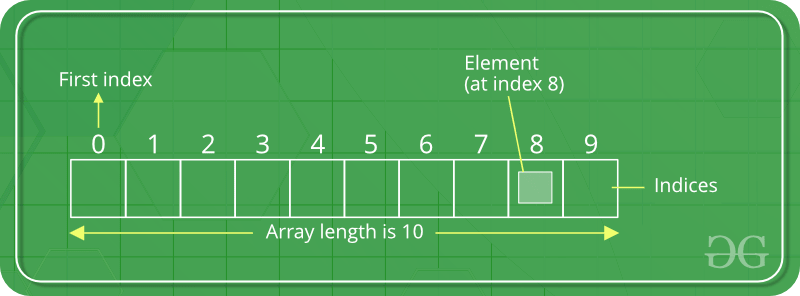
Una array es una colección de elementos almacenados en ubicaciones de memoria contiguas. La idea es almacenar varios artículos del mismo tipo juntos. Esto facilita el cálculo de la posición de cada elemento simplemente agregando un desplazamiento a un valor base, es decir, la ubicación de memoria del primer elemento de la array (generalmente indicado por el nombre de la array).
Para simplificar, podemos pensar en una serie de escaleras donde en cada escalón se coloca un valor (digamos uno de tus amigos). Aquí, puede identificar la ubicación de cualquiera de sus amigos simplemente sabiendo el recuento del paso en el que se encuentran. Array puede ser manejado en Python por un módulo llamado array . Pueden ser útiles cuando tenemos que manipular solo valores de un tipo de datos específico. Un usuario puede tratar listascomo arrays. Sin embargo, el usuario no puede restringir el tipo de elementos almacenados en una lista. Si crea arrays utilizando el módulo de array , todos los elementos de la array deben ser del mismo tipo.
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Creation of Array
# importing "array" for array creations
import array as arr
# creating an array with integer type
a = arr.array('i', [1, 2, 3])
# printing original array
print ("The new created array is : ", end =" ")
for i in range (0, 3):
print (a[i], end =" ")
print()
# creating an array with float type
b = arr.array('d', [2.5, 3.2, 3.3])
# printing original array
print ("The new created array is : ", end =" ")
for i in range (0, 3):
print (b[i], end =" ")
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Adding Elements to a Array
# importing "array" for array creations
import array as arr
# array with int type
a = arr.array('i', [1, 2, 3])
print ("Array before insertion : ", end =" ")
for i in range (0, 3):
print (a[i], end =" ")
print()
# inserting array using
# insert() function
a.insert(1, 4)
print ("Array after insertion : ", end =" ")
for i in (a):
print (i, end =" ")
print()
# array with float type
b = arr.array('d', [2.5, 3.2, 3.3])
print ("Array before insertion : ", end =" ")
for i in range (0, 3):
print (b[i], end =" ")
print()
# adding an element using append()
b.append(4.4)
print ("Array after insertion : ", end =" ")
for i in (b):
print (i, end =" ")
print()
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# accessing of element from list
# importing array module
import array as arr
# array with int type
a = arr.array('i', [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
# accessing element of array
print("Access element is: ", a[0])
# accessing element of array
print("Access element is: ", a[3])
# array with float type
b = arr.array('d', [2.5, 3.2, 3.3])
# accessing element of array
print("Access element is: ", b[1])
# accessing element of array
print("Access element is: ", b[2])
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# Removal of elements in a Array
# importing "array" for array operations
import array
# initializing array with array values
# initializes array with signed integers
arr = array.array('i', [1, 2, 3, 1, 5])
# printing original array
print ("The new created array is : ", end ="")
for i in range (0, 5):
print (arr[i], end =" ")
print ("\r")
# using pop() to remove element at 2nd position
print ("The popped element is : ", end ="")
print (arr.pop(2))
# printing array after popping
print ("The array after popping is : ", end ="")
for i in range (0, 4):
print (arr[i], end =" ")
print("\r")
# using remove() to remove 1st occurrence of 1
arr.remove(1)
# printing array after removing
print ("The array after removing is : ", end ="")
for i in range (0, 3):
print (arr[i], end =" ")
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate
# slicing of elements in a Array
# importing array module
import array as arr
# creating a list
l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
a = arr.array('i', l)
print("Initial Array: ")
for i in (a):
print(i, end =" ")
# Print elements of a range
# using Slice operation
Sliced_array = a[3:8]
print("\nSlicing elements in a range 3-8: ")
print(Sliced_array)
# Print elements from a
# pre-defined point to end
Sliced_array = a[5:]
print("\nElements sliced from 5th "
"element till the end: ")
print(Sliced_array)
# Printing elements from
# beginning till end
Sliced_array = a[:]
print("\nPrinting all elements using slice operation: ")
print(Sliced_array)
Python3
# Python code to demonstrate
# searching an element in array
# importing array module
import array
# initializing array with array values
# initializes array with signed integers
arr = array.array('i', [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 5])
# printing original array
print ("The new created array is : ", end ="")
for i in range (0, 6):
print (arr[i], end =" ")
print ("\r")
# using index() to print index of 1st occurrence of 2
print ("The index of 1st occurrence of 2 is : ", end ="")
print (arr.index(2))
# using index() to print index of 1st occurrence of 1
print ("The index of 1st occurrence of 1 is : ", end ="")
print (arr.index(1))
Python3
# Python code to demonstrate
# how to update an element in array
# importing array module
import array
# initializing array with array values
# initializes array with signed integers
arr = array.array('i', [1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 5])
# printing original array
print ("Array before updation : ", end ="")
for i in range (0, 6):
print (arr[i], end =" ")
print ("\r")
# updating a element in a array
arr[2] = 6
print("Array after updation : ", end ="")
for i in range (0, 6):
print (arr[i], end =" ")
print()
# updating a element in a array
arr[4] = 8
print("Array after updation : ", end ="")
for i in range (0, 6):
print (arr[i], end =" ")
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por ABHISHEK TIWARI 13 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA