Dado un arreglo y un número k donde k es más pequeño que el tamaño del arreglo, necesitamos encontrar el k-ésimo elemento más pequeño en el arreglo dado. Se da que todos los elementos de la array son distintos.
Ejemplos:
Entrada : arr[] = {7, 10, 4, 3, 20, 15}, k = 3
Salida : 7Entrada : arr[] = {7, 10, 4, 3, 20, 15}, k = 4
Salida : 10
Hemos discutido un problema similar para imprimir k elementos más grandes .
Método 1 (Solución simple)
Una solución simple es ordenar la array dada usando un algoritmo de clasificación O(N log N) como Merge Sort , Heap Sort , etc., y devolver el elemento en el índice k-1 en la array ordenada.
La complejidad temporal de esta solución es O(N log N)
C++
// Simple C++ program to find k'th smallest element
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to return k'th smallest element in a given array
int kthSmallest(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
// Sort the given array
sort(arr, arr + n);
// Return k'th element in the sorted array
return arr[k - 1];
}
// Driver program to test above methods
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]), k = 2;
cout << "K'th smallest element is "
<< kthSmallest(arr, n, k);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Sania Kumari Gupta (kriSania804)
C
// Simple C program to find k'th smallest element
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Compare function for qsort
int cmpfunc(const void* a, const void* b)
{
return (*(int*)a - *(int*)b);
}
// Function to return k'th smallest element in a given array
int kthSmallest(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
// Sort the given array
qsort(arr, n, sizeof(int), cmpfunc);
// Return k'th element in the sorted array
return arr[k - 1];
}
// Driver program to test above methods
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]), k = 2;
printf("K'th smallest element is %d",
kthSmallest(arr, n, k));
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Sania Kumari Gupta (kriSania804)
Java
// Java code for kth smallest element
// in an array
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
class GFG {
// Function to return k'th smallest
// element in a given array
public static int kthSmallest(Integer[] arr,
int k)
{
// Sort the given array
Arrays.sort(arr);
// Return k'th element in
// the sorted array
return arr[k - 1];
}
// driver program
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Integer arr[] = new Integer[] { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 };
int k = 2;
System.out.print("K'th smallest element is " + kthSmallest(arr, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Chhavi
Python3
# Python3 program to find k'th smallest
# element
# Function to return k'th smallest
# element in a given array
def kthSmallest(arr, n, k):
# Sort the given array
arr.sort()
# Return k'th element in the
# sorted array
return arr[k-1]
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
arr = [12, 3, 5, 7, 19]
n = len(arr)
k = 2
print("K'th smallest element is",
kthSmallest(arr, n, k))
# This code is contributed by
# Shrikant13
C#
// C# code for kth smallest element
// in an array
using System;
class GFG {
// Function to return k'th smallest
// element in a given array
public static int kthSmallest(int[] arr,
int k)
{
// Sort the given array
Array.Sort(arr);
// Return k'th element in
// the sorted array
return arr[k - 1];
}
// driver program
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = new int[] { 12, 3, 5,
7, 19 };
int k = 2;
Console.Write("K'th smallest element"
+ " is " + kthSmallest(arr, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by nitin mittal.
PHP
<?php
// Simple PHP program to find
// k'th smallest element
// Function to return k'th smallest
// element in a given array
function kthSmallest($arr, $n, $k)
{
// Sort the given array
sort($arr);
// Return k'th element
// in the sorted array
return $arr[$k - 1];
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(12, 3, 5, 7, 19);
$n =count($arr);
$k = 2;
echo "K'th smallest element is ", kthSmallest($arr, $n, $k);
// This code is contributed by anuj_67.
?>
Javascript
<script>
// Simple Javascript program to find k'th smallest element
// Function to return k'th smallest element in a given array
function kthSmallest(arr, n, k)
{
// Sort the given array
arr.sort((a,b) => a-b);
// Return k'th element in the sorted array
return arr[k - 1];
}
// Driver program to test above methods
let arr = [ 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 ];
let n = arr.length, k = 2;
document.write("K'th smallest element is " + kthSmallest(arr, n, k));
//This code is contributed by Mayank Tyagi
</script>
K'th smallest element is 5
Método 2 (usando el conjunto de C++ STL)
podemos encontrar el k-ésimo elemento más pequeño en la complejidad del tiempo mejor que O(N log N). sabemos que el conjunto en C++ STL se implementa utilizando el árbol de búsqueda binaria y también sabemos que la complejidad temporal de todos los casos (búsqueda, inserción, eliminación) en BST es log (n) en el caso promedio y O (n) en el peor caso. Estamos usando set porque se menciona en la pregunta que todos los elementos de una array son distintos.
La siguiente es la implementación en C++ del método anterior.
C++
/* the following code demonstrates how to find kth smallest
element using set from C++ STL */
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int k = 4;
set<int> s(arr, arr + n);
set<int>::iterator itr
= s.begin(); // s.begin() returns a pointer to first
// element in the set
advance(itr, k - 1); // itr points to kth element in set
cout << *itr << "\n";
return 0;
}
Java
/* the following code demonstrates how to find kth smallest
element using set from Java Collections */
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19, 1, 2, 3, 4 };
int n = arr.length;
int k = 4;
//since counting starts from 0 so to find kth
//element we need to reduce k by 1
k--;
//for storing elements in sorted form
//in set we will use TreeSet
Set<Integer> s = new TreeSet<Integer>();
//adding elements to set
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
s.add(arr[i]);
//we need iterator method of Iterator
//for the traversal
Iterator<Integer> itr = s.iterator();
while(k>0)
{
itr.next();
k--;
}//itr points to the kth element in the set
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
//This code is contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403)
Python3
# the following code demonstrates how to find kth smallest # element using set from Python arr = [12, 3, 5, 7, 19] n = len(arr) k = 4 s = set(arr) for itr in s: if k == 1: print(itr) # itr is the kth element in the set break k -= 1 #This code is contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403)
C#
/* the following code demonstrates how to find kth smallest
element using set from C# collections */
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 };
int n = arr.Length;
int k = 4;
SortedSet<int> s = new SortedSet<int>();
foreach(int i in arr) s.Add(i);
foreach(int itr in s)
{
if (k == 1) {
Console.WriteLine(itr);// itr is the kth element in the set
break;
}
k--;
}
}
}
//This code is contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403)
12
Complejidad de tiempo: O(N*log N) en el caso promedio y O(N) en el peor de los casos
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Método 3 (Usando Min Heap – HeapSelect)
Podemos encontrar el k-ésimo elemento más pequeño en complejidad de tiempo mejor que O(N Log N). Una optimización simple es crear un Min Heap de los n elementos dados y llamar a extractMin() k veces.
La siguiente es la implementación en C++ del método anterior.
C++
// A C++ program to find k'th smallest element using min heap
#include <climits>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Prototype of a utility function to swap two integers
void swap(int* x, int* y);
// A class for Min Heap
class MinHeap {
int* harr; // pointer to array of elements in heap
int capacity; // maximum possible size of min heap
int heap_size; // Current number of elements in min heap
public:
MinHeap(int a[], int size); // Constructor
void MinHeapify(int i); // To minheapify subtree rooted with index i
int parent(int i) { return (i - 1) / 2; }
int left(int i) { return (2 * i + 1); }
int right(int i) { return (2 * i + 2); }
int extractMin(); // extracts root (minimum) element
int getMin() { return harr[0]; } // Returns minimum
};
MinHeap::MinHeap(int a[], int size)
{
heap_size = size;
harr = a; // store address of array
int i = (heap_size - 1) / 2;
while (i >= 0) {
MinHeapify(i);
i--;
}
}
// Method to remove minimum element (or root) from min heap
int MinHeap::extractMin()
{
if (heap_size == 0)
return INT_MAX;
// Store the minimum value.
int root = harr[0];
// If there are more than 1 items, move the last item to root
// and call heapify.
if (heap_size > 1) {
harr[0] = harr[heap_size - 1];
MinHeapify(0);
}
heap_size--;
return root;
}
// A recursive method to heapify a subtree with root at given index
// This method assumes that the subtrees are already heapified
void MinHeap::MinHeapify(int i)
{
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int smallest = i;
if (l < heap_size && harr[l] < harr[i])
smallest = l;
if (r < heap_size && harr[r] < harr[smallest])
smallest = r;
if (smallest != i) {
swap(&harr[i], &harr[smallest]);
MinHeapify(smallest);
}
}
// A utility function to swap two elements
void swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = temp;
}
// Function to return k'th smallest element in a given array
int kthSmallest(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
// Build a heap of n elements: O(n) time
MinHeap mh(arr, n);
// Do extract min (k-1) times
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++)
mh.extractMin();
// Return root
return mh.getMin();
}
// Driver program to test above methods
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]), k = 2;
cout << "K'th smallest element is " << kthSmallest(arr, n, k);
return 0;
}
Java
// A Java program to find k'th smallest element using min heap
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// A class for Max Heap
class MinHeap
{
int[] harr; // pointer to array of elements in heap
int capacity; // maximum possible size of min heap
int heap_size; // Current number of elements in min heap
int parent(int i) { return (i - 1) / 2; }
int left(int i) { return ((2 * i )+ 1); }
int right(int i) { return ((2 * i) + 2); }
int getMin() { return harr[0]; } // Returns minimum
// to replace root with new node x and heapify() new root
void replaceMax(int x)
{
this.harr[0] = x;
minHeapify(0);
}
MinHeap(int a[], int size)
{
heap_size = size;
harr = a; // store address of array
int i = (heap_size - 1) / 2;
while (i >= 0)
{
minHeapify(i);
i--;
}
}
// Method to remove maximum element (or root) from min heap
int extractMin()
{
if (heap_size == 0)
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// Store the maximum value.
int root = harr[0];
// If there are more than 1 items, move the last item to root
// and call heapify.
if (heap_size > 1)
{
harr[0] = harr[heap_size - 1];
minHeapify(0);
}
heap_size--;
return root;
}
// A recursive method to heapify a subtree with root at given index
// This method assumes that the subtrees are already heapified
void minHeapify(int i)
{
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int smallest = i;
if (l < heap_size && harr[l] < harr[i])
smallest = l;
if (r < heap_size && harr[r] < harr[smallest])
smallest = r;
if (smallest != i)
{
int t = harr[i];
harr[i] = harr[smallest];
harr[smallest] = t;
minHeapify(smallest);
}
}
};
// Function to return k'th largest element in a given array
int kthSmallest(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
// Build a heap of first k elements: O(k) time
MinHeap mh = new MinHeap(arr, n);
// Process remaining n-k elements. If current element is
// smaller than root, replace root with current element
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++)
mh.extractMin();
// Return root
return mh.getMin();
}
// Driver program to test above methods
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 };
int n = arr.length, k = 2;
GFG gfg = new GFG();
System.out.print("K'th smallest element is " +
gfg.kthSmallest(arr, n, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
Python3
# Python3 program to find k'th smallest element
# using min heap
# Class for Min Heap
class MinHeap:
# Constructor
def __init__(self, a, size):
# list of elements in the heap
self.harr = a
# maximum possible size of min heap
self.capacity = None
# current number of elements in min heap
self.heap_size = size
i = int((self.heap_size - 1) / 2)
while i >= 0:
self.minHeapify(i)
i -= 1
def parent(self, i):
return (i - 1) / 2
def left(self, i):
return 2 * i + 1
def right(self, i):
return 2 * i + 2
# Returns minimum
def getMin(self):
return self.harr[0]
# Method to remove minimum element (or root)
# from min heap
def extractMin(self):
if self.heap_size == 0:
return float("inf")
# Store the minimum value
root = self.harr[0]
# If there are more than 1 items, move the last item
# to root and call heapify
if self.heap_size > 1:
self.harr[0] = self.harr[self.heap_size - 1]
self.minHeapify(0)
self.heap_size -= 1
return root
# A recursive method to heapify a subtree with root at
# given index. This method assumes that the subtrees
# are already heapified
def minHeapify(self, i):
l = self.left(i)
r = self.right(i)
smallest = i
if ((l < self.heap_size) and
(self.harr[l] < self.harr[i])):
smallest = l
if ((r < self.heap_size) and
(self.harr[r] < self.harr[smallest])):
smallest = r
if smallest != i:
self.harr[i], self.harr[smallest] = (
self.harr[smallest], self.harr[i])
self.minHeapify(smallest)
# Function to return k'th smallest element in a given array
def kthSmallest(arr, n, k):
# Build a heap of n elements in O(n) time
mh = MinHeap(arr, n)
# Do extract min (k-1) times
for i in range(k - 1):
mh.extractMin()
# Return root
return mh.getMin()
# Driver code
arr = [12, 3, 5, 7, 19]
n = len(arr)
k = 2
print("K'th smallest element is", kthSmallest(arr, n, k))
# This Code is contributed by Kevin Joshi
C#
using System;
public class GFG
{
public class MinHeap
{
int[] harr; // pointer to array of elements in heap
// int capacity; // maximum possible size of min heap
int heap_size; // Current number of elements in min heap
int parent(int i) { return (i - 1) / 2; }
int left(int i) { return ((2 * i )+ 1); }
int right(int i) { return ((2 * i) + 2); }
public int getMin() { return harr[0]; } // Returns minimum
// to replace root with new node x and heapify() new root
public void replaceMax(int x)
{
this.harr[0] = x;
minHeapify(0);
}
public MinHeap(int[] a, int size)
{
heap_size = size;
harr = a; // store address of array
int i = (heap_size - 1) / 2;
while (i >= 0)
{
minHeapify(i);
i--;
}
}
// Method to remove maximum element (or root) from min heap
public int extractMin()
{
if (heap_size == 0)
return Int32.MaxValue;
// Store the maximum value.
int root = harr[0];
// If there are more than 1 items, move the last item to root
// and call heapify.
if (heap_size > 1)
{
harr[0] = harr[heap_size - 1];
minHeapify(0);
}
heap_size--;
return root;
}
// A recursive method to heapify a subtree with root at given index
// This method assumes that the subtrees are already heapified
public void minHeapify(int i)
{
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int smallest = i;
if (l < heap_size && harr[l] < harr[i])
smallest = l;
if (r < heap_size && harr[r] < harr[smallest])
smallest = r;
if (smallest != i)
{
int t = harr[i];
harr[i] = harr[smallest];
harr[smallest] = t;
minHeapify(smallest);
}
}
};
// Function to return k'th largest element in a given array
int kthSmallest(int[] arr, int n, int k)
{
// Build a heap of first k elements: O(k) time
MinHeap mh = new MinHeap(arr, n);
// Process remaining n-k elements. If current element is
// smaller than root, replace root with current element
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; i++)
mh.extractMin();
// Return root
return mh.getMin();
}
// Driver program to test above methods
static public void Main (){
int[] arr = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 };
int n = arr.Length, k = 2;
GFG gfg = new GFG();
Console.Write("K'th smallest element is " +
gfg.kthSmallest(arr, n, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by rag2127
Javascript
<script>
// A Javascript program to find k'th smallest element using min heap
// A class for Max Heap
class MinHeap {
parent(i) {
return (i - 1) / 2;
};
left(i) {
return ((2 * i) + 1);
};
right(i) {
return ((2 * i) + 2);
}
getMin() {
return this.harr[0];
} // Returns minimum
// to replace root with new node x and heapify() new root
replaceMax(x) {
this.harr[0] = x;
minHeapify(0);
}
constructor(a, size) {
this.heap_size = size;
this.harr = a; // store address of array
let i = (this.heap_size - 1) / 2;
while (i >= 0) {
this.minHeapify(i);
i--;
}
}
// Method to remove maximum element (or root) from min heap
extractMin() {
if (this.heap_size == 0)
return Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
// Store the maximum value.
let root = this.harr[0];
// If there are more than 1 items, move the last item to root
// and call heapify.
if (this.heap_size > 1) {
this.harr[0] = this.harr[this.heap_size - 1];
this.minHeapify(0);
}
this.heap_size--;
return root;
}
// A recursive method to heapify a subtree with root at given index
// This method assumes that the subtrees are already heapified
minHeapify(i) {
let l = this.left(i);
let r = this.right(i);
let smallest = i;
if (l < this.heap_size && this.harr[l] < this.harr[i])
smallest = l;
if (r < this.heap_size && this.harr[r] < this.harr[smallest])
smallest = r;
if (smallest != i) {
let t = this.harr[i];
this.harr[i] = this.harr[smallest];
this.harr[smallest] = t;
this.minHeapify(smallest);
}
}
};
// Function to return k'th largest element in a given array
function kthSmallest(arr, n, k) {
// Build a heap of first k elements: O(k) time
let mh = new MinHeap(arr, n);
// Process remaining n-k elements. If current element is
// smaller than root, replace root with current element
for (let i = 0; i < k - 1; i++)
mh.extractMin();
// Return root
return mh.getMin();
}
// Driver program to test above methods
let arr = [12, 3, 5, 7, 19];
let n = arr.length, k = 2;
document.write("K'th smallest element is " + kthSmallest(arr, n, k));
// This code is contributed by gfgking.
</script>
K'th smallest element is 5
Complejidad temporal: O(n + kLogn).
Complejidad del espacio : O (n) para la pila de llamadas
Método 4 (usando Max-Heap)
También podemos usar Max Heap para encontrar el k-ésimo elemento más pequeño. Lo siguiente es un algoritmo.
1) Cree un Max-Heap MH de los primeros k elementos (arr[0] a arr[k-1]) de la array dada. O(k)
2) Para cada elemento, después del k’ésimo elemento (arr[k] a arr[n-1]), compárelo con la raíz de MH.
……a) Si el elemento es menor que la raíz, conviértalo en root y llame a heapify para MH
……b) De lo contrario, ignórelo.
// El paso 2 es O((nk)*logk)
3) Finalmente, la raíz de MH es el k-ésimo elemento más pequeño.
La complejidad temporal de esta solución es O(k + (nk)*Logk)
La siguiente es la implementación en C++ del algoritmo anterior
C++
// A C++ program to find k'th smallest element using max heap
#include <climits>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Prototype of a utility function to swap two integers
void swap(int* x, int* y);
// A class for Max Heap
class MaxHeap {
int* harr; // pointer to array of elements in heap
int capacity; // maximum possible size of max heap
int heap_size; // Current number of elements in max heap
public:
MaxHeap(int a[], int size); // Constructor
void maxHeapify(int i); // To maxHeapify subtree rooted with index i
int parent(int i) { return (i - 1) / 2; }
int left(int i) { return (2 * i + 1); }
int right(int i) { return (2 * i + 2); }
int extractMax(); // extracts root (maximum) element
int getMax() { return harr[0]; } // Returns maximum
// to replace root with new node x and heapify() new root
void replaceMax(int x)
{
harr[0] = x;
maxHeapify(0);
}
};
MaxHeap::MaxHeap(int a[], int size)
{
heap_size = size;
harr = a; // store address of array
int i = (heap_size - 1) / 2;
while (i >= 0) {
maxHeapify(i);
i--;
}
}
// Method to remove maximum element (or root) from max heap
int MaxHeap::extractMax()
{
if (heap_size == 0)
return INT_MAX;
// Store the maximum value.
int root = harr[0];
// If there are more than 1 items, move the last item to root
// and call heapify.
if (heap_size > 1) {
harr[0] = harr[heap_size - 1];
maxHeapify(0);
}
heap_size--;
return root;
}
// A recursive method to heapify a subtree with root at given index
// This method assumes that the subtrees are already heapified
void MaxHeap::maxHeapify(int i)
{
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int largest = i;
if (l < heap_size && harr[l] > harr[i])
largest = l;
if (r < heap_size && harr[r] > harr[largest])
largest = r;
if (largest != i) {
swap(&harr[i], &harr[largest]);
maxHeapify(largest);
}
}
// A utility function to swap two elements
void swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = temp;
}
// Function to return k'th largest element in a given array
int kthSmallest(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
// Build a heap of first k elements: O(k) time
MaxHeap mh(arr, k);
// Process remaining n-k elements. If current element is
// smaller than root, replace root with current element
for (int i = k; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] < mh.getMax())
mh.replaceMax(arr[i]);
// Return root
return mh.getMax();
}
// Driver program to test above methods
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]), k = 4;
cout << "K'th smallest element is " << kthSmallest(arr, n, k);
return 0;
}
Java
// A Java program to find k'th smallest element using max heap
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// A class for Max Heap
class MaxHeap
{
int[] harr; // pointer to array of elements in heap
int capacity; // maximum possible size of max heap
int heap_size; // Current number of elements in max heap
int parent(int i) { return (i - 1) / 2; }
int left(int i) { return (2 * i + 1); }
int right(int i) { return (2 * i + 2); }
int getMax() { return harr[0]; } // Returns maximum
// to replace root with new node x and heapify() new root
void replaceMax(int x)
{
this.harr[0] = x;
maxHeapify(0);
}
MaxHeap(int a[], int size)
{
heap_size = size;
harr = a; // store address of array
int i = (heap_size - 1) / 2;
while (i >= 0)
{
maxHeapify(i);
i--;
}
}
// Method to remove maximum element (or root) from max heap
int extractMax()
{
if (heap_size == 0)
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// Store the maximum value.
int root = harr[0];
// If there are more than 1 items, move the last item to root
// and call heapify.
if (heap_size > 1)
{
harr[0] = harr[heap_size - 1];
maxHeapify(0);
}
heap_size--;
return root;
}
// A recursive method to heapify a subtree with root at given index
// This method assumes that the subtrees are already heapified
void maxHeapify(int i)
{
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int largest = i;
if (l < heap_size && harr[l] > harr[i])
largest = l;
if (r < heap_size && harr[r] > harr[largest])
largest = r;
if (largest != i)
{
int t = harr[i];
harr[i] = harr[largest];
harr[largest] = t;
maxHeapify(largest);
}
}
};
// Function to return k'th largest element in a given array
int kthSmallest(int arr[], int n, int k)
{
// Build a heap of first k elements: O(k) time
MaxHeap mh = new MaxHeap(arr, k);
// Process remaining n-k elements. If current element is
// smaller than root, replace root with current element
for (int i = k; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] < mh.getMax())
mh.replaceMax(arr[i]);
// Return root
return mh.getMax();
}
// Driver program to test above methods
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 };
int n = arr.length, k = 4;
GFG gfg = new GFG();
System.out.print("K'th smallest element is " +
gfg.kthSmallest(arr, n, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Python3
# Python3 program to find k'th smallest element
# using max heap
# Class for Max Heap
class MaxHeap:
# Constructor
def __init__(self, a, size):
# list of elements in the heap
self.harr = a
# maximum possible size of max heap
self.capacity = None
# current number of elements in max heap
self.heap_size = size
i = int((self.heap_size - 1) / 2)
while i >= 0:
self.maxHeapify(i)
i -= 1
def parent(self, i):
return (i - 1) / 2
def left(self, i):
return 2 * i + 1
def right(self, i):
return 2 * i + 2
# Returns maximum
def getMax(self):
return self.harr[0]
# to replace root with new node x and heapify() new root
def replaceMax(self, x):
self.harr[0] = x
self.maxHeapify(0)
# Method to remove maximum element (or root)
# from max heap
def extractMin(self):
if self.heap_size == 0:
return float("inf")
# Store the maximum value.
root = self.harr[0]
# If there are more than 1 items, move the
# last item to root and call heapify
if self.heap_size > 1:
self.harr[0] = self.harr[self.heap_size - 1]
self.maxHeapify(0)
self.heap_size -= 1
return root
# A recursive method to heapify a subtree with root at
# given index. This method assumes that the subtrees
# are already heapified
def maxHeapify(self, i):
l = self.left(i)
r = self.right(i)
largest = i
if ((l < self.heap_size) and
(self.harr[l] > self.harr[i])):
largest = l
if ((r < self.heap_size) and
(self.harr[r] > self.harr[largest])):
largest = r
if largest != i:
self.harr[i], self.harr[largest] = (
self.harr[largest], self.harr[i])
self.maxHeapify(largest)
# Function to return k'th smallest element in a given array
def kthSmallest(arr, n, k):
# Build a heap of first k elements in O(k) time
mh = MaxHeap(arr, k)
# Process remaining n-k elements. If current element is
# smaller than root, replace root with current element
for i in range(k, n):
if arr[i] < mh.getMax():
mh.replaceMax(arr[i])
# Return root
return mh.getMax()
# Driver code
arr = [12, 3, 5, 7, 19]
n = len(arr)
k = 4
print("K'th smallest element is", kthSmallest(arr, n, k))
# Code contributed by Kevin Joshi
C#
// A C# program to find k'th smallest element using max heap
using System;
public class GFG {
// A class for Max Heap
public
class MaxHeap {
public
int[] harr; // pointer to array of elements in
// heap
public
int capacity; // maximum possible size of max
// heap
public
int heap_size; // Current number of elements in
// max heap
public
int
parent(int i)
{
return (i - 1) / 2;
}
public
int
left(int i)
{
return (2 * i + 1);
}
public
int
right(int i)
{
return (2 * i + 2);
}
public
int
getMax()
{
return harr[0];
} // Returns maximum
// to replace root with new node x and heapify() new
// root
public
void
replaceMax(int x)
{
this.harr[0] = x;
maxHeapify(0);
}
public
MaxHeap(int[] a, int size)
{
heap_size = size;
harr = a; // store address of array
int i = (heap_size - 1) / 2;
while (i >= 0) {
maxHeapify(i);
i--;
}
}
// Method to remove maximum element (or root) from
// max heap
public
int
extractMax()
{
if (heap_size == 0)
return int.MaxValue;
// Store the maximum value.
int root = harr[0];
// If there are more than 1 items, move the last
// item to root and call heapify.
if (heap_size > 1) {
harr[0] = harr[heap_size - 1];
maxHeapify(0);
}
heap_size--;
return root;
}
// A recursive method to heapify a subtree with root
// at given index This method assumes that the
// subtrees are already heapified
public
void
maxHeapify(int i)
{
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int largest = i;
if (l < heap_size && harr[l] > harr[i])
largest = l;
if (r < heap_size && harr[r] > harr[largest])
largest = r;
if (largest != i) {
int t = harr[i];
harr[i] = harr[largest];
harr[largest] = t;
maxHeapify(largest);
}
}
};
// Function to return k'th largest element in a given
// array
int kthSmallest(int[] arr, int n, int k)
{
// Build a heap of first k elements: O(k) time
MaxHeap mh = new MaxHeap(arr, k);
// Process remaining n-k elements. If current
// element is smaller than root, replace root with
// current element
for (int i = k; i < n; i++)
if (arr[i] < mh.getMax())
mh.replaceMax(arr[i]);
// Return root
return mh.getMax();
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int[] arr = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 };
int n = arr.Length, k = 4;
GFG gfg = new GFG();
Console.Write("K'th smallest element is "
+ gfg.kthSmallest(arr, n, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
K'th smallest element is 12
Método 5 (QuickSelect)
Esta es una optimización sobre el método 1 si QuickSort se usa como algoritmo de clasificación en el primer paso. En QuickSort, elegimos un elemento pivote, luego movemos el elemento pivote a su posición correcta y dividimos la array circundante. La idea es, no hacer una ordenación rápida completa, sino detenerse en el punto donde el pivote mismo es el k’ésimo elemento más pequeño. Además, no repetir para los lados izquierdo y derecho del pivote, sino repetir para uno de ellos según la posición del pivote. La complejidad de tiempo del peor caso de este método es O(n 2 ), pero funciona en O(n) en promedio.
C++
#include <climits>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int partition(int arr[], int l, int r);
// This function returns k'th smallest element in arr[l..r] using
// QuickSort based method. ASSUMPTION: ALL ELEMENTS IN ARR[] ARE DISTINCT
int kthSmallest(int arr[], int l, int r, int k)
{
// If k is smaller than number of elements in array
if (k > 0 && k <= r - l + 1) {
// Partition the array around last element and get
// position of pivot element in sorted array
int pos = partition(arr, l, r);
// If position is same as k
if (pos - l == k - 1)
return arr[pos];
if (pos - l > k - 1) // If position is more, recur for left subarray
return kthSmallest(arr, l, pos - 1, k);
// Else recur for right subarray
return kthSmallest(arr, pos + 1, r, k - pos + l - 1);
}
// If k is more than number of elements in array
return INT_MAX;
}
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// Standard partition process of QuickSort(). It considers the last
// element as pivot and moves all smaller element to left of it
// and greater elements to right
int partition(int arr[], int l, int r)
{
int x = arr[r], i = l;
for (int j = l; j <= r - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] <= x) {
swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
i++;
}
}
swap(&arr[i], &arr[r]);
return i;
}
// Driver program to test above methods
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 4, 19, 26 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]), k = 3;
cout << "K'th smallest element is " << kthSmallest(arr, 0, n - 1, k);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java code for kth smallest element in an array
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
class GFG {
// Standard partition process of QuickSort.
// It considers the last element as pivot
// and moves all smaller element to left of
// it and greater elements to right
public static int partition(Integer[] arr, int l,
int r)
{
int x = arr[r], i = l;
for (int j = l; j <= r - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] <= x) {
// Swapping arr[i] and arr[j]
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
i++;
}
}
// Swapping arr[i] and arr[r]
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[r];
arr[r] = temp;
return i;
}
// This function returns k'th smallest element
// in arr[l..r] using QuickSort based method.
// ASSUMPTION: ALL ELEMENTS IN ARR[] ARE DISTINCT
public static int kthSmallest(Integer[] arr, int l,
int r, int k)
{
// If k is smaller than number of elements
// in array
if (k > 0 && k <= r - l + 1) {
// Partition the array around last
// element and get position of pivot
// element in sorted array
int pos = partition(arr, l, r);
// If position is same as k
if (pos - l == k - 1)
return arr[pos];
// If position is more, recur for
// left subarray
if (pos - l > k - 1)
return kthSmallest(arr, l, pos - 1, k);
// Else recur for right subarray
return kthSmallest(arr, pos + 1, r, k - pos + l - 1);
}
// If k is more than number of elements
// in array
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
// Driver program to test above methods
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Integer arr[] = new Integer[] { 12, 3, 5, 7, 4, 19, 26 };
int k = 3;
System.out.print("K'th smallest element is " + kthSmallest(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Chhavi
Python3
# This function returns k'th smallest element
# in arr[l..r] using QuickSort based method.
# ASSUMPTION: ALL ELEMENTS IN ARR[] ARE DISTINCT
import sys
def kthSmallest(arr, l, r, k):
# If k is smaller than number of
# elements in array
if (k > 0 and k <= r - l + 1):
# Partition the array around last
# element and get position of pivot
# element in sorted array
pos = partition(arr, l, r)
# If position is same as k
if (pos - l == k - 1):
return arr[pos]
if (pos - l > k - 1): # If position is more,
# recur for left subarray
return kthSmallest(arr, l, pos - 1, k)
# Else recur for right subarray
return kthSmallest(arr, pos + 1, r,
k - pos + l - 1)
# If k is more than number of
# elements in array
return sys.maxsize
# Standard partition process of QuickSort().
# It considers the last element as pivot and
# moves all smaller element to left of it
# and greater elements to right
def partition(arr, l, r):
x = arr[r]
i = l
for j in range(l, r):
if (arr[j] <= x):
arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
i += 1
arr[i], arr[r] = arr[r], arr[i]
return i
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [12, 3, 5, 7, 4, 19, 26]
n = len(arr)
k = 3;
print("K'th smallest element is",
kthSmallest(arr, 0, n - 1, k))
# This code is contributed by ita_c
C#
// C# code for kth smallest element
// in an array
using System;
class GFG {
// Standard partition process of QuickSort.
// It considers the last element as pivot
// and moves all smaller element to left of
// it and greater elements to right
public static int partition(int[] arr,
int l, int r)
{
int x = arr[r], i = l;
int temp = 0;
for (int j = l; j <= r - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] <= x) {
// Swapping arr[i] and arr[j]
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
i++;
}
}
// Swapping arr[i] and arr[r]
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[r];
arr[r] = temp;
return i;
}
// This function returns k'th smallest
// element in arr[l..r] using QuickSort
// based method. ASSUMPTION: ALL ELEMENTS
// IN ARR[] ARE DISTINCT
public static int kthSmallest(int[] arr, int l,
int r, int k)
{
// If k is smaller than number
// of elements in array
if (k > 0 && k <= r - l + 1) {
// Partition the array around last
// element and get position of pivot
// element in sorted array
int pos = partition(arr, l, r);
// If position is same as k
if (pos - l == k - 1)
return arr[pos];
// If position is more, recur for
// left subarray
if (pos - l > k - 1)
return kthSmallest(arr, l, pos - 1, k);
// Else recur for right subarray
return kthSmallest(arr, pos + 1, r,
k - pos + l - 1);
}
// If k is more than number
// of elements in array
return int.MaxValue;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 4, 19, 26 };
int k = 3;
Console.Write("K'th smallest element is " + kthSmallest(arr, 0, arr.Length - 1, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript code for kth smallest
// element in an array
// Standard partition process of QuickSort.
// It considers the last element as pivot
// and moves all smaller element to left of
// it and greater elements to right
function partition( arr , l , r)
{
var x = arr[r], i = l;
for (j = l; j <= r - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] <= x) {
// Swapping arr[i] and arr[j]
var temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
i++;
}
}
// Swapping arr[i] and arr[r]
var temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[r];
arr[r] = temp;
return i;
}
// This function returns k'th smallest element
// in arr[l..r] using QuickSort based method.
// ASSUMPTION: ALL ELEMENTS IN ARR ARE DISTINCT
function kthSmallest( arr , l , r , k) {
// If k is smaller than number of elements
// in array
if (k > 0 && k <= r - l + 1) {
// Partition the array around last
// element and get position of pivot
// element in sorted array
var pos = partition(arr, l, r);
// If position is same as k
if (pos - l == k - 1)
return arr[pos];
// If position is more, recur for
// left subarray
if (pos - l > k - 1)
return kthSmallest(arr, l, pos - 1, k);
// Else recur for right subarray
return kthSmallest(arr, pos + 1, r,
k - pos + l - 1);
}
// If k is more than number of elements
// in array
return Number.MAX_VALUE;
}
// Driver program to test above methods
var arr = [ 12, 3, 5, 7, 4, 19, 26 ];
var k = 3;
document.write("K'th smallest element is " +
kthSmallest(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, k));
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
K'th smallest element is 5
Método 6 (Mapa STL)
Un enfoque STL basado en mapas es muy similar al algoritmo de clasificación de selección rápida y conteo, pero mucho más fácil de implementar. Podemos usar un mapa ordenado y mapear cada elemento con su frecuencia. Y como sabemos que un mapa ordenado almacenaría los datos de manera ordenada, seguimos sumando la frecuencia de cada elemento hasta que no sea mayor o igual a k, de modo que lleguemos al k-ésimo elemento desde el principio, es decir el k’ésimo elemento más pequeño.
P.ej –
Array = {7,0,25,6,16,17,0}
k = 3
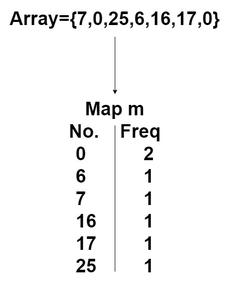
Ahora, para obtener el k-ésimo elemento más grande, necesitamos sumar las frecuencias hasta que sea mayor o igual a 3. Está claro de lo anterior que la frecuencia de 0 + la frecuencia de 6 será igual a 3, por lo que la el tercer número más pequeño de la array será 6.
Podemos lograr lo anterior usando un iterador para recorrer el mapa.
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int Kth_smallest(map<int, int> m, int k)
{
int freq = 0;
for (auto it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++) {
freq += (it->second); // adding the frequencies of
// each element
if (freq >= k) // if at any point frequency becomes
// greater than or equal to k then
// return that element
{
return it->first;
}
}
return -1; // returning -1 if k>size of the array which
// is an impossible scenario
}
int main()
{
int n = 5;
int k = 2;
vector<int> arr = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 };
map<int, int> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
m[arr[i]] += 1; // mapping every element with it's
// frequency
}
int ans = Kth_smallest(m, k);
if(k==1){
cout << "The " << k << "st smallest element is " << ans
<< endl;
}
else if(k==2){
cout << "The " << k << "nd smallest element is " << ans
<< endl;
}
else if(k==3){
cout << "The " << k << "rd smallest element is " << ans
<< endl;
}
else{
cout << "The " << k << "th smallest element is " << ans
<< endl;
}
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int Kth_smallest(TreeMap<Integer, Integer> m,
int k)
{
int freq = 0;
for (Map.Entry it : m.entrySet())
{
// adding the frequencies of each element
freq += (int)it.getValue();
// if at any point frequency becomes
// greater than or equal to k then
// return that element
if (freq >= k) {
return (int)it.getKey();
}
}
return -1; // returning -1 if k>size of the array
// which is an impossible scenario
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
int k = 2;
int[] arr = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 };
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> m = new TreeMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// mapping every element with
// it's
// frequency
m.put(arr[i], m.getOrDefault(arr[i], 0) + 1);
}
int ans = Kth_smallest(m, k);
if(k==1){
System.out.println(
"The " + k + "st smallest element is " + ans);
}
else if(k==2){
System.out.println(
"The " + k + "nd smallest element is " + ans);
}
else if(k==3){
System.out.println(
"The " + k + "rd smallest element is " + ans);
}
else{
System.out.println(
"The " + k + "th smallest element is " + ans);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by harshit17.
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
def Kth_smallest(m, k):
freq = 0
for it in sorted(m.keys()):
freq += m[it] # adding the frequencies of
# each element
if freq >= k: # if at any point frequency becomes
return it # greater than or equal to k then
# return that element
return -1 # returning -1 if k>size of the array which
# is an impossible scenario
# driver code
n = 5;
k = 2;
arr = [ 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 ]
m = {}
for i in range(n):
if arr[i] in m: # mapping every element with it's
m[arr[i]] = m[arr[i]] + 1 # frequency
else:
m[arr[i]] = 1
ans = Kth_smallest(m, k)
if(k==1):
print("The " , k ,"st smallest element is " ,ans)
elif(k==2):
print("The " , k ,"nd smallest element is " ,ans)
elif(k==2):
print("The " , k ,"rd smallest element is " ,ans)
else:
print("The " , k ,"th smallest element is " ,ans)
# This code is contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403)
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG {
static int Kth_smallest(SortedDictionary<int, int> m,
int k)
{
int freq = 0;
foreach(var it in m) {
// adding the frequencies of each element
freq += (int)it.Value;
// if at any point frequency becomes
// greater than or equal to k then
// return that element
if (freq >= k) {
return (int)it.Key;
}
}
return -1; // returning -1 if k>size of the array
// which is an impossible scenario
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
int k = 2;
int[] arr = { 12, 3, 5, 7, 19 };
SortedDictionary<int, int> m =
new SortedDictionary<int, int>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// mapping every element with
// it's
// frequency
m.Add(arr[i], m.ContainsKey(arr[i])?m[arr[i]]+1:1);
}
int ans = Kth_smallest(m, k);
if (k == 1) {
Console.WriteLine("The " + k
+ "st smallest element is "
+ ans);
}
else if (k == 2) {
Console.WriteLine("The " + k
+ "nd smallest element is "
+ ans);
}
else if (k == 3) {
Console.WriteLine("The " + k
+ "rd smallest element is "
+ ans);
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("The " + k
+ "th smallest element is "
+ ans);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Abhijeet Kumar(abhijeet19403)
The 2nd smallest element is 5
Hay dos soluciones más que son mejores que las mencionadas anteriormente: una solución es hacer una versión aleatoria de quickSelect() y la otra solución es el algoritmo de tiempo lineal en el peor de los casos (consulte las siguientes publicaciones).
Método 7 (montón máximo usando STL):
Podemos implementar un montón máximo y mínimo usando una cola de prioridad.
Para encontrar el k-ésimo elemento mínimo en una array, maximizaremos la array hasta que el tamaño de la pila se convierta en k.
Después de eso, para cada entrada, sacaremos el elemento superior del montón/Cola de prioridad.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ code to implement the approach
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the kth smallest array element
int kthSmallest(int arr[], int n, int k) {
// For finding min element we need (Max heap)priority queue
priority_queue<int> pq;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
// First push first K elememts into heap
pq.push(arr[i]);
}
// Now check from k to last element
for(int i = k; i < n; i++)
{
// If current element is < top that means
// there are other k-1 lesser elements
// are present at bottom thus, pop that element
// and add kth largest element into the heap till curr
// at last all the greater element than kth element will get pop off
// and at the top of heap there will be kth smallest element
if(arr[i] < pq.top())
{
pq.pop();
// Push curr element
pq.push(arr[i]);
}
}
// Return top of element
return pq.top();
}
// Driver's code:
int main()
{
int n = 10;
int arr[n] = {10, 5, 4 , 3 ,48, 6 , 2 , 33, 53, 10};
int k = 4;
cout<< "Kth Smallest Element is: "<<kthSmallest(arr, n, k);
}
Java
// Java code to implement the approach
import java.util.*;
//Custom comparator class to form the Max heap
class MinHeapComparator implements Comparator<Integer> {
@Override
public int compare(Integer number1, Integer number2) {
int value = number1.compareTo(number2);
// Elements are sorted in reverse order
if (value > 0) {
return -1;
}
else if (value < 0) {
return 1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
}
class GFG{
// Function to find kth smallest array element
static int kthSmallest(int []v, int N, int K)
{
//For finding min element we need (Max heap)priority queue
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap1 = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(new MinHeapComparator());
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
// Insert elements into
// the priority queue
heap1.add(v[i]);
//If current element is less than top, that means there are
//other k-1 lesser elements are present at bottom
// thus pop that element and add kth largest element into the heap till curr
// at last all the greater element than kth element will get pop off
// and at the top of heap there will be kth smallest element
if (heap1.size() > K) {
heap1.remove();
}
}
//Return the top of the heap as kth smallest element
return heap1.peek();
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Given array
int []vec = {10, 5, 4 , 3 ,48, 15, 6 , 2 , 33, 53, 10};
// Size of array
int N = vec.length;
// Given K
int K = 4;
// Function Call
System.out.println("Kth Smallest Element: " + kthSmallest(vec, N, K)) ;
}
}
Python3
# Python code to implement the approach
import heapq
# Function to find the kth smallest array element
def kthSmallest(arr, n, k):
# For finding min element we need (Max heap)priority queue
pq = []
for i in range(k):
# First push first K elememts into heap
heapq.heappush(pq, arr[i])
heapq._heapify_max(pq)
# Now check from k to last element
for i in range(k, n):
# If current element is < first that means
# there are other k-1 lesser elements
# are present at bottom thus, pop that element
# and add kth largest element into the heap till curr
# at last all the greater element than kth element will get pop off
# and at the top of heap there will be kth smallest element
if arr[i] < pq[0]:
heapq.heappop(pq)
# Push curr element
heapq.heappush(pq, arr[i])
heapq._heapify_max(pq)
# Return first of element
return pq[0]
# Driver's code:
n = 10
arr = [10, 5, 4, 3, 48, 6, 2, 33, 53, 10]
k = 4
print("Kth Smallest Element is:", kthSmallest(arr, n, k))
# This code is contributed by Tapesh(tapeshdua420)
C#
// C# program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Function to find the kth smallest array element
static int kthSmallest(int[] arr, int n, int k) {
// For finding min element we need (Max heap)priority queue
List<int> pq = new List<int>();
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
// First push first K elememts into heap
pq.Add(arr[i]);
}
// Now check from k to last element
for(int i = k; i < n; i++)
{
// If current element is < top that means
// there are other k-1 lesser elements
// are present at bottom thus, pop that element
// and add kth largest element into the heap till curr
// at last all the greater element than kth element will get pop off
// and at the top of heap there will be kth smallest element
if(arr[i] < pq[0])
{
pq.Sort();
pq.Reverse();
pq.RemoveAt(0);
// Push curr element
pq.Add(arr[i]);
}
}
// Return top of element
return pq[0];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Given array
int []vec = {10, 5, 4 , 3 ,48, 15, 6 , 2 , 33, 53, 10};
// Size of array
int N = vec.Length;
// Given K
int K = 4;
// Function Call
Console.WriteLine("Kth Smallest Element: " + kthSmallest(vec, N, K)) ;
}
}
// This code is contributed by sanjoy_62.
Kth Smallest Element is: 5
Complejidad temporal: O(nlogk)
Espacio auxiliar: O(logK)
Este método es aportado por rupeshsk30.
Método 8 (usando la búsqueda binaria):
la idea para resolver este problema es que el k-ésimo elemento más pequeño sería el elemento en la k-ésima posición si la array se ordenara en orden creciente. Usando esta lógica, usamos la búsqueda binaria para predecir el índice de un elemento como si la array estuviera ordenada pero sin ordenar realmente la array.
Ejemplo: {1, 4, 5, 3, 19, 3} & k = 2
Aquí encontramos ese elemento que tiene exactamente k + 1 elementos (incluido él mismo) menor que él. Por lo tanto, el k-ésimo elemento más pequeño sería 3 en este caso.
Siga los pasos a continuación para implementar la idea anterior:
- Encuentre bajo y alto que es el rango donde puede estar nuestra respuesta.
- Aplicar búsqueda binaria en este rango.
- Si el elemento seleccionado que sería medio tiene menos de k elementos menores, aumente el número que es bajo = medio + 1 .
- De lo contrario, disminuya el número e intente encontrar una mejor respuesta (para comprender esto, intente ejecutar en una array que contenga duplicados).
- La búsqueda binaria terminará cuando solo quede un elemento en el espacio de respuesta que sería nuestra respuesta.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int count(vector <int>& nums, int& mid)
{//function to calculate number of elements less than equal to mid
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
if(nums[i] <= mid)
cnt++;
return cnt;
}
int kthSmallest(vector <int> nums, int& k)
{
int low = INT_MAX;
int high = INT_MIN;
//calculate minimum and maximum the array.
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
low = min(low, nums[i]);
high = max(high, nums[i]);
}
//Our answer range lies between minimum and maximum element of the array on which Binary Search is Applied
while(low < high)
{
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
/*if the count of number of elements in the array less than equal to mid is less than k
then increase the number. Otherwise decrement the number and try to find a better answer.
*/
if(count(nums, mid) < k)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid;
}
return low;
}
int main()
{
vector <int> nums{1, 4, 5, 3, 19, 3};
int k = 3;
cout << "K'th smallest element is " << kthSmallest(nums, k);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by garvjuneja98
Java
// Java code for kth smallest element in an array
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
class GFG {
static int count(int [] nums, int mid)
{
// function to calculate number of elements less than equal to mid
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
if(nums[i] <= mid)
cnt++;
return cnt;
}
static int kthSmallest(int [] nums, int k)
{
int low = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int high = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
//calculate minimum and maximum the array.
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
{
low = Math.min(low, nums[i]);
high = Math.max(high, nums[i]);
}
//Our answer range lies between minimum and maximum element of the array on which Binary Search is Applied
while(low < high)
{
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
/*if the count of number of elements in the array less than equal to mid is less than k
then increase the number. Otherwise decrement the number and try to find a better answer.
*/
if(count(nums, mid) < k)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid;
}
return low;
}
// Driver program to test above methods
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = {1, 4, 5, 3, 19, 3};
int k = 3;
System.out.print("Kth smallest element is " + kthSmallest(arr, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by CodeWithMini
Python3
# Python code for kth smallest element in an array
import sys
# function to calculate number of elements
# less than equal to mid
def count(nums, mid):
cnt = 0
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] <= mid:
cnt += 1
return cnt
def kthSmallest(nums, k):
low = sys.maxsize
high = -sys.maxsize - 1
# calculate minimum and maximum the array.
for i in range(len(nums)):
low = min(low, nums[i])
high = max(high, nums[i])
# Our answer range lies between minimum and maximum element
# of the array on which Binary Search is Applied
while low < high:
mid = low + (high - low) // 2
# if the count of number of elements in the array less than equal
# to mid is less than k then increase the number. Otherwise decrement
# the number and try to find a better answer.
if count(nums, mid) < k:
low = mid + 1
else:
high = mid
return low
nums = [1, 4, 5, 3, 19, 3]
k = 3
print("K'th smallest element is", kthSmallest(nums, k))
# This code is contributed by Tapesh(tapeshdua420)
C#
// C# program to implement
// the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int count(int []nums, int mid)
{
// function to calculate number of elements less than equal to mid
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)
if(nums[i] <= mid)
cnt++;
return cnt;
}
static int kthSmallest(int []nums, int k)
{
int low = Int32.MaxValue;
int high = Int32.MinValue;
// calculate minimum and maximum the array.
for(int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)
{
low = Math.Min(low, nums[i]);
high = Math.Max(high, nums[i]);
}
// Our answer range lies between minimum
// and maximum element of the array on which Binary Search is Applied
while(low < high)
{
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
/*if the count of number of elements in the
array less than equal to mid is less than k
then increase the number. Otherwise
decrement the number and try to find a better answer.
*/
if(count(nums, mid) < k)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid;
}
return low;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
// Given array
int []vec = {1, 4, 5, 3, 19, 3};
// Given K
int K = 3;
// Function Call
Console.WriteLine("Kth Smallest Element: " + kthSmallest(vec, K)) ;
}
}
// This code is contributed by CodeWithMini
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to find the K’th
// Smallest/Largest Element in Unsorted Array
function count(nums, mid)
{
// function to calculate number of elements less than equal to mid
var cnt = 0;
for(var i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
if(nums[i] <= mid)
cnt++;
return cnt;
}
function kthSmallest(nums,k){
var low = Number. MAX_VALUE;
var high = Number. MIN_VALUE;
// calculate minimum and maximum the array.
for(var i = 0; i < nums.length; i++)
{
low = Math.min(low, nums[i]);
high = Math.max(high, nums[i]);
}
// Our answer range lies between minimum and
// maximum element of the array on which Binary Search is Applied
while(low < high)
{
var mid = Math.floor(low + ((high - low) / 2));
/*if the count of number of elements in the array
less than equal to mid is less than k
then increase the number. Otherwise
decrement the number and try to find a better answer.
*/
if(count(nums, mid) < k)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid;
}
return low;
}
var k=3;
var nums = [1, 4, 5, 3, 19, 3];
document.write("K'th smallest element is " + kthSmallest(nums, k));
// This code is contributed by shruti456rawal
</script>
K'th smallest element is 3
Complejidad temporal: O((mx-mn)(log(mx-mn))), donde mn es el mínimo y mx es el máximo.
Espacio auxiliar: O(1)
K’ésimo elemento más pequeño/más grande en array no ordenada | Conjunto 2 (Tiempo lineal esperado)
K’th Elemento más pequeño/más grande en array no ordenada | Conjunto 3 (Tiempo lineal en el peor de los casos)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
