Kotlin Flow es una de las últimas incorporaciones a Kotlin Coroutines. Con Kotlin Flow podemos manejar flujos de datos de forma asincrónica que se ejecutan secuencialmente.
¿Qué vamos a construir en este artículo?
Crearemos una aplicación simple que obtenga algunos datos de la API y los muestre en la pantalla. Es una aplicación simple que demuestra el funcionamiento del flujo de Kotlin. Utilizará la arquitectura MVVM.
requisitos previos:
- Buen conocimiento de Android
- Conocimiento de Kotlin
- Conceptos básicos de la arquitectura MVVM
- Conceptos básicos de la biblioteca de actualización
- Conceptos básicos de las corrutinas de Kotlin
- Conceptos básicos de la vinculación de vistas
Implementación paso a paso
Paso 1: Crear un nuevo proyecto
Para crear un nuevo proyecto en Android Studio, consulte Cómo crear/iniciar un nuevo proyecto en Android Studio . Tenga en cuenta que seleccione Kotlin como lenguaje de programación.
Paso 2: Estructura del proyecto
Estaremos siguiendo algunos patrones para mantener nuestros archivos. Cree carpetas y archivos de acuerdo con la estructura de este proyecto. Los usos se explicarán más adelante en este artículo.
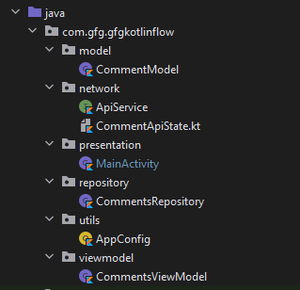
Estructura del proyecto
Paso 3: agregue las dependencias requeridas
Navegue a Gradle Scripts > build.gradle(Module:app) y agregue la siguiente dependencia en la sección de dependencias.
// Dependencia de actualización
implementación ‘com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.9.0’
// fábrica de convertidores json
implementación ‘com.squareup.retrofit2:convertidor-gson:2.1.0’
// Corrutinas (incluye flujo de kotlin)
implementación ‘org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:1.5.0’
// componentes del ciclo de vida
implementación ‘androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-extensions:2.2.0’
implementación «androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:2.3.1»
implementación «androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-runtime-ktx:2.3.1»
Paso 4: Trabajando con activity_main.xml
Vaya a la aplicación > res > diseño > actividad_principal.xml y agregue el siguiente código a ese archivo. A continuación se muestra el código para el archivo activity_main.xml .
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:padding="16dp" tools:context=".presentation.MainActivity"> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.Guideline android:id="@+id/guideline2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="vertical" app:layout_constraintGuide_percent="0.3" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/search_edit_text" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:autofillHints="Search Comments By Id" android:inputType="numberSigned" app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent" app:layout_constraintRight_toLeftOf="@id/button" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Search" app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> <ProgressBar android:layout_width="match_parent" android:id="@+id/progress_bar" android:layout_height="wrap_content" app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/textView" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" android:visibility="gone" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/search_edit_text" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" android:layout_marginEnd="20dp" android:layout_marginRight="20dp" android:text="Comment Id" android:textStyle="bold" app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/guideline2" app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="1.0" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/search_edit_text" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/comment_id_textview" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginStart="20dp" android:layout_marginLeft="20dp" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" android:textStyle="bold" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="@+id/textView" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.0" app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/guideline2" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/search_edit_text" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" android:layout_marginEnd="20dp" android:layout_marginRight="20dp" android:text="Name" android:textStyle="bold" app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/guideline2" app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="1.0" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/comment_id_textview" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/name_textview" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginStart="20dp" android:layout_marginLeft="20dp" android:textStyle="bold" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="@+id/textView2" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.0" app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/guideline2" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="@+id/textView2" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" android:layout_marginEnd="20dp" android:layout_marginRight="20dp" android:text="Email" android:textStyle="bold" app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/guideline2" app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="1.0" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/name_textview" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/email_textview" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginStart="20dp" android:layout_marginLeft="20dp" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" android:textStyle="bold" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="@+id/textView3" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.0" app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/guideline2" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/name_textview" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView4" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" android:layout_marginEnd="20dp" android:layout_marginRight="20dp" android:text="Comment" android:textStyle="bold" app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/guideline2" app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="1.0" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/email_textview" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/comment_textview" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginStart="20dp" android:layout_marginLeft="20dp" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" android:textStyle="bold" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="@+id/textView4" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.0" app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/guideline2" app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/email_textview" /> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Su interfaz de usuario se ve así:

Paso 5: trabajar con la API
Usaremos la API https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/comments . Proporciona algunos datos JSON cuando se pasa la identificación como ruta. Por ejemplo, https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/comments/2 proporciona JSON que contiene algunos datos aleatorios. Usaremos estos datos y los mostraremos en la pantalla usando kotlin flow. Abra el modelo > CommentModel y cree una clase de modelo para analizar los datos que se reciben de la API.

Respuesta de ejemplo
Necesitamos crear una clase de datos para esta respuesta. Agregue el siguiente código en CommentModel
Kotlin
data class CommentModel(
val postId: Int?=null,
val id: Int?=null,
val email: String?=null,
val name:String?=null,
@SerializedName("body")
val comment: String?=null
)
Creación de interfaz API
Necesitamos crear una interfaz de API para llamar a la API mediante una actualización. Abra red > ApiService y agregue el siguiente código
Kotlin
import retrofit2.http.GET
import retrofit2.http.Path
interface ApiService {
// Get method to call the api ,passing id as a path
@GET("/comments/{id}")
suspend fun getComments(@Path("id") id: Int): CommentModel
}
Agreguemos algunas clases auxiliares para manejar la carga o el estado de error de la API. Abra la red > CommentApiState. Consulte el comentario en el código para obtener una explicación.
Kotlin
// A helper class to handle states
data class CommentApiState<out T>(val status: Status, val data: T?, val message: String?) {
companion object {
// In case of Success,set status as
// Success and data as the response
fun <T> success(data: T?): CommentApiState<T> {
return CommentApiState(Status.SUCCESS, data, null)
}
// In case of failure ,set state to Error ,
// add the error message,set data to null
fun <T> error(msg: String): CommentApiState<T> {
return CommentApiState(Status.ERROR, null, msg)
}
// When the call is loading set the state
// as Loading and rest as null
fun <T> loading(): CommentApiState<T> {
return CommentApiState(Status.LOADING, null, null)
}
}
}
// An enum to store the
// current state of api call
enum class Status {
SUCCESS,
ERROR,
LOADING
}
Abra utils > AppConfig y agregue código para crear un servicio de API, que se usará para realizar llamadas a la API.
Kotlin
import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder
import retrofit2.Retrofit
import retrofit2.converter.gson.GsonConverterFactory
object AppConfig {
// Base url of the api
private const val BASE_URL = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/"
// create retrofit service
fun ApiService(): ApiService =
Retrofit.Builder().baseUrl(BASE_URL)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create(GsonBuilder().create()))
.build()
.create(ApiService::class.java)
}
La parte API de la aplicación está completa. Ahora necesitamos trabajar en ViewModel y el repositorio.
Paso 6: trabajar con el repositorio
Abrir repositorio > ComentariosRepositorio. Agrega el siguiente código. Consulte los comentarios para obtener una explicación.
Kotlin
class CommentsRepository(private val apiService: ApiService) {
suspend fun getComment(id: Int): Flow<CommentApiState<CommentModel>> {
return flow {
// get the comment Data from the api
val comment=apiService.getComments(id)
// Emit this data wrapped in
// the helper class [CommentApiState]
emit(CommentApiState.success(comment))
}.flowOn(Dispatchers.IO)
}
}
Paso 7: Trabajando con ViewModel
Abra ViewModel > CommentViewModel. Agrega el siguiente código. Consulte los comentarios para obtener una explicación.
Kotlin
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel
import androidx.lifecycle.viewModelScope
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.MutableStateFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.catch
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.collect
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
class CommentsViewModel : ViewModel() {
// Create a Repository and pass the api
// service we created in AppConfig file
private val repository = CommentsRepository(
AppConfig.ApiService()
)
val commentState = MutableStateFlow(
CommentApiState(
Status.LOADING,
CommentModel(), ""
)
)
init {
// Initiate a starting
// search with comment Id 1
getNewComment(1)
}
// Function to get new Comments
fun getNewComment(id: Int) {
// Since Network Calls takes time,Set the
// initial value to loading state
commentState.value = CommentApiState.loading()
// ApiCalls takes some time, So it has to be
// run and background thread. Using viewModelScope
// to call the api
viewModelScope.launch {
// Collecting the data emitted
// by the function in repository
repository.getComment(id)
// If any errors occurs like 404 not found
// or invalid query, set the state to error
// State to show some info
// on screen
.catch {
commentState.value =
CommentApiState.error(it.message.toString())
}
// If Api call is succeeded, set the State to Success
// and set the response data to data received from api
.collect {
commentState.value = CommentApiState.success(it.data)
}
}
}
}
casi hemos terminado, ahora necesitamos llamar a la API desde la vista (MainActivity) y mostrar los datos en la pantalla.
Paso 8: trabajar con la vista (MainActivity.kt)
Abrir presentación > MainActivity.kt. Agregue el siguiente código, consulte los comentarios para obtener una explicación.
Kotlin
import android.os.Bundle
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.core.view.isVisible
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModelProvider
import androidx.lifecycle.lifecycleScope
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.collect
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
// create a CommentsViewModel
// variable to initialize it later
private lateinit var viewModel: CommentsViewModel
// create a view binding variable
private lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// instantiate view binding
binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
// initialize viewModel
viewModel = ViewModelProvider(this).get(CommentsViewModel::class.java)
// Listen for the button click event to search
binding.button.setOnClickListener {
// check to prevent api call with no parameters
if (binding.searchEditText.text.isNullOrEmpty()) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Query Can't be empty", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} else {
// if Query isn't empty, make the api call
viewModel.getNewComment(binding.searchEditText.text.toString().toInt())
}
}
// Since flow run asynchronously,
// start listening on background thread
lifecycleScope.launch {
viewModel.commentState.collect {
// When state to check the
// state of received data
when (it.status) {
// If its loading state then
// show the progress bar
Status.LOADING -> {
binding.progressBar.isVisible = true
}
// If api call was a success , Update the Ui with
// data and make progress bar invisible
Status.SUCCESS -> {
binding.progressBar.isVisible = false
// Received data can be null, put a check to prevent
// null pointer exception
it.data?.let { comment ->
binding.commentIdTextview.text = comment.id.toString()
binding.nameTextview.text = comment.name
binding.emailTextview.text = comment.email
binding.commentTextview.text = comment.comment
}
}
// In case of error, show some data to user
else -> {
binding.progressBar.isVisible = false
Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "${it.message}", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
}
}
}
}
Ahora ejecuta la aplicación, pon algunos números y haz clic en buscar. Ingrese cualquier número del 1 al 500, devolverá un estado exitoso.
Producción:
Obtenga el proyecto completo de GitHub .
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por sunny52525 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA