setPrevious(tail);
tail = newNode;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object for the class
GFG list = new GFG();
// Adding data to the linked list
list.push(1);
list.push(2);
list.push(3);
list.push(4);
list.push(5);
// Calling the function
int K = 2;
list.swapNode(list.getHead(),
list.getTail(), K);
list.printList(list.getHead());
}
}
C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
public class GFG {
// Doubly Linked List implementation
private class Node {
private int data;
private Node next;
private Node previous;
public Node(int data, Node next,
Node previous)
{
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
this.previous = previous;
}
public int getData()
{
return data;
}
public void setData(int data)
{
this.data = data;
}
public Node getNext()
{
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node next)
{
this.next = next;
}
public Node getPrevious()
{
return previous;
}
public void setPrevious(Node previous)
{
this.previous = previous;
}
}
private Node head;
private Node tail;
public GFG()
{
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
}
Node getHead()
{
return head;
}
void setHead(Node head)
{
this.head = head;
}
Node getTail()
{
return tail;
}
void setTail(Node tail)
{
this.tail = tail;
}
// Function to replace Kth node from
// beginning with Kth node from end
void swapNode(Node headReference,
Node tailReference, int k)
{
// If K is 1, then the first node
// has to be swapped with the
// last node in the doubly linked list
if (k == 1) {
swapFirstAndLast(headReference,
tailReference);
return;
}
// If k is N, then the last node
// has to be swapped with the
// first node in the doubly linked list
int nodeCount = getCount(headReference);
if (k == nodeCount) {
swapFirstAndLast(headReference,
tailReference);
return;
}
// If the K<sup>th</sup> node from
// the beginning and K<sup>th</sup> node
// from the ending are same
if (2 * k - 1 == nodeCount) {
return;
}
// fNode represents K<sup>th</sup> node
// from the beginning
Node fNode = headReference;
for (int i = 1; i < k; i++) {
fNode = fNode.getNext();
}
Node fNodePrevious = fNode.getPrevious();
Node fNodeNext = fNode.getNext();
// sNode represents K<sup>th</sup> node
// from the ending
Node sNode = tailReference;
for (int i = 1; i < k; i++) {
sNode = sNode.getPrevious();
}
Node sNodePrevious = sNode.getPrevious();
Node sNodeNext = sNode.getNext();
// Checking if any of the pointers is null
// and interchanging the pointers
if (fNodePrevious != null && sNode != null) {
fNodePrevious.setNext(sNode);
sNode.setPrevious(fNodePrevious);
sNode.setNext(fNodeNext);
fNodeNext.setPrevious(sNode);
}
if (sNodePrevious != null && sNodeNext != null) {
sNodeNext.setPrevious(fNode);
fNode.setNext(sNodeNext);
sNodePrevious.setNext(fNode);
fNode.setPrevious(sNodePrevious);
}
}
// Function to swap the first and
// last node in the doubly linked list
private void swapFirstAndLast(
Node headReference,
Node tailReference)
{
Node headRef = headReference;
Node tailRef = tailReference;
headReference
= headReference.getNext();
tailReference
= tailReference.getPrevious();
tailReference.setNext(headRef);
headRef.setPrevious(tailReference);
headRef.setNext(null);
this.setTail(tailReference.getNext());
headReference.setPrevious(tailRef);
tailRef.setNext(headReference);
tailRef.setPrevious(null);
this.setHead(headReference
.getPrevious());
}
// Function to return the number of nodes
// in the linked list
private int getCount(Node headReference)
{
int nodeCount = 0;
while (headReference != null) {
nodeCount++;
headReference = headReference
.getNext();
}
return nodeCount;
}
// Function to print the Linked List
void printList(Node headReference)
{
if (headReference == null) {
Console.WriteLine(
"Doubly linked list is empty");
return;
}
else {
while (headReference != null) {
Console.Write(
headReference.getData()
+ " ");
headReference
= headReference.getNext();
}
}
}
// Function to insert a node at
// the end of the doubly linked list
void Push(int data)
{
Node newNode
= new Node(data, null, null);
if (head == null) {
head = tail = newNode;
}
else {
tail.setNext(newNode);
newNode.setPrevious(tail);
tail = newNode;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object for the class
GFG list = new GFG();
// Adding data to the linked list
list.Push(1);
list.Push(2);
list.Push(3);
list.Push(4);
list.Push(5);
// Calling the function
int K = 2;
list.swapNode(list.getHead(),
list.getTail(), K);
list.printList(list.getHead());
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
1 4 3 2 5
Método 2: sin intercambiar los elementos y sin usar un Node temporal.
Enfoque: Hay 3 casos para intercambiar los Nodes.
- Intercambiando el primer y el último Node (k = 1)
- Intercambiando el Node Kth ordinario desde el principio y el Node Kth desde el final.
- Intercambio de Nodes medios
Caso 1: intercambiar el primer y el último Node (k = 1)
Pasos:
- Hacer la lista como una lista enlazada circular
- Cambie el puntero anterior del primer Node al penúltimo Node (20 en la figura de ejemplo)
- Cambie el siguiente puntero del penúltimo Node al último Node. En este caso serán 60.
- Después de intercambiar, haga la cabeza como el primer Node.
Consider p and q are the nodes which are to be swapped, head = q; //change head pointer to point to head node last = p; //change last pointer to point to last node
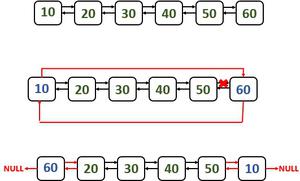
intercambiando el primer y el último Node
Caso 2: Intercambio del Node Kth ordinario desde el principio y el Node Kth desde el final.
Pasos:
- Consideremos K = 2. Entonces, los Nodes que se intercambiarán o cambiarán son 20 y 50, como se muestra en la figura.
- Haga que los punteros primero y siguiente de los Nodes que se van a intercambiar apunten a los Nodes anteriores. Para hacer esto, necesitamos cambiar los enlaces de los Nodes anteriores para que apunten al Node que está después del Node que se va a intercambiar.
Consider the nodes to be swapped are p and q:
//Change the link of the next pointer of the previous node to point to
//the next node of to be swapped node.
q.first.next = q.next;
p.first.next = p.next; // Same procedure for the other node
//Make sure to change the previous/first pointer of the next node to
//point to the previous of to be swapped node.
q.next.first = q.first;
p.next.first = p.first;
//Both the first and next pointers points to the previous node as shown in the below figure.
q.next = q.first;
p.next = p.first;
3. Intercambie los punteros de un Node para intercambiar Nodes con el otro Node para intercambiar. (el paso 3 denota la figura después de intercambiar).
4. Realice los cambios necesarios en los enlaces para que sea una lista completa.
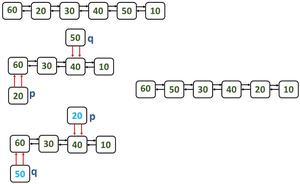
Caso general
Caso 3: Intercambio de los Nodes medios
Pasos:
- Este caso es el mismo que el caso 2 y el único cambio es que los Nodes que se intercambiarán son Nodes intermedios. Así que ambos están juntos (lado a lado).
- Considere que p es el primer Node que se intercambiará y q es el segundo Node que se intercambiará.
- Apunte el siguiente puntero del Node anterior de p al siguiente Node de q. Este paso se realiza para omitir los Nodes p y q.
- De la misma manera, apunte el primer puntero del siguiente Node de q al Node anterior de q.
- Cambie los enlaces de p y q para que ambos Nodes apunten al Node anterior de p (paso 2 en la siguiente figura).
- Haga los enlaces de p y q en consecuencia para que los Nodes intercambien sus posiciones.
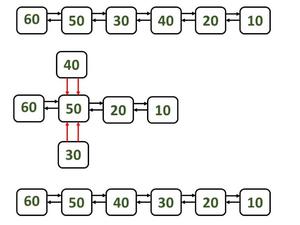
Para intercambiar Nodes intermedios
Implementación:
Java
//java program to swap Kth node from beginning with
//the Kth node from the end without using temporary
//node and without swapping the data
public class GFG {
//head pointer for pointing to start of the linked list
//last pointer for pointing to last node of the linked list
Node head = null,last = null;
//class Node
class Node{
int data;
Node first,next;
Node(int data){
this.data = data;
first = null;
next = null;
}
}
//function for inserting new node at the
//end of the list using last pointer
void AddLast(int data) {
Node temp = new Node(data);
if(head == null) {
head = temp;
last = temp;
}
else {
last.next = temp;
temp.first = last;
last = temp;
}
}
//function for printing the doubly linked list
void printList() {
Node p = head;
while(p!=null) {
System.out.print(p.data+"<->");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("null");
System.out.println();
}
//function for swapping Kth node from
//beginning with Kth node from the end
void swapKthNodes(int k) {
int count = 1;
Node p = head, q = last;
//case 1: to swap the start and end nodes
//case 1 figure
if(k == 1) {
q.first.next = p;
p.first = q.first;
q.next = p.next;
p.next.first = q;
//change these links to null to the break circular link
p.next = null;
q.first = null;
head = q;
last = p;
}
else {
while(p!=null && q!=null && count<k) {
count++;
p = p.next;
q = q.first;
}
//case 3: if the nodes to be swapped are the middle nodes
//given in the figure
if(p.next == q) {
p.first.next = p.next.next;
q.next.first = p.first;
p.next = p.first;
q.first = q.next = p.first;
q.next = p;
p.next.next.first = p;
p.next = p.first.next;
p.first.next = q;
p.first = q;
}
//case 2: other than middle nodes
//given in case 2 figure
else {
q.first.next = q.next;
q.next.first = q.first;
q.next = q.first;
p.first.next = p.next;
p.next.first = p.first;
p.next = p.first;
p.first = q.first;
q.first = p.next;
p.next = p.first;
q.next = q.first;
q.next = q.next.next;
q.first.next = q;
q.next.first = q;
p.next = p.next.next;
p.first.next = p;
p.next.first = p;
}
}
}
//Driver function
public static void main(String args[]) {
//class object
GFG list = new GFG();
//function calls for inserting
//at the end of the list
list.AddLast(10);
list.AddLast(20);
list.AddLast(30);
list.AddLast(40);
list.AddLast(50);
list.AddLast(60);
System.out.println("Before swapping:");
//print list before swapping the nodes
list.printList();
System.out.println();
//function call for swapping Kth nodes
list.swapKthNodes(1);
System.out.println("After swapping nodes for k = 1:");
//print list after swapping the nodes
list.printList();
System.out.println();
list.swapKthNodes(2);
System.out.println("After swapping nodes for k = 2:");
list.printList();
System.out.println();
list.swapKthNodes(3);
System.out.println("After swapping nodes for k = 3 (middle):");
list.printList();
System.out.println();
}
}
//This code is contributed by Likhita AVL
C#
// C# program to swap Kth node from beginning with the Kth
// node from the end without using temporary node and without
// swapping the data
using System;
public class GFG {
// class Node
class Node {
public int data;
public Node first, next;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
first = null;
next = null;
}
}
// head pointer for pointing to start of the linked list
// last pointer for pointing to last node of the linked
// list
Node head = null, last = null;
// function for inserting new node at the end of the
// list using last pointer
void AddLast(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = temp;
last = temp;
}
else {
last.next = temp;
temp.first = last;
last = temp;
}
}
// function for printing the doubly linked list
void printList()
{
Node p = head;
while (p != null) {
Console.Write(p.data + "<->");
p = p.next;
}
Console.Write("null");
Console.WriteLine();
}
// function for swapping Kth node from beginning with
// Kth node from the end
void swapKthNodes(int k)
{
int count = 1;
Node p = head, q = last;
// case 1: to swap the start and end nodes case 1
// figure
if (k == 1) {
q.first.next = p;
p.first = q.first;
q.next = p.next;
p.next.first = q;
// change these links to null to the break
// circular link
p.next = null;
q.first = null;
head = q;
last = p;
}
else {
while (p != null && q != null && count < k) {
count++;
p = p.next;
q = q.first;
}
// case 3: if the nodes to be swapped are the
// middle nodes given in the figure
if (p.next == q) {
p.first.next = p.next.next;
q.next.first = p.first;
p.next = p.first;
q.first = q.next = p.first;
q.next = p;
p.next.next.first = p;
p.next = p.first.next;
p.first.next = q;
p.first = q;
}
// case 2: other than middle nodes given in case
// 2 figure
else {
q.first.next = q.next;
q.next.first = q.first;
q.next = q.first;
p.first.next = p.next;
p.next.first = p.first;
p.next = p.first;
p.first = q.first;
q.first = p.next;
p.next = p.first;
q.next = q.first;
q.next = q.next.next;
q.first.next = q;
q.next.first = q;
p.next = p.next.next;
p.first.next = p;
p.next.first = p;
}
}
}
static public void Main()
{
GFG list = new GFG();
// function calls for inserting
// at the end of the list
list.AddLast(10);
list.AddLast(20);
list.AddLast(30);
list.AddLast(40);
list.AddLast(50);
list.AddLast(60);
Console.WriteLine("Before swapping:");
// print list before swapping the nodes
list.printList();
Console.WriteLine();
// function call for swapping Kth nodes
list.swapKthNodes(1);
Console.WriteLine(
"After swapping nodes for k = 1:");
// print list after swapping the nodes
list.printList();
Console.WriteLine();
list.swapKthNodes(2);
Console.WriteLine(
"After swapping nodes for k = 2:");
list.printList();
Console.WriteLine();
list.swapKthNodes(3);
Console.WriteLine(
"After swapping nodes for k = 3 (middle):");
list.printList();
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// This code is contributed by lokesh (lokeshmvs21).
Before swapping: 10<->20<->30<->40<->50<->60<->null After swapping nodes for k = 1: 60<->20<->30<->40<->50<->10<->null After swapping nodes for k = 2: 60<->50<->30<->40<->20<->10<->null After swapping nodes for k = 3 (middle): 60<->50<->40<->30<->20<->10<->null
Complejidad de tiempo : O(N) donde N es el número de Nodes en la lista enlazada
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por asraarwani y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA