Requisito previo: Arrays en Java
Un arreglo irregular es un arreglo de arreglos tales que los arreglos de miembros pueden ser de diferentes tamaños, es decir, podemos crear un arreglo 2-D pero con un número variable de columnas en cada fila. Estos tipos de arrays también se conocen como arrays Jagged.
Representación pictórica de la array irregular en la memoria:
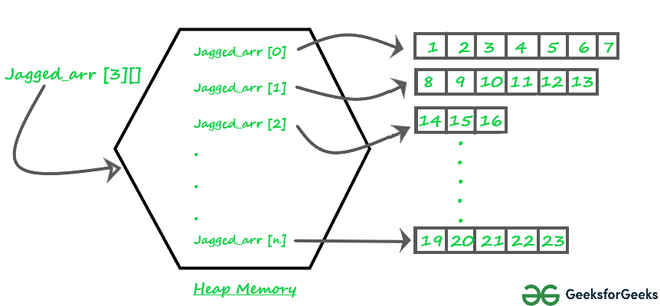
array_dentada
Declaración e inicialización de array irregular:
Syntax: data_type array_name[][] = new data_type[n][]; //n: no. of rows
array_name[] = new data_type[n1] //n1= no. of columns in row-1
array_name[] = new data_type[n2] //n2= no. of columns in row-2
array_name[] = new data_type[n3] //n3= no. of columns in row-3
.
.
.
array_name[] = new data_type[nk] //nk=no. of columns in row-n
Alternativas, formas de inicializar una array irregular:
int arr_name[][] = new int[][] {
new int[] {10, 20, 30 ,40},
new int[] {50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100},
new int[] {110, 120}
};
OR
int[][] arr_name = {
new int[] {10, 20, 30 ,40},
new int[] {50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100},
new int[] {110, 120}
};
OR
int[][] arr_name = {
{10, 20, 30 ,40},
{50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100},
{110, 120}
};
Los siguientes son programas Java para demostrar el concepto anterior.
Java
// Program to demonstrate 2-D jagged array in Java
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring 2-D array with 2 rows
int arr[][] = new int[2][];
// Making the above array Jagged
// First row has 3 columns
arr[0] = new int[3];
// Second row has 2 columns
arr[1] = new int[2];
// Initializing array
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++)
arr[i][j] = count++;
// Displaying the values of 2D Jagged array
System.out.println("Contents of 2D Jagged Array");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++)
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Contents of 2D Jagged Array 0 1 2 3 4
El siguiente es otro ejemplo donde la i-ésima fila tiene i columnas, es decir, la primera fila tiene 1 elemento, la segunda fila tiene dos elementos y así sucesivamente.
Java
// Another Java program to demonstrate 2-D jagged
// array such that first row has 1 element, second
// row has two elements and so on.
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int r = 5;
// Declaring 2-D array with 5 rows
int arr[][] = new int[r][];
// Creating a 2D array such that first row
// has 1 element, second row has two
// elements and so on.
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
arr[i] = new int[i + 1];
// Initializing array
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++)
arr[i][j] = count++;
// Displaying the values of 2D Jagged array
System.out.println("Contents of 2D Jagged Array");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++)
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
Contents of 2D Jagged Array 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Este artículo es una contribución de Rahul Agrawal . Si le gusta GeeksforGeeks y le gustaría contribuir, también puede escribir un artículo y enviarlo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA