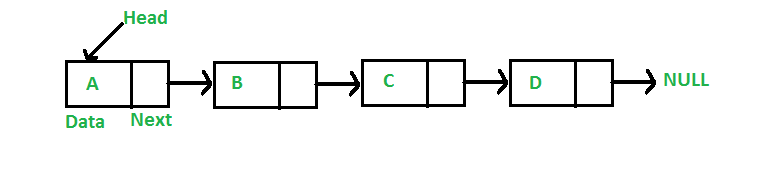
Al igual que las arrays, la lista enlazada es una estructura de datos lineal. A diferencia de las arrays, los elementos de la lista enlazada no se almacenan en una ubicación contigua; los elementos se vinculan mediante punteros. Incluyen una serie de Nodes conectados. Aquí, cada Node almacena los datos y la dirección del siguiente Node.
C
// A linked list node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
C++
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
Java
class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of the list
/* Linked list Node*/
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor to create a new node
// Next is by default initialized
// as null
Node(int d) {
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
}
Python
# Node class class Node: # Function to initialize the node object def __init__(self, data): self.data = data # Assign data self.next = None # Initialize # next as null # Linked List class class LinkedList: # Function to initialize the Linked # List object def __init__(self): self.head = None
C#
class LinkedList {
// The first node(head) of the linked list
// Will be an object of type Node (null by default)
Node head;
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
// Constructor to create a new node
Node(int d) { data = d; }
}
}
Javascript
<script>
var head; // head of the list
/* Linked list Node*/
class Node
{
// Constructor to create a new node
// Next is by default initialized
// as null
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
C++
// A simple CPP program to introduce
// a linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
// Program to create a simple linked
// list with 3 nodes
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
Node* second = NULL;
Node* third = NULL;
// allocate 3 nodes in the heap
head = new Node();
second = new Node();
third = new Node();
/* Three blocks have been allocated dynamically.
We have pointers to these three blocks as head,
second and third
head second third
| | |
| | |
+---+-----+ +----+----+ +----+----+
| # | # | | # | # | | # | # |
+---+-----+ +----+----+ +----+----+
# represents any random value.
Data is random because we haven’t assigned
anything yet */
head->data = 1; // assign data in first node
head->next = second; // Link first node with
// the second node
/* data has been assigned to the data part of first
block (block pointed by the head). And next
pointer of the first block points to second.
So they both are linked.
head second third
| | |
| | |
+---+---+ +----+----+ +-----+----+
| 1 | o----->| # | # | | # | # |
+---+---+ +----+----+ +-----+----+
*/
// assign data to second node
second->data = 2;
// Link second node with the third node
second->next = third;
/* data has been assigned to the data part of the second
block (block pointed by second). And next
pointer of the second block points to the third
block. So all three blocks are linked.
head second third
| | |
| | |
+---+---+ +---+---+ +----+----+
| 1 | o----->| 2 | o-----> | # | # |
+---+---+ +---+---+ +----+----+ */
third->data = 3; // assign data to third node
third->next = NULL;
/* data has been assigned to the data part of the third
block (block pointed by third). And next pointer
of the third block is made NULL to indicate
that the linked list is terminated here.
We have the linked list ready.
head
|
|
+---+---+ +---+---+ +----+------+
| 1 | o----->| 2 | o-----> | 3 | NULL |
+---+---+ +---+---+ +----+------+
Note that only the head is sufficient to represent
the whole list. We can traverse the complete
list by following the next pointers. */
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
// A simple C program to introduce
// a linked list
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// Program to create a simple linked
// list with 3 nodes
int main()
{
struct Node* head = NULL;
struct Node* second = NULL;
struct Node* third = NULL;
// allocate 3 nodes in the heap
head = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
second = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
third = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* Three blocks have been allocated dynamically.
We have pointers to these three blocks as head,
second and third
head second third
| | |
| | |
+---+-----+ +----+----+ +----+----+
| # | # | | # | # | | # | # |
+---+-----+ +----+----+ +----+----+
# represents any random value.
Data is random because we haven’t assigned
anything yet */
head->data = 1; // assign data in first node
head->next = second; // Link first node with
// the second node
/* data has been assigned to the data part of the first
block (block pointed by the head). And next
pointer of first block points to second.
So they both are linked.
head second third
| | |
| | |
+---+---+ +----+----+ +-----+----+
| 1 | o----->| # | # | | # | # |
+---+---+ +----+----+ +-----+----+
*/
// assign data to second node
second->data = 2;
// Link second node with the third node
second->next = third;
/* data has been assigned to the data part of the second
block (block pointed by second). And next
pointer of the second block points to the third
block. So all three blocks are linked.
head second third
| | |
| | |
+---+---+ +---+---+ +----+----+
| 1 | o----->| 2 | o-----> | # | # |
+---+---+ +---+---+ +----+----+ */
third->data = 3; // assign data to third node
third->next = NULL;
/* data has been assigned to data part of third
block (block pointed by third). And next pointer
of the third block is made NULL to indicate
that the linked list is terminated here.
We have the linked list ready.
head
|
|
+---+---+ +---+---+ +----+------+
| 1 | o----->| 2 | o-----> | 3 | NULL |
+---+---+ +---+---+ +----+------+
Note that only head is sufficient to represent
the whole list. We can traverse the complete
list by following next pointers. */
return 0;
}
Java
// A simple Java program to introduce a linked list
class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node. This inner class is made static so that
main() can access it */
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
} // Constructor
}
/* method to create a simple linked list with 3 nodes*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list. */
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.head = new Node(1);
Node second = new Node(2);
Node third = new Node(3);
/* Three nodes have been allocated dynamically.
We have references to these three blocks as head,
second and third
llist.head second third
| | |
| | |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
| 1 | null | | 2 | null | | 3 | null |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ */
llist.head.next = second; // Link first node with the second node
/* Now next of the first Node refers to the second. So they
both are linked.
llist.head second third
| | |
| | |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
| 1 | o-------->| 2 | null | | 3 | null |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ */
second.next = third; // Link second node with the third node
/* Now next of the second Node refers to third. So all three
nodes are linked.
llist.head second third
| | |
| | |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
| 1 | o-------->| 2 | o-------->| 3 | null |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ */
}
}
Python
# A simple Python program to introduce a linked list # Node class class Node: # Function to initialise the node object def __init__(self, data): self.data = data # Assign data self.next = None # Initialize next as null # Linked List class contains a Node object class LinkedList: # Function to initialize head def __init__(self): self.head = None # Code execution starts here if __name__=='__main__': # Start with the empty list llist = LinkedList() llist.head = Node(1) second = Node(2) third = Node(3) ''' Three nodes have been created. We have references to these three blocks as head, second and third llist.head second third | | | | | | +----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ | 1 | None | | 2 | None | | 3 | None | +----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ ''' llist.head.next = second; # Link first node with second ''' Now next of first Node refers to second. So they both are linked. llist.head second third | | | | | | +----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ | 1 | o-------->| 2 | null | | 3 | null | +----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ ''' second.next = third; # Link second node with the third node ''' Now next of second Node refers to third. So all three nodes are linked. llist.head second third | | | | | | +----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ | 1 | o-------->| 2 | o-------->| 3 | null | +----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ '''
C#
// A simple C# program to introduce a linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node. This inner class is made static so that
main() can access it */
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
} // Constructor
}
/* method to create a simple linked list with 3 nodes*/
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list. */
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.head = new Node(1);
Node second = new Node(2);
Node third = new Node(3);
/* Three nodes have been allocated dynamically.
We have references to these three blocks as head,
second and third
llist.head second third
| | |
| | |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
| 1 | null | | 2 | null | | 3 | null |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ */
llist.head.next = second; // Link first node with the second node
/* Now next of first Node refers to second. So they
both are linked.
llist.head second third
| | |
| | |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
| 1 | o-------->| 2 | null | | 3 | null |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ */
second.next = third; // Link second node with the third node
/* Now next of the second Node refers to third. So all three
nodes are linked.
llist.head second third
| | |
| | |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
| 1 | o-------->| 2 | o-------->| 3 | null |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ */
}
}
// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// A simple javascript program to introduce a linked list
var head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node. This inner class is made so that
main() can access it */
class Node {
constructor(d)
{
this.data = d;
this.next = null;
} // Constructor
}
/* method to create a simple linked list with 3 nodes*/
var head = new Node(1);
var second = new Node(2);
var third = new Node(3);
/* Three nodes have been allocated dynamically.
We have references to these three blocks as head,
second and third
llist.head second third
| | |
| | |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
| 1 | null | | 2 | null | | 3 | null |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ */
head.next = second; // Link first node with the second node
/* Now next of the first Node refers to the second. So they
both are linked.
llist.head second third
| | |
| | |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
| 1 | o-------->| 2 | null | | 3 | null |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ */
second.next = third; // Link second node with the third node
/* Now next of the second Node refers to third. So all three
nodes are linked.
llist.head second third
| | |
| | |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
| 1 | o-------->| 2 | o-------->| 3 | null |
+----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ */
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
</script>
C++
// A simple C++ program for traversal of a linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
// This function prints contents of linked list
// starting from the given node
void printList(Node* n)
{
while (n != NULL) {
cout << n->data << " ";
n = n->next;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
Node* second = NULL;
Node* third = NULL;
// allocate 3 nodes in the heap
head = new Node();
second = new Node();
third = new Node();
head->data = 1; // assign data in first node
head->next = second; // Link first node with second
second->data = 2; // assign data to second node
second->next = third;
third->data = 3; // assign data to third node
third->next = NULL;
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// This is code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
// A simple C program for traversal of a linked list
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// This function prints contents of linked list starting from
// the given node
void printList(struct Node* n)
{
while (n != NULL) {
printf(" %d ", n->data);
n = n->next;
}
}
int main()
{
struct Node* head = NULL;
struct Node* second = NULL;
struct Node* third = NULL;
// allocate 3 nodes in the heap
head = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
second = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
third = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
head->data = 1; // assign data in first node
head->next = second; // Link first node with second
second->data = 2; // assign data to second node
second->next = third;
third->data = 3; // assign data to third node
third->next = NULL;
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Java
// A simple Java program for traversal of a linked list
class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node. This inner class is made static so that
main() can access it */
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
this.data = d;
next = null;
} // Constructor
}
/* This function prints contents of linked list starting from head */
public void printList()
{
Node n = head;
while (n != null) {
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
/* method to create a simple linked list with 3 nodes*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list. */
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.head = new Node(1);
Node second = new Node(2);
Node third = new Node(3);
llist.head.next = second; // Link first node with the second node
second.next = third; // Link second node with the third node
llist.printList();
}
}
Python3
# A simple Python program for traversal of a linked list # Node class class Node: # Function to initialise the node object def __init__(self, data): self.data = data # Assign data self.next = None # Initialize next as null # Linked List class contains a Node object class LinkedList: # Function to initialize head def __init__(self): self.head = None # This function prints contents of linked list # starting from head def printList(self): temp = self.head while (temp): print (temp.data) temp = temp.next # Code execution starts here if __name__=='__main__': # Start with the empty list llist = LinkedList() llist.head = Node(1) second = Node(2) third = Node(3) llist.head.next = second; # Link first node with second second.next = third; # Link second node with the third node llist.printList()
C#
// A simple C# program for traversal of a linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node. This inner
class is made static so that
main() can access it */
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
} // Constructor
}
/* This function prints contents of
linked list starting from head */
public void printList()
{
Node n = head;
while (n != null) {
Console.Write(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
/* method to create a simple linked list with 3 nodes*/
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* Start with the empty list. */
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
llist.head = new Node(1);
Node second = new Node(2);
Node third = new Node(3);
llist.head.next = second; // Link first node with the second node
second.next = third; // Link second node with the third node
llist.printList();
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
Javascript
<script>
// A simple javascript program for traversal of a linked list
var head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node. This inner class is made so that
main() can access it */
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
/* This function prints contents of linked list starting from head */
function printList()
{
var n = head;
while (n != null) {
document.write(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
/* method to create a simple linked list with 3 nodes*/
/* Start with the empty list. */
var head = new Node(1);
var second = new Node(2);
var third = new Node(3);
head.next = second; // Link first node with the second node
second.next = third; // Link second node with the third node
printList();
// This code contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA