Dada una array arr[] que contiene N enteros, la tarea es encontrar la suma máxima que se obtiene al sumar los elementos en el mismo índice de la array original y de la array invertida.
Ejemplo:
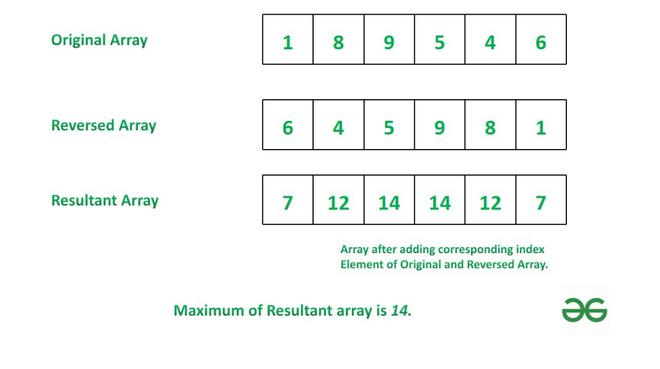
Entrada : arr[]={ 1, 8, 9, 5, 4, 6 }
Salida : 14
Explicación:
Array original: {1, 8, 9, 5, 4, 6}
Array invertida: {6, 4, 5, 9, 8, 1}
Agregando el elemento de índices correspondiente:
{1+6=7, 8+4=12, 9+5=14, 5+9=14, 4+8=12, 6+1=7}
Entonces, La suma máxima es 14.Entrada: arr[]={-31, 5, -1, 7, -5}
Salida: 12
Enfoque ingenuo: cree una array invertida y devuelva la suma máxima después de agregar los elementos de índice correspondientes.
Suma máxima después de agregar el elemento de array invertido correspondiente
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the maximum
// sum obtained by adding the
// elements at the same index of
// the original array and of
// the reversed array
int maximumSum(int arr[], int n)
{
int c = 0;
// Creating reversed array
int reversed[n];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
reversed = arr[i];
int res = INT_MIN;
// Adding corresponding
// indexes of original
// and reversed array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res = std::max(res,
arr[i] + reversed[i]);
}
return res;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 8, 9, 5, 4, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << maximumSum(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Java
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Function to find the maximum
// sum obtained by adding the
// elements at the same index of
// the original array and of
// the reversed array
static int maximumSum(int[] arr, int n)
{
int c = 0;
// Creating reversed array
int[] reversed = new int[n];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
reversed = arr[i];
int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// Adding corresponding
// indexes of original
// and reversed array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res = Math.max(res, arr[i] + reversed[i]);
}
return res;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 8, 9, 5, 4, 6 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println(maximumSum(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by maddler.
Python3
# Python 3 program for the above approach import sys # Function to find the maximum # sum obtained by adding the # elements at the same index of # the original array and of # the reversed array def maximumSum(arr, n): c = 0 # Creating reversed array reversed = [0]*n for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1): reversed= arr[i] c += 1 res = -sys.maxsize - 1 # Adding corresponding # indexes of original # and reversed array for i in range(n): res = max(res, arr[i] + reversed[i]) return res # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": arr = [1, 8, 9, 5, 4, 6] n = len(arr) print(maximumSum(arr, n)) # This code is contributed by ukasp.
C#
/*package whatever //do not write package name here */
using System;
public class GFG {
// Function to find the maximum
// sum obtained by adding the
// elements at the same index of
// the original array and of
// the reversed array
static int maximumSum(int[] arr, int n) {
int c = 0;
// Creating reversed array
int[] reversed = new int[n];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
reversed = arr[i];
int res = int.MinValue;
// Adding corresponding
// indexes of original
// and reversed array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res = Math.Max(res, arr[i] + reversed[i]);
}
return res;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args) {
int []arr = { 1, 8, 9, 5, 4, 6 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine(maximumSum(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
<script>
// Function to find the maximum
// sum obtained by adding the
// elements at the same index of
// the original array and of
// the reversed array
function maximumSum(arr, n) {
let c = 0;
// Creating reversed array
let reversed = new Array(n);
for (let i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
reversed = arr[i];
let res = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
// Adding corresponding
// indexes of original
// and reversed array
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res = Math.max(res, arr[i] + reversed[i]);
}
return res;
}
// Driver Code
let arr = [1, 8, 9, 5, 4, 6];
let n = arr.length;
document.write(maximumSum(arr, n));
// This code is contributed by saurabh_jaiswal.
</script>
14
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Enfoque efectivo: este problema se puede resolver utilizando el algoritmo de dos punteros . Así que sigue los pasos a continuación para encontrar la respuesta:
- Cree un puntero frontal que apunte al primer elemento de la array y un puntero posterior que apunte al último elemento.
- Ahora ejecute un bucle hasta que estos dos punteros se crucen. En cada iteración:
- Agregue los elementos a los que apuntan los punteros delantero y trasero. Esta es la suma de los elementos correspondientes en la array original e invertida.
- Aumenta el puntero delantero en 1 y disminuye el puntero trasero en 1.
- Después de que termine el ciclo, devuelva la suma máxima obtenida.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the maximum
// sum obtained by adding the
// elements at the same index of
// the original array and of
// the reversed array
int maximumSum(int arr[], int n)
{
// Creating i as front pointer
// and j as rear pointer
int i = 0, j = n - 1;
int max = INT_MIN;
while (i <= j) {
if (max < arr[i] + arr[j])
max = arr[i] + arr[j];
i++;
j--;
}
// Returning the maximum value
return max;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 8, 9, 5, 4, 6 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << maximumSum(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
// Function to find the maximum
// sum obtained by adding the
// elements at the same index of
// the original array and of
// the reversed array
static int maximumSum(int []arr, int n)
{
// Creating i as front pointer
// and j as rear pointer
int i = 0, j = n - 1;
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
while (i <= j) {
if (max < arr[i] + arr[j])
max = arr[i] + arr[j];
i++;
j--;
}
// Returning the maximum value
return max;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int []arr = { 1, 8, 9, 5, 4, 6 };
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println(maximumSum(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Samim Hossain Mondal.
Python3
# python program for the above approach INT_MIN = -2147483647 - 1 # Function to find the maximum # sum obtained by adding the # elements at the same index of # the original array and of # the reversed array def maximumSum(arr, n): # Creating i as front pointer # and j as rear pointer i = 0 j = n - 1 max = INT_MIN while (i <= j): if (max < arr[i] + arr[j]): max = arr[i] + arr[j] i += 1 j -= 1 # Returning the maximum value return max # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": arr = [1, 8, 9, 5, 4, 6] n = len(arr) print(maximumSum(arr, n)) # This code is contributed by rakeshsahni
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to find the maximum
// sum obtained by adding the
// elements at the same index of
// the original array and of
// the reversed array
static int maximumSum(int []arr, int n)
{
// Creating i as front pointer
// and j as rear pointer
int i = 0, j = n - 1;
int max = Int32.MinValue;
while (i <= j) {
if (max < arr[i] + arr[j])
max = arr[i] + arr[j];
i++;
j--;
}
// Returning the maximum value
return max;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
int []arr = { 1, 8, 9, 5, 4, 6 };
int n = arr.Length;
Console.Write(maximumSum(arr, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Samim Hossain Mondal.
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for the above approach
// Function to find the maximum
// sum obtained by adding the
// elements at the same index of
// the original array and of
// the reversed array
function maximumSum(arr, n)
{
// Creating i as front pointer
// and j as rear pointer
let i = 0, j = n - 1;
let max = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER;
while (i <= j) {
if (max < arr[i] + arr[j])
max = arr[i] + arr[j];
i++;
j--;
}
// Returning the maximum value
return max;
}
// Driver Code
let arr = [ 1, 8, 9, 5, 4, 6 ];
let n = arr.length;
document.write(maximumSum(arr, n));
// This code is contributed by Samim Hossain Mondal.
</script>
14
Complejidad Temporal: O(N)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1).
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por manishguptagkp06 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA