Dado un arreglo y un número k donde k es más pequeño que el tamaño del arreglo, necesitamos encontrar el k-ésimo elemento más grande en el arreglo dado. Se da que todos los elementos de la array son distintos.
Recomendamos leer la siguiente publicación como requisito previo a esta publicación. K’th elemento más pequeño/más grande en array no ordenada | Serie 1
Ejemplos:
Input: arr[] = {7, 10, 4, 3, 20, 15}
k = 3
Output: 7
Input: arr[] = {7, 10, 4, 3, 20, 15}
k = 4
Output: 10
Hemos discutido tres soluciones diferentes aquí . En esta publicación, se analiza el método 4, que es principalmente una extensión del método 3 (QuickSelect) discutido en la publicación anterior .
El diagrama de flujo es el siguiente:
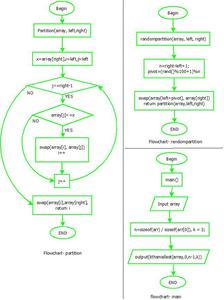
diagrama de flujo
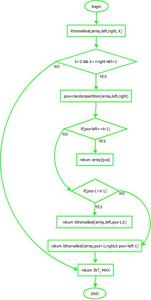
diagrama de flujo- kth más pequeño
C++
// C++ program of above implementation
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Standard partition process of QuickSort().
// It considers the last element as pivot and
// oves all smaller element to left of it
// and greater elements to right
int partition(int* arr, int l, int r)
{
int x = arr[r], i = l;
for (int j = l; j <= r - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] <= x) {
swap(arr[i], arr[j]);
i++;
}
}
swap(arr[i], arr[r]);
return i;
}
int randomPartition(int* arr, int l, int r)
{
int n = r - l + 1;
int pivot = (rand() % 100 + 1) % n;
swap(arr[l + pivot], arr[r]);
return partition(arr, l, r);
}
// This function returns k'th smallest
// element in arr[l..r] using
// QuickSort based method. ASSUMPTION:
// ALL ELEMENTS IN ARR[] ARE DISTINCT
int kthSmallest(int* arr, int l, int r, int k)
{
// If k is smaller than number
// of elements in array
if (k > 0 && k <= r - l + 1) {
// Partition the array around last
// element and get position of pivot
// element in sorted array
int pos = randomPartition(arr, l, r);
// If position is same as k
if (pos - l == k - 1) {
return arr[pos];
}
// If position is more, recur
// for left subarray
if (pos - l > k - 1) {
return kthSmallest(arr, l, pos - 1, k);
}
// Else recur for right subarray
return kthSmallest(arr, pos + 1, r,
k - pos + l - 1);
}
// If k is more than number of
// elements in array
return INT_MAX;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 4, 19, 26 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]), k = 3;
cout << "K'th smallest element is "
<< kthSmallest(arr, 0, n - 1, k);
}
Java
// Java program of above implementation
import java.util.Random;
public class GFG {
// This function returns k'th smallest element in arr[l..r] using
// QuickSort based method. ASSUMPTION: ALL ELEMENTS IN ARR[] ARE DISTINCT
static int kthSmallest(int arr[], int l, int r, int k) {
// If k is smaller than number of elements in array
if (k > 0 && k <= r - l + 1) {
// Partition the array around last element and get
// position of pivot element in sorted array
int pos = randomPartition(arr, l, r);
// If position is same as k
if (pos - l == k - 1) {
return arr[pos];
}
if (pos - l > k - 1) // If position is more, recur for left subarray
{
return kthSmallest(arr, l, pos - 1, k);
}
// Else recur for right subarray
return kthSmallest(arr, pos + 1, r, k - pos + l - 1);
}
// If k is more than number of elements in array
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
// Standard partition process of QuickSort(). It considers the last
// element as pivot and moves all smaller element to left of it
// and greater elements to right
static int partition(int arr[], int l, int r) {
int x = arr[r], i = l;
for (int j = l; j <= r - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] <= x) {
swap(arr, i, j);
i++;
}
}
swap(arr, i, r);
return i;
}
static int randomPartition(int arr[], int l, int r) {
int n = r - l + 1;
int pivot = new Random().nextInt(n);
swap(arr, l + pivot, r);
return partition(arr, l, r);
}
// Driver program to test above methods
public static void main(String args[]) {
int arr[] = {12, 3, 5, 7, 4, 19, 26};
int n = arr.length, k = 3;
System.out.println("K'th smallest element is " + kthSmallest(arr, 0, n - 1, k));
}
}
/*This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar*/
Python3
# Python3 implementation of above implementation
# This function returns k'th smallest element
# in arr[l..r] using QuickSort based method.
# ASSUMPTION: ALL ELEMENTS IN ARR[] ARE DISTINCT
from random import randint
def randomPartition(arr, l, r):
n = r - l + 1
pivot = randint(1, 100) % n
arr[l + pivot], arr[r] = arr[l + pivot], arr[r]
return partition(arr, l, r)
def kthSmallest(arr, l, r, k):
# If k is smaller than
# number of elements in array
if (k > 0 and k <= r - l + 1):
# Partition the array around last element and
# get position of pivot element in sorted array
pos = randomPartition(arr, l, r)
# If position is same as k
if (pos - l == k - 1):
return arr[pos]
# If position is more, recur for left subarray
if (pos - l > k - 1):
return kthSmallest(arr, l, pos - 1, k)
# Else recur for right subarray
return kthSmallest(arr, pos + 1, r,
k - pos + l - 1)
# If k is more than number of elements in array
return 10**9
# Standard partition process of QuickSort().
# It considers the last element as pivot and
# moves all smaller element to left of it
# and greater elements to right
def partition(arr, l, r):
x = arr[r]
i = l
for j in range(l, r):
if (arr[j] <= x):
arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
i += 1
arr[i], arr[r] = arr[r], arr[i]
return i
# Driver Code
arr = [12, 3, 5, 7, 4, 19, 26]
n = len(arr)
k = 3
print("K'th smallest element is",
kthSmallest(arr, 0, n - 1, k))
# This code is contributed by Mohit Kumar
C#
// C# program of above implementation
using System;
class GFG
{
// This function returns k'th smallest
// element in arr[l..r] using
// QuickSort based method. ASSUMPTION:
// ALL ELEMENTS IN ARR[] ARE DISTINCT
static int kthSmallest(int []arr, int l,
int r, int k)
{
// If k is smaller than number
// of elements in array
if (k > 0 && k <= r - l + 1)
{
// Partition the array around last
// element and get position of pivot
// element in sorted array
int pos = randomPartition(arr, l, r);
// If position is same as k
if (pos - l == k - 1)
{
return arr[pos];
}
// If position is more, recur
// for left subarray
if (pos - l > k - 1)
{
return kthSmallest(arr, l, pos - 1, k);
}
// Else recur for right subarray
return kthSmallest(arr, pos + 1, r,
k - pos + l - 1);
}
// If k is more than number of
// elements in array
return int.MaxValue;
}
static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j)
{
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
// Standard partition process of QuickSort().
// It considers the last element as pivot and
// oves all smaller element to left of it
// and greater elements to right
static int partition(int []arr, int l, int r)
{
int x = arr[r], i = l;
for (int j = l; j <= r - 1; j++)
{
if (arr[j] <= x)
{
swap(arr, i, j);
i++;
}
}
swap(arr, i, r);
return i;
}
static int randomPartition(int []arr, int l, int r)
{
int n = r - l + 1;
int pivot = new Random().Next(1);
swap(arr, l + pivot, r);
return partition(arr, l, r);
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int []arr = {12, 3, 5, 7, 4, 19, 26};
int n = arr.Length, k = 3;
Console.WriteLine("K'th smallest element is " +
kthSmallest(arr, 0, n - 1, k));
}
}
// his code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program of above implementation
// This function returns k'th smallest element
// in arr[l..r] using QuickSort based method.
// ASSUMPTION: ALL ELEMENTS IN ARR[] ARE DISTINCT
function kthSmallest(arr, l, r, k)
{
// If k is smaller than number of
// elements in array
if (k > 0 && k <= r - l + 1)
{
// Partition the array around last
// element and get position of pivot
// element in sorted array
let pos = randomPartition(arr, l, r);
// If position is same as k
if (pos - l == k - 1)
{
return arr[pos];
}
// If position is more,
// recur for left subarray
if (pos - l > k - 1)
{
return kthSmallest(arr, l, pos - 1, k);
}
// Else recur for right subarray
return kthSmallest(arr, pos + 1, r,
k - pos + l - 1);
}
// If k is more than number
// of elements in array
return Number.MAX_VALUE;
}
function swap(arr, i, j)
{
let temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
// Standard partition process of QuickSort().
// It considers the last element as pivot and
// moves all smaller element to left of it
// and greater elements to right
function partition(arr, l, r)
{
let x = arr[r], i = l;
for(let j = l; j <= r - 1; j++)
{
if (arr[j] <= x)
{
swap(arr, i, j);
i++;
}
}
swap(arr, i, r);
return i;
}
function randomPartition(arr, l, r)
{
let n = r - l + 1;
let pivot = (Math.floor(Math.random() * 101)) % n;
swap(arr, l + pivot, r);
return partition(arr, l, r);
}
// Driver code
let arr = [ 12, 3, 5, 7, 4, 19, 26 ];
let n = arr.length, k = 3;
document.write("K'th smallest element is " +
kthSmallest(arr, 0, n - 1, k));
</script>
K'th smallest element is 5
Referencias: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/kth-smallestlargest-element-unsorted-array/
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA