Dado un árbol de búsqueda binaria (BST) y un número entero positivo k, busque el k-ésimo elemento más pequeño en el árbol de búsqueda binaria.
Por ejemplo, en el siguiente BST, si k = 3, la salida debería ser 10, y si k = 5, la salida debería ser 14.
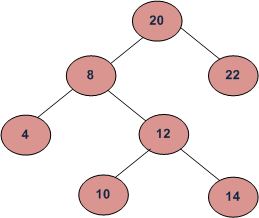
Hemos discutido dos métodos en esta publicación y un método en esta publicación. Todos los métodos anteriores requieren espacio adicional. ¿Cómo encontrar el k’th elemento más grande sin espacio extra?
La idea es utilizar Morris Traversal . En este recorrido, primero creamos enlaces al sucesor Inorder e imprimimos los datos usando estos enlaces, y finalmente revertimos los cambios para restaurar el árbol original. Vea esto para más detalles.
A continuación se muestra la implementación de la idea.
C++
// C++ program to find k'th largest element in BST
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A BST node
struct Node
{
int key;
Node *left, *right;
};
// A function to find
int KSmallestUsingMorris(Node *root, int k)
{
// Count to iterate over elements till we
// get the kth smallest number
int count = 0;
int ksmall = INT_MIN; // store the Kth smallest
Node *curr = root; // to store the current node
while (curr != NULL)
{
// Like Morris traversal if current does
// not have left child rather than printing
// as we did in inorder, we will just
// increment the count as the number will
// be in an increasing order
if (curr->left == NULL)
{
count++;
// if count is equal to K then we found the
// kth smallest, so store it in ksmall
if (count==k)
ksmall = curr->key;
// go to current's right child
curr = curr->right;
}
else
{
// we create links to Inorder Successor and
// count using these links
Node *pre = curr->left;
while (pre->right != NULL && pre->right != curr)
pre = pre->right;
// building links
if (pre->right==NULL)
{
//link made to Inorder Successor
pre->right = curr;
curr = curr->left;
}
// While breaking the links in so made temporary
// threaded tree we will check for the K smallest
// condition
else
{
// Revert the changes made in if part (break link
// from the Inorder Successor)
pre->right = NULL;
count++;
// If count is equal to K then we found
// the kth smallest and so store it in ksmall
if (count==k)
ksmall = curr->key;
curr = curr->right;
}
}
}
return ksmall; //return the found value
}
// A utility function to create a new BST node
Node *newNode(int item)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->key = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
/* A utility function to insert a new node with given key in BST */
Node* insert(Node* node, int key)
{
/* If the tree is empty, return a new node */
if (node == NULL) return newNode(key);
/* Otherwise, recur down the tree */
if (key < node->key)
node->left = insert(node->left, key);
else if (key > node->key)
node->right = insert(node->right, key);
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return node;
}
// Driver Program to test above functions
int main()
{
/* Let us create following BST
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80 */
Node *root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 50);
insert(root, 30);
insert(root, 20);
insert(root, 40);
insert(root, 70);
insert(root, 60);
insert(root, 80);
for (int k=1; k<=7; k++)
cout << KSmallestUsingMorris(root, k) << " ";
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find k'th largest element in BST
import java.util.*;
class GfG {
// A BST node
static class Node
{
int key;
Node left, right;
}
// A function to find
static int KSmallestUsingMorris(Node root, int k)
{
// Count to iterate over elements till we
// get the kth smallest number
int count = 0;
int ksmall = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // store the Kth smallest
Node curr = root; // to store the current node
while (curr != null)
{
// Like Morris traversal if current does
// not have left child rather than printing
// as we did in inorder, we will just
// increment the count as the number will
// be in an increasing order
if (curr.left == null)
{
count++;
// if count is equal to K then we found the
// kth smallest, so store it in ksmall
if (count==k)
ksmall = curr.key;
// go to current's right child
curr = curr.right;
}
else
{
// we create links to Inorder Successor and
// count using these links
Node pre = curr.left;
while (pre.right != null && pre.right != curr)
pre = pre.right;
// building links
if (pre.right== null)
{
//link made to Inorder Successor
pre.right = curr;
curr = curr.left;
}
// While breaking the links in so made temporary
// threaded tree we will check for the K smallest
// condition
else
{
// Revert the changes made in if part (break link
// from the Inorder Successor)
pre.right = null;
count++;
// If count is equal to K then we found
// the kth smallest and so store it in ksmall
if (count==k)
ksmall = curr.key;
curr = curr.right;
}
}
}
return ksmall; //return the found value
}
// A utility function to create a new BST node
static Node newNode(int item)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = item;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
/* A utility function to insert a new node with given key in BST */
static Node insert(Node node, int key)
{
/* If the tree is empty, return a new node */
if (node == null) return newNode(key);
/* Otherwise, recur down the tree */
if (key < node.key)
node.left = insert(node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = insert(node.right, key);
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return node;
}
// Driver Program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create following BST
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80 */
Node root = null;
root = insert(root, 50);
insert(root, 30);
insert(root, 20);
insert(root, 40);
insert(root, 70);
insert(root, 60);
insert(root, 80);
for (int k=1; k<=7; k++)
System.out.print(KSmallestUsingMorris(root, k) + " ");
}
}
Python3
# Python 3 program to find k'th # largest element in BST # A BST node class Node: # Constructor to create a new node def __init__(self, data): self.key = data self.left = None self.right = None # A function to find def KSmallestUsingMorris(root, k): # Count to iterate over elements # till we get the kth smallest number count = 0 ksmall = -9999999999 # store the Kth smallest curr = root # to store the current node while curr != None: # Like Morris traversal if current does # not have left child rather than # printing as we did in inorder, we # will just increment the count as the # number will be in an increasing order if curr.left == None: count += 1 # if count is equal to K then we # found the kth smallest, so store # it in ksmall if count == k: ksmall = curr.key # go to current's right child curr = curr.right else: # we create links to Inorder Successor # and count using these links pre = curr.left while (pre.right != None and pre.right != curr): pre = pre.right # building links if pre.right == None: # link made to Inorder Successor pre.right = curr curr = curr.left # While breaking the links in so made # temporary threaded tree we will check # for the K smallest condition else: # Revert the changes made in if part # (break link from the Inorder Successor) pre.right = None count += 1 # If count is equal to K then we # found the kth smallest and so # store it in ksmall if count == k: ksmall = curr.key curr = curr.right return ksmall # return the found value # A utility function to insert a new # node with given key in BST def insert(node, key): # If the tree is empty, # return a new node if node == None: return Node(key) # Otherwise, recur down the tree if key < node.key: node.left = insert(node.left, key) elif key > node.key: node.right = insert(node.right, key) # return the (unchanged) node pointer return node # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # Let us create following BST # 50 # / \ # 30 70 # / \ / \ # 20 40 60 80 root = None root = insert(root, 50) insert(root, 30) insert(root, 20) insert(root, 40) insert(root, 70) insert(root, 60) insert(root, 80) for k in range(1,8): print(KSmallestUsingMorris(root, k), end = " ") # This code is contributed by PranchalK
C#
// C# program to find k'th largest element in BST
using System;
class GfG
{
// A BST node
public class Node
{
public int key;
public Node left, right;
}
// A function to find
static int KSmallestUsingMorris(Node root, int k)
{
// Count to iterate over elements till we
// get the kth smallest number
int count = 0;
int ksmall = int.MinValue; // store the Kth smallest
Node curr = root; // to store the current node
while (curr != null)
{
// Like Morris traversal if current does
// not have left child rather than printing
// as we did in inorder, we will just
// increment the count as the number will
// be in an increasing order
if (curr.left == null)
{
count++;
// if count is equal to K then we found the
// kth smallest, so store it in ksmall
if (count==k)
ksmall = curr.key;
// go to current's right child
curr = curr.right;
}
else
{
// we create links to Inorder Successor and
// count using these links
Node pre = curr.left;
while (pre.right != null && pre.right != curr)
pre = pre.right;
// building links
if (pre.right == null)
{
// link made to Inorder Successor
pre.right = curr;
curr = curr.left;
}
// While breaking the links in so made temporary
// threaded tree we will check for the K smallest
// condition
else
{
// Revert the changes made in if part (break link
// from the Inorder Successor)
pre.right = null;
count++;
// If count is equal to K then we found
// the kth smallest and so store it in ksmall
if (count == k)
ksmall = curr.key;
curr = curr.right;
}
}
}
return ksmall; //return the found value
}
// A utility function to create a new BST node
static Node newNode(int item)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = item;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
/* A utility function to insert a new node with given key in BST */
static Node insert(Node node, int key)
{
/* If the tree is empty, return a new node */
if (node == null) return newNode(key);
/* Otherwise, recur down the tree */
if (key < node.key)
node.left = insert(node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = insert(node.right, key);
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return node;
}
// Driver Program to test above functions
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create following BST
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80 */
Node root = null;
root = insert(root, 50);
insert(root, 30);
insert(root, 20);
insert(root, 40);
insert(root, 70);
insert(root, 60);
insert(root, 80);
for (int k = 1; k <= 7; k++)
Console.Write(KSmallestUsingMorris(root, k) + " ");
}
}
// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program to find k'th largest element in BST
// A BST node
class Node {
constructor() {
this.key = 0;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// A function to find
function KSmallestUsingMorris(root , k)
{
// Count to iterate over elements till we
// get the kth smallest number
var count = 0;
var ksmall = Number.MIN_VALUE; // store the Kth smallest
var curr = root; // to store the current node
while (curr != null)
{
// Like Morris traversal if current does
// not have left child rather than printing
// as we did in inorder, we will just
// increment the count as the number will
// be in an increasing order
if (curr.left == null)
{
count++;
// if count is equal to K then we found the
// kth smallest, so store it in ksmall
if (count==k)
ksmall = curr.key;
// go to current's right child
curr = curr.right;
}
else
{
// we create links to Inorder Successor and
// count using these links
var pre = curr.left;
while (pre.right != null && pre.right != curr)
pre = pre.right;
// building links
if (pre.right== null)
{
//link made to Inorder Successor
pre.right = curr;
curr = curr.left;
}
// While breaking the links in so made temporary
// threaded tree we will check for the K smallest
// condition
else
{
// Revert the changes made in if part (break link
// from the Inorder Successor)
pre.right = null;
count++;
// If count is equal to K then we found
// the kth smallest and so store it in ksmall
if (count==k)
ksmall = curr.key;
curr = curr.right;
}
}
}
return ksmall; //return the found value
}
// A utility function to create a new BST node
function newNode(item)
{
var temp = new Node();
temp.key = item;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
/* A utility function to insert a new node with given key in BST */
function insert(node , key)
{
/* If the tree is empty, return a new node */
if (node == null) return newNode(key);
/* Otherwise, recur down the tree */
if (key < node.key)
node.left = insert(node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = insert(node.right, key);
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return node;
}
// Driver Program to test above functions
/* Let us create following BST
50
/ \
30 70
/ \ / \
20 40 60 80 */
var root = null;
root = insert(root, 50);
insert(root, 30);
insert(root, 20);
insert(root, 40);
insert(root, 70);
insert(root, 60);
insert(root, 80);
for (k=1; k<=7; k++)
document.write(KSmallestUsingMorris(root, k) + " ");
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Complejidad de tiempo : O(n) donde n es el tamaño de BST
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
Este artículo es una contribución de Abhishek Somani. Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA