Dada una lista doblemente enlazada , la tarea es invertir la lista doblemente enlazada dada.
Vea los diagramas a continuación, por ejemplo.
(a) Original Doubly Linked List
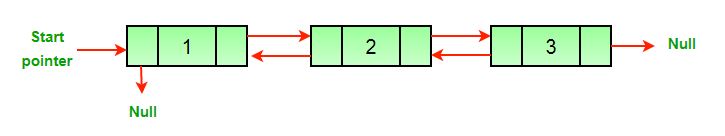
(b) Reversed Doubly Linked List
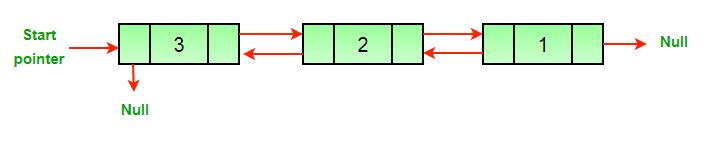
Aquí hay un método simple para invertir una lista doblemente enlazada. Todo lo que tenemos que hacer es intercambiar los punteros anterior y siguiente para todos los Nodes, cambiar la anterior del encabezado (o inicio) y cambiar el puntero del encabezado al final.
C++
/* C++ program to reverse a doubly linked list */
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* a node of the doubly linked list */
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
Node *prev;
};
/* Function to reverse a Doubly Linked List */
void reverse(Node **head_ref)
{
Node *temp = NULL;
Node *current = *head_ref;
/* swap next and prev for all nodes of
doubly linked list */
while (current != NULL)
{
temp = current->prev;
current->prev = current->next;
current->next = temp;
current = current->prev;
}
/* Before changing the head, check for the cases like empty
list and list with only one node */
if(temp != NULL )
*head_ref = temp->prev;
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the
beginning of the Doubly Linked List */
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node->prev = NULL;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node ;
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
This function is same as printList() of singly linked list */
void printList(Node *node)
{
while(node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Driver code */
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
Node* head = NULL;
/* Let us create a sorted linked list to test the functions
Created linked list will be 10->8->4->2 */
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 10);
cout << "Original Linked list" << endl;
printList(head);
/* Reverse doubly linked list */
reverse(&head);
cout << "\nReversed Linked list" << endl;
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
/* Program to reverse a doubly linked list */
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* a node of the doubly linked list */
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
struct Node *prev;
};
/* Function to reverse a Doubly Linked List */
void reverse(struct Node **head_ref)
{
struct Node *temp = NULL;
struct Node *current = *head_ref;
/* swap next and prev for all nodes of
doubly linked list */
while (current != NULL)
{
temp = current->prev;
current->prev = current->next;
current->next = temp;
current = current->prev;
}
/* Before changing head, check for the cases like empty
list and list with only one node */
if(temp != NULL )
*head_ref = temp->prev;
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the beginning of the Doubly Linked List */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node->prev = NULL;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node ;
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
This function is same as printList() of singly linked list */
void printList(struct Node *node)
{
while(node!=NULL)
{
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* head = NULL;
/* Let us create a sorted linked list to test the functions
Created linked list will be 10->8->4->2 */
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 10);
printf("\n Original Linked list ");
printList(head);
/* Reverse doubly linked list */
reverse(&head);
printf("\n Reversed Linked list ");
printList(head);
getchar();
}
Java
// Java program to reverse a doubly linked list
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = prev = null;
}
}
/* Function to reverse a Doubly Linked List */
void reverse()
{
Node temp = null;
Node current = head;
/* swap next and prev for all nodes of
doubly linked list */
while (current != null) {
temp = current.prev;
current.prev = current.next;
current.next = temp;
current = current.prev;
}
/* Before changing head, check for the cases like
empty list and list with only one node */
if (temp != null) {
head = temp.prev;
}
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the beginning of the
* Doubly Linked List */
void push(int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node.prev = null;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node.next = head;
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if (head != null) {
head.prev = new_node;
}
/* move the head to point to the new node */
head = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
This function is same as printList() of singly linked
list */
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
/* Let us create a sorted linked list to test the
functions Created linked list will be 10->8->4->2
*/
list.push(2);
list.push(4);
list.push(8);
list.push(10);
System.out.println("Original linked list ");
list.printList(head);
list.reverse();
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("The reversed Linked List is ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal
Python3
# Program to reverse a doubly linked list
# A node of the doubly linked list
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.prev = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
# Constructor for empty Doubly Linked List
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function reverse a Doubly Linked List
def reverse(self):
temp = None
current = self.head
# Swap next and prev for all nodes of
# doubly linked list
while current is not None:
temp = current.prev
current.prev = current.next
current.next = temp
current = current.prev
# Before changing head, check for the cases like
# empty list and list with only one node
if temp is not None:
self.head = temp.prev
# Given a reference to the head of a list and an
# integer,inserts a new node on the front of list
def push(self, new_data):
# 1. Allocates node
# 2. Put the data in it
new_node = Node(new_data)
# 3. Make next of new node as head and
# previous as None (already None)
new_node.next = self.head
# 4. change prev of head node to new_node
if self.head is not None:
self.head.prev = new_node
# 5. move the head to point to the new node
self.head = new_node
def printList(self, node):
while(node is not None):
print(node.data,end=' ')
node = node.next
# Driver code
dll = DoublyLinkedList()
dll.push(2)
dll.push(4)
dll.push(8)
dll.push(10)
print ("\nOriginal Linked List")
dll.printList(dll.head)
# Reverse doubly linked list
dll.reverse()
print ("\nReversed Linked List")
dll.printList(dll.head)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
C#
// A C# program to reverse a doubly linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
static Node head;
class Node {
public int data;
public Node next, prev;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = prev = null;
}
}
/* Function to reverse a Doubly Linked List */
void reverse()
{
Node temp = null;
Node current = head;
/* swap next and prev for all nodes of
doubly linked list */
while (current != null) {
temp = current.prev;
current.prev = current.next;
current.next = temp;
current = current.prev;
}
/* Before changing head, check for
the cases like empty list and
list with only one node */
if (temp != null) {
head = temp.prev;
}
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the
beginning of the Doubly Linked List */
void push(int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node.prev = null;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node.next = head;
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if (head != null) {
head.prev = new_node;
}
/* move the head to point to the new node */
head = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given
doubly linked list This function is
same as printList() of singly linked list */
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
/* Let us create a sorted linked list
to test the functions Created linked
list will be 10->8->4->2 */
list.push(2);
list.push(4);
list.push(8);
list.push(10);
Console.WriteLine("Original linked list ");
list.printList(head);
list.reverse();
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.WriteLine("The reversed Linked List is ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program to reverse a doubly linked list
var head;
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}
}
/* Function to reverse a Doubly Linked List */
function reverse() {
var temp = null;
var current = head;
/*
* swap next and prev for all nodes of doubly linked list
*/
while (current != null) {
temp = current.prev;
current.prev = current.next;
current.next = temp;
current = current.prev;
}
/*
* Before changing head, check for the cases like empty list and list with only
* one node
*/
if (temp != null) {
head = temp.prev;
}
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/*
* Function to insert a node at the beginning of the Doubly Linked List
*/
function push(new_data) {
/* allocate node */
var new_node = new Node(new_data);
/*
* since we are adding at the beginning, prev is always NULL
*/
new_node.prev = null;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node.next = head;
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if (head != null) {
head.prev = new_node;
}
/* move the head to point to the new node */
head = new_node;
}
/*
* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list This function is same
* as printList() of singly linked list
*/
function printList(node) {
while (node != null) {
document.write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
/*
* Let us create a sorted linked list to test the functions Created linked list
* will be 10->8->4->2
*/
push(2);
push(4);
push(8);
push(10);
document.write("Original linked list <br/>");
printList(head);
reverse();
document.write("<br/>");
document.write("The reversed Linked List is <br/>");
printList(head);
// This code contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
Producción:
Original linked list 10 8 4 2 The reversed Linked List is 2 4 8 10
Complejidad temporal: O(N), donde N denota el número de Nodes en la lista doblemente enlazada.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
También podemos intercambiar datos en lugar de punteros para invertir la lista doblemente enlazada. El método utilizado para invertir la array se puede utilizar para intercambiar datos. El intercambio de datos puede ser costoso en comparación con los punteros si el tamaño de los elementos de datos es mayor.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra que alguno de los códigos/algoritmos anteriores es incorrecto o encuentra mejores formas de resolver el mismo problema.
Método 2: La misma pregunta también se puede hacer usando Stacks.
Pasos:
- Siga empujando los datos del Node en la pila. -> O(n)
- Sigue sacando los elementos y actualizando la lista doblemente enlazada
C++
// C++ program to reverse a doubly linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct LinkedList {
struct Node {
int data;
Node *next, *prev;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = prev = NULL;
}
};
Node* head = NULL;
/* Function to reverse a Doubly Linked List using Stacks
*/
void reverse()
{
stack<int> st;
Node* temp = head;
while (temp != NULL) {
st.push(temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
// added all the elements sequence wise in the
// st
temp = head;
while (temp != NULL) {
temp->data = st.top();
st.pop();
temp = temp->next;
}
// popped all the elements and the added in the
// linked list,
// which are in the reversed order->
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the beginning of the
* Doubly Linked List */
void Push(int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node->prev = NULL;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = head;
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if (head != NULL) {
head->prev = new_node;
}
/* move the head to point to the new node */
head = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
This function is same as printList() of singly linked
list */
void printList(Node* node)
{
while (node) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
};
// Driver Code
int main()
{
LinkedList list;
/* Let us create a sorted linked list to test the
functions Created linked list will be 10->8->4->2
*/
list.Push(2);
list.Push(4);
list.Push(8);
list.Push(10);
cout << "Original linked list " << endl;
list.printList(list.head);
list.reverse();
cout << endl;
cout << "The reversed Linked List is " << endl;
list.printList(list.head);
}
// This code is contributed by Pratham76
Java
// Java program to reverse a doubly linked list
import java.util.*;
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next, prev;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = prev = null;
}
}
/* Function to reverse a Doubly Linked List using Stacks
*/
void reverse()
{
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
stack.push(temp.data);
temp = temp.next;
}
// added all the elements sequence wise in the
// stack
temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
temp.data = stack.pop();
temp = temp.next;
}
// popped all the elements and the added in the
// linked list,
// which are in the reversed order.
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the beginning of the
* Doubly Linked List */
void push(int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node.prev = null;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node.next = head;
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if (head != null) {
head.prev = new_node;
}
/* move the head to point to the new node */
head = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
This function is same as printList() of singly linked
list */
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
/* Let us create a sorted linked list to test the
functions Created linked list will be 10->8->4->2
*/
list.push(2);
list.push(4);
list.push(8);
list.push(10);
System.out.println("Original linked list ");
list.printList(head);
list.reverse();
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("The reversed Linked List is ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Rashita Mehta
Python3
"""
function to reverse a doubly-linked list
swap next and prev pointers for all the nodes
change prev of the head node
change head pointer
"""
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.prev = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
"""
method to reverse a Doubly-Linked List using Stacks
"""
def reverseUsingStacks(self):
stack = []
temp = self.head
while temp is not None:
stack.append(temp.data)
temp = temp.next
# Add all the elements in the stack
# in a sequence to the stack
temp = self.head
while temp is not None:
temp.data = stack.pop()
temp = temp.next
# Popped all the elements and the
# added in the linked list,
# in a reversed order.
"""
method to push a new item before the head
"""
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
if self.head is not None:
self.head.prev = new_node
self.head = new_node
"""
method to traverse the doubly-linked
list and print every node in the list
"""
def printList(self, node):
while(node is not None):
print(node.data)
node = node. next
# driver program for the doubly-linked list
dll = DoublyLinkedList()
dll.push(2)
dll.push(4)
dll.push(8)
dll.push(10)
print("original doubly-linked list")
dll.printList(dll.head)
# reverse a doubly-linked list
dll.reverseUsingStacks()
print(" reversed doubly-linked list")
dll.printList(dll.head)
C#
// C# program to reverse a doubly linked list
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class LinkedList {
public static Node head;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next, prev;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = prev = null;
}
}
/* Function to reverse a Doubly Linked List using Stacks
*/
public void reverse()
{
Stack stack = new Stack();
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
stack.Push(temp.data);
temp = temp.next;
}
// added all the elements sequence wise in the
// stack
temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
temp.data = (int)stack.Pop();
temp = temp.next;
}
// popped all the elements and the added in the
// linked list,
// which are in the reversed order.
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the beginning of the
* Doubly Linked List */
public void Push(int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node.prev = null;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node.next = head;
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if (head != null) {
head.prev = new_node;
}
/* move the head to point to the new node */
head = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
This function is same as printList() of singly linked
list */
public void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
/* Let us create a sorted linked list to test the
functions Created linked list will be 10->8->4->2
*/
list.Push(2);
list.Push(4);
list.Push(8);
list.Push(10);
Console.WriteLine("Original linked list ");
list.printList(head);
list.reverse();
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.WriteLine("The reversed Linked List is ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rutvik_56
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to reverse a doubly linked list
class Node
{
constructor(d)
{
this.data = d;
this.next = this.prev = null;
}
}
let head;
// Function to reverse a Doubly
// Linked List using Stacks
function reverse()
{
let stack = [];
let temp = head;
while (temp != null)
{
stack.push(temp.data);
temp = temp.next;
}
// Added all the elements sequence
// wise in the stack
temp = head;
while (temp != null)
{
temp.data = stack.pop();
temp = temp.next;
}
// Popped all the elements and the
// added in the linked list,
// which are in the reversed order.
}
// UTILITY FUNCTIONS
// Function to insert a node at the
// beginning of the Doubly Linked List
function push(new_data)
{
/* Allocate node */
let new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* Since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node.prev = null;
/* Link the old list off the new node */
new_node.next = head;
/* Change prev of head node to new node */
if (head != null) {
head.prev = new_node;
}
/* Move the head to point to the new node */
head = new_node;
}
// Function to print nodes in a given
// doubly linked list. This function
// is same as printList() of singly
// linked list
function printList(node)
{
while (node != null)
{
document.write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver Code
// Let us create a sorted linked list
// to test the functions Created linked
// list will be 10->8->4->2
push(2);
push(4);
push(8);
push(10);
document.write("Original linked list <br>");
printList(head);
reverse();
document.write("<br>");
document.write("The reversed Linked List is <br>");
printList(head);
// This code is contributed by rag2127
</script>
Original linked list 10 8 4 2 The reversed Linked List is 2 4 8 10
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
En este método, recorremos la lista enlazada una vez y agregamos elementos a la pila, y nuevamente recorremos el conjunto para actualizar todos los elementos. El todo toma 2n tiempo, que es la complejidad temporal de O(n).
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
