Clase de artista de Matplotlib en un FigureCanvas. Todos los elementos visibles en una figura son subclases de Artista.
Método Matplotlib.artist.Artist.get_label()
El método set_label() en el módulo de artista de la biblioteca matplotlib
Sintaxis: Artista.g
Parámetros: Este método no acepta ningún parámetro.
Devoluciones: este método devuelve la etiqueta utilizada para este artista en la leyenda.
Los siguientes ejemplos ilustran la función matplotlib.artist.Artist.get_label() en matplotlib:
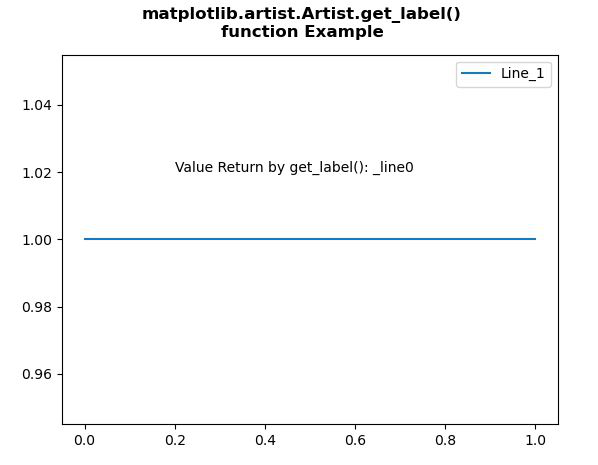
Ejemplo 1:
# Implementation of matplotlib function
from matplotlib.artist import Artist
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = [0, 1]
y = [1, 1]
line, = ax.plot(x, y)
ax.legend(("Line_1", ))
ax.text(0.2, 1.02, "Value Return by get_label()\
: " + str(Artist.get_label(line)))
fig.suptitle("""matplotlib.artist.Artist.get_label()
function Example""", fontweight="bold")
plt.show()
Producción:
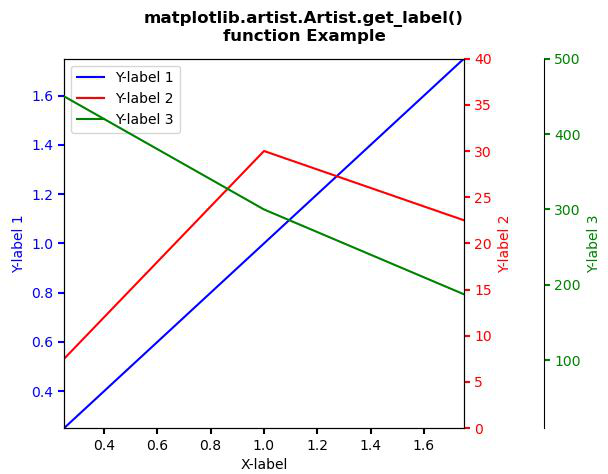
Ejemplo 2:
# Implementation of matplotlib function
from matplotlib.artist import Artist
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def make_patch_spines_invisible(ax):
ax.set_frame_on(True)
ax.patch.set_visible(False)
for sp in ax.spines.values():
sp.set_visible(False)
fig, host = plt.subplots()
fig.subplots_adjust(right = 0.75)
par1 = host.twinx()
par2 = host.twinx()
par2.spines["right"].set_position(("axes", 1.2))
make_patch_spines_invisible(par2)
par2.spines["right"].set_visible(True)
p1, = host.plot([0, 1, 2], [0, 1, 2],
"b-", label ="Y-label 1")
p2, = par1.plot([0, 1, 2], [0, 30, 20],
"r-", label ="Y-label 2")
p3, = par2.plot([0, 1, 2], [500, 300, 150],
"g-", label ="Y-label 3")
host.set_xlim(0.25, 1.75)
host.set_ylim(0.25, 1.75)
par1.set_ylim(0, 40)
par2.set_ylim(10, 500)
host.set_xlabel("X-label")
host.set_ylabel("Y-label 1")
par1.set_ylabel("Y-label 2")
par2.set_ylabel("Y-label 3")
host.yaxis.label.set_color(p1.get_color())
par1.yaxis.label.set_color(p2.get_color())
par2.yaxis.label.set_color(p3.get_color())
tkw = dict(size = 4, width = 1.5)
host.tick_params(axis ='y',
colors = p1.get_color(),
**tkw)
par1.tick_params(axis ='y',
colors = p2.get_color(),
**tkw)
par2.tick_params(axis ='y',
colors = p3.get_color(),
**tkw)
host.tick_params(axis ='x',
**tkw)
lines = [p1, p2, p3]
host.legend(lines, [Artist.get_label(l) for l in lines])
fig.suptitle("""matplotlib.artist.Artist.get_label()
function Example""", fontweight="bold")
plt.show()
Producción:
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por shivanisinghss2110 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA