Dada una cuerda de n metros de largo, corte la cuerda en diferentes partes de longitudes enteras de manera que maximice el producto de las longitudes de todas las partes. Debes hacer al menos un corte. Suponga que la longitud de la cuerda es más de 2 metros.
Ejemplos:
Input: n = 2 Output: 1 (Maximum obtainable product is 1*1) Input: n = 3 Output: 2 (Maximum obtainable product is 1*2) Input: n = 4 Output: 4 (Maximum obtainable product is 2*2) Input: n = 5 Output: 6 (Maximum obtainable product is 2*3) Input: n = 10 Output: 36 (Maximum obtainable product is 3*3*4)
1) Subestructura óptima:
Este problema es similar al problema de corte de varillas. Podemos obtener el máximo producto haciendo un corte en diferentes posiciones y comparando los valores obtenidos después de un corte. Podemos llamar recursivamente a la misma función para una pieza obtenida después de un corte.
Sea maxProd(n) el producto máximo de una cuerda de longitud n. maxProd(n) se puede escribir de la siguiente manera.
maxProd(n) = max(i*(ni), maxProdRec(ni)*i) para todo i en {1, 2, 3 .. n}
2) Subproblemas superpuestos:
A continuación se muestra una implementación recursiva simple del problema. La implementación simplemente sigue la estructura recursiva mencionada anteriormente.
C++
// A Naive Recursive method to find maximum product
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Utility function to get the maximum of two and three integers
int max(int a, int b) { return (a > b)? a : b;}
int max(int a, int b, int c) { return max(a, max(b, c));}
// The main function that returns maximum product obtainable
// from a rope of length n
int maxProd(int n)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0 || n == 1) return 0;
// Make a cut at different places and take the maximum of all
int max_val = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
max_val = max(max_val, i*(n-i), maxProd(n-i)*i);
// Return the maximum of all values
return max_val;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
cout << "Maximum Product is " << maxProd(10);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find maximum product
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// The main function that returns
// maximum product obtainable from
// a rope of length n
static int maxProd(int n)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0 || n == 1) return 0;
// Make a cut at different places
// and take the maximum of all
int max_val = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
max_val = Math.max(max_val,
Math.max(i * (n - i),
maxProd(n - i) * i));
// Return the maximum of all values
return max_val;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Maximum Product is "
+ maxProd(10));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Prerna Saini
Python3
# The main function that returns maximum
# product obtainable from a rope of length n
def maxProd(n):
# Base cases
if (n == 0 or n == 1):
return 0
# Make a cut at different places
# and take the maximum of all
max_val = 0
for i in range(1, n - 1):
max_val = max(max_val, max(i * (n - i), maxProd(n - i) * i))
#Return the maximum of all values
return max_val;
# Driver program to test above functions
print("Maximum Product is ", maxProd(10));
# This code is contributed
# by Sumit Sudhakar
C#
// C# program to find maximum product
using System;
class GFG {
// The main function that returns
// the max possible product
static int maxProd(int n)
{
// n equals to 2 or 3 must
// be handled explicitly
if (n == 2 || n == 3)
return (n - 1);
// Keep removing parts of size
// 3 while n is greater than 4
int res = 1;
while (n > 4) {
n -= 3;
// Keep multiplying 3 to res
res *= 3;
}
// The last part multiplied
// by previous parts
return (n * res);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("Maximum Product is "
+ maxProd(10));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007
PHP
<?php
// A Naive Recursive method to
// find maximum product
// Utility function to get the
// maximum of two and three integers
function max_1($a, $b, $c)
{
return max($a, max($b, $c));
}
// The main function that returns
// maximum product obtainable
// from a rope of length n
function maxProd($n)
{
// Base cases
if ($n == 0 || $n == 1) return 0;
// Make a cut at different places
// and take the maximum of all
$max_val = 0;
for ($i = 1; $i < $n; $i++)
$max_val = max_1($max_val, $i * ($n - $i),
maxProd($n - $i) * $i);
// Return the maximum of all values
return $max_val;
}
// Driver Code
echo "Maximum Product is " . maxProd(10);
// This code is contributed
// by ChitraNayal
?>
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to find maximum product
// The main function that returns
// maximum product obtainable from
// a rope of length n
function maxProd(n)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
return 0;
// Make a cut at different places
// and take the maximum of all
let max_val = 0;
for (let i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
max_val = Math.max(max_val,
Math.max(i * (n - i),
maxProd(n - i) * i));
}
// Return the maximum of all values
return max_val;
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
document.write("Maximum Product is "
+ maxProd(10));
// This code is contributed by rag2127
</script>
Maximum Product is 36
Teniendo en cuenta la implementación anterior, el siguiente es un árbol de recursión para una cuerda de longitud 5.
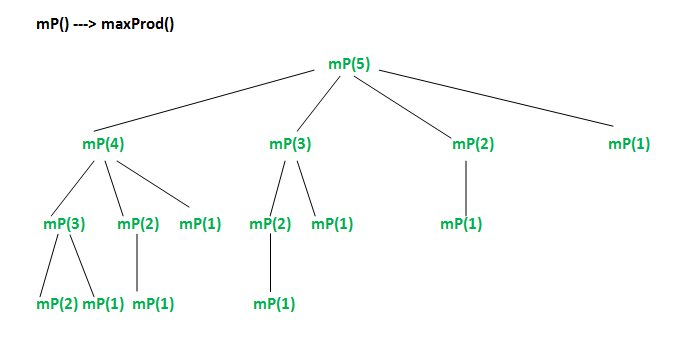
En el árbol de recursión parcial anterior, mP(3) se resuelve dos veces. Podemos ver que hay muchos subproblemas que se resuelven una y otra vez. Dado que los mismos subproblemas se vuelven a llamar, este problema tiene la propiedad Superposición de subproblemas. Entonces el problema tiene ambas propiedades (ver this y this ) de un problema de programación dinámica. Al igual que otros problemas típicos de programación dinámica (DP) , los cálculos de los mismos subproblemas se pueden evitar mediante la construcción de una array temporal val[] de forma ascendente.
C++
// C++ code to implement the approach\
// A Dynamic Programming solution for Max Product Problem
int maxProd(int n)
{
int val[n+1];
val[0] = val[1] = 0;
// Build the table val[] in bottom up manner and return
// the last entry from the table
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int max_val = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
max_val = max(max_val, (i-j)*j, j*val[i-j]);
val[i] = max_val;
}
return val[n];
}
// This code is contributed by sanjoy_62.
C
// A Dynamic Programming solution for Max Product Problem
int maxProd(int n)
{
int val[n+1];
val[0] = val[1] = 0;
// Build the table val[] in bottom up manner and return
// the last entry from the table
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int max_val = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
max_val = max(max_val, (i-j)*j, j*val[i-j]);
val[i] = max_val;
}
return val[n];
}
Java
// A Dynamic Programming solution for Max Product Problem
int maxProd(int n)
{
int val[n+1];
val[0] = val[1] = 0;
// Build the table val[] in bottom up manner and return
// the last entry from the table
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int max_val = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
max_val = Math.max(max_val, (i-j)*j, j*val[i-j]);
val[i] = max_val;
}
return val[n];
}
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
Python3
# A Dynamic Programming solution for Max Product Problem def maxProd(n): val= [0 for i in range(n+1)]; # Build the table val in bottom up manner and return # the last entry from the table for i in range(1,n+1): max_val = 0; for j in range(1,i): max_val = max(max_val, (i-j)*j, j*val[i-j]); val[i] = max_val; return val[n]; # This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
C#
// A Dynamic Programming solution for Max Product Problem
int maxProd(int n)
{
int []val = new int[n+1];
val[0] = val[1] = 0;
// Build the table val[] in bottom up manner and return
// the last entry from the table
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int max_val = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
max_val = Math.Max(max_val, (i-j)*j, j*val[i-j]);
val[i] = max_val;
}
return val[n];
}
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
Javascript
<script>
// A Dynamic Programming solution for Max Product Problem
function maxProd(n)
{
var val = Array(n+1).fill(0;
val[0] = val[1] = 0;
// Build the table val in bottom up manner and return
// the last entry from the table
for (var 1; i <= n; i++)
{
var max_val = 0;
for ( var ; j <= i; j++)
max_val = Math.max(max_val, (i-j)*j, j*val[i-j]);
val[i] = max_val;
}
return val[n];
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
</script>
La complejidad temporal de la solución de programación dinámica es O(n^2) y requiere O(n) espacio extra.
Una solución complicada:
Si vemos algunos ejemplos de estos problemas, podemos observar fácilmente el siguiente patrón.
El producto máximo se puede obtener cortando repetidamente piezas de tamaño 3 mientras que el tamaño es mayor que 4, manteniendo la última pieza como tamaño de 2 o 3 o 4. Por ejemplo, n = 10, el producto máximo se obtiene por 3, 3, 4. Para n = 11, el producto máximo se obtiene por 3, 3, 3, 2. A continuación se muestra la implementación de este enfoque.
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/* The main function that returns the max possible product */
int maxProd(int n)
{
// n equals to 2 or 3 must be handled explicitly
if (n == 2 || n == 3) return (n-1);
// Keep removing parts of size 3 while n is greater than 4
int res = 1;
while (n > 4)
{
n -= 3;
res *= 3; // Keep multiplying 3 to res
}
return (n * res); // The last part multiplied by previous parts
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
cout << "Maximum Product is " << maxProd(10);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find maximum product
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
/* The main function that returns the
max possible product */
static int maxProd(int n)
{
// n equals to 2 or 3 must be handled
// explicitly
if (n == 2 || n == 3) return (n-1);
// Keep removing parts of size 3
// while n is greater than 4
int res = 1;
while (n > 4)
{
n -= 3;
// Keep multiplying 3 to res
res *= 3;
}
// The last part multiplied by
// previous parts
return (n * res);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Maximum Product is "
+ maxProd(10));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Prerna Saini
Python3
# The main function that returns the
# max possible product
def maxProd(n):
# n equals to 2 or 3 must
# be handled explicitly
if (n == 2 or n == 3):
return (n - 1)
# Keep removing parts of size 3
# while n is greater than 4
res = 1
while (n > 4):
n -= 3;
# Keep multiplying 3 to res
res *= 3;
# The last part multiplied
# by previous parts
return (n * res)
# Driver program to test above functions
print("Maximum Product is ", maxProd(10));
# This code is contributed
# by Sumit Sudhakar
C#
// C# program to find maximum product
using System;
class GFG {
// The main function that returns
// maximum product obtainable from
// a rope of length n
static int maxProd(int n)
{
// Base cases
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
return 0;
// Make a cut at different places
// and take the maximum of all
int max_val = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
max_val = Math.Max(max_val,
Math.Max(i * (n - i),
maxProd(n - i) * i));
// Return the maximum of all values
return max_val;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine("Maximum Product is "
+ maxProd(10));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007
PHP
<?php
/* The main function that returns
the max possible product */
function maxProd($n)
{
// n equals to 2 or 3 must
// be handled explicitly
if ($n == 2 || $n == 3)
return ($n - 1);
// Keep removing parts of size
// 3 while n is greater than 4
$res = 1;
while ($n > 4)
{
$n = $n - 3;
// Keep multiplying 3 to res
$res = $res * 3;
}
// The last part multiplied
// by previous parts
return ($n * $res);
}
// Driver code
echo ("Maximum Product is ");
echo(maxProd(10));
// This code is contributed
// by Shivi_Aggarwal
?>
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program to find maximum product
/* The main function that returns the
max possible product */
function maxProd(n)
{
// n equals to 2 or 3 must be handled
// explicitly
if (n == 2 || n == 3)
{
return (n-1);
}
// Keep removing parts of size 3
// while n is greater than 4
let res = 1;
while (n > 4)
{
n -= 3;
// Keep multiplying 3 to res
res *= 3;
}
// The last part multiplied by
// previous parts
return (n * res);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
document.write("Maximum Product is " + maxProd(10));
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
Maximum Product is 36
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA