En BFS y DFS , cuando estamos en un Node, podemos considerar cualquiera de los adyacentes como el siguiente Node. Entonces, tanto BFS como DFS exploran caminos a ciegas sin considerar ninguna función de costo.
La idea de Best First Search es utilizar una función de evaluación para decidir qué adyacente es más prometedor y luego explorar.
La mejor primera búsqueda se incluye en la categoría de búsqueda heurística o búsqueda informada.
Implementación de Best First Search:
Usamos una cola de prioridad o un montón para almacenar los costos de los Nodes que tienen el valor de función de evaluación más bajo. Entonces, la implementación es una variación de BFS, solo necesitamos cambiar Queue a PriorityQueue.
// Pseudocode for Best First Search
Best-First-Search(Graph g, Node start)
1) Create an empty PriorityQueue
PriorityQueue pq;
2) Insert "start" in pq.
pq.insert(start)
3) Until PriorityQueue is empty
u = PriorityQueue.DeleteMin
If u is the goal
Exit
Else
Foreach neighbor v of u
If v "Unvisited"
Mark v "Visited"
pq.insert(v)
Mark u "Examined"
End procedure
Ilustración:
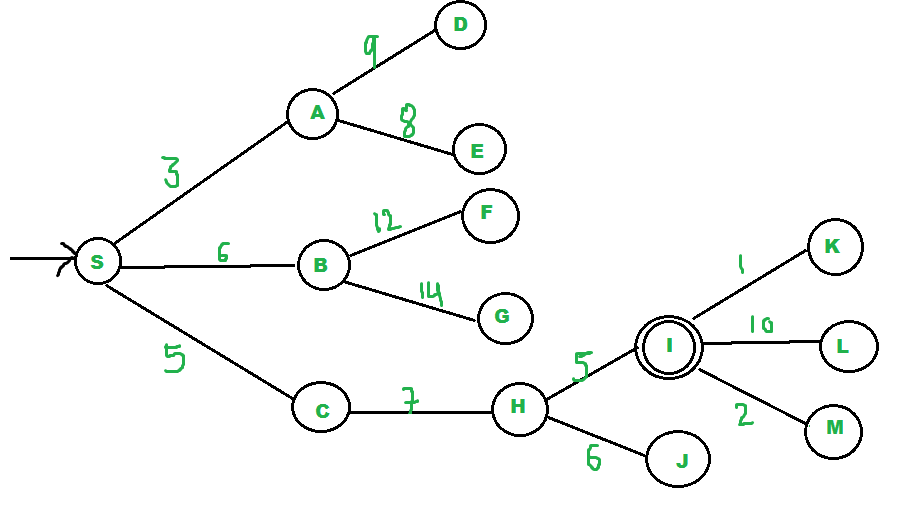
Consideremos el siguiente ejemplo:
- Comenzamos desde la fuente «S» y buscamos el objetivo «I» utilizando los costos dados y la búsqueda Best First.
- pq inicialmente contiene S
- Eliminamos s de y procesamos vecinos no visitados de S a pq.
- pq ahora contiene {A, C, B} (C se pone antes de B porque C tiene un costo menor)
- Eliminamos A de pq y procesamos vecinos no visitados de A a pq.
- pq ahora contiene {C, B, E, D}
- Eliminamos C de pq y procesamos vecinos no visitados de C a pq.
- pq ahora contiene {B, H, E, D}
- Eliminamos B de pq y procesamos vecinos no visitados de B a pq.
- pq ahora contiene {H, E, D, F, G}
- Quitamos H de pq.
- Como nuestro objetivo “I” es vecino de H, volvemos.
A continuación se muestra la implementación de la idea anterior:
C++
// C++ program to implement Best First Search using priority
// queue
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pi;
vector<vector<pi> > graph;
// Function for adding edges to graph
void addedge(int x, int y, int cost)
{
graph[x].push_back(make_pair(cost, y));
graph[y].push_back(make_pair(cost, x));
}
// Function For Implementing Best First Search
// Gives output path having lowest cost
void best_first_search(int actual_Src, int target, int n)
{
vector<bool> visited(n, false);
// MIN HEAP priority queue
priority_queue<pi, vector<pi>, greater<pi> > pq;
// sorting in pq gets done by first value of pair
pq.push(make_pair(0, actual_Src));
int s = actual_Src;
visited[s] = true;
while (!pq.empty()) {
int x = pq.top().second;
// Displaying the path having lowest cost
cout << x << " ";
pq.pop();
if (x == target)
break;
for (int i = 0; i < graph[x].size(); i++) {
if (!visited[graph[x][i].second]) {
visited[graph[x][i].second] = true;
pq.push(make_pair(graph[x][i].first,graph[x][i].second));
}
}
}
}
// Driver code to test above methods
int main()
{
// No. of Nodes
int v = 14;
graph.resize(v);
// The nodes shown in above example(by alphabets) are
// implemented using integers addedge(x,y,cost);
addedge(0, 1, 3);
addedge(0, 2, 6);
addedge(0, 3, 5);
addedge(1, 4, 9);
addedge(1, 5, 8);
addedge(2, 6, 12);
addedge(2, 7, 14);
addedge(3, 8, 7);
addedge(8, 9, 5);
addedge(8, 10, 6);
addedge(9, 11, 1);
addedge(9, 12, 10);
addedge(9, 13, 2);
int source = 0;
int target = 9;
// Function call
best_first_search(source, target, v);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to implement Best First Search using priority
// queue
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class GFG
{
static ArrayList<ArrayList<edge> > adj = new ArrayList<>();
// Function for adding edges to graph
static class edge implements Comparable<edge>
{
int v, cost;
edge(int v, int cost)
{
this.v = v;
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override public int compareTo(edge o)
{
if (o.cost < cost) {
return 1;
}
else
return -1;
}
}
public GFG(int v)
{
for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) {
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
}
// Function For Implementing Best First Search
// Gives output path having lowest cost
static void best_first_search(int source, int target, int v)
{
// MIN HEAP priority queue
PriorityQueue<edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
boolean visited[] = new boolean[v];
visited = true;
// sorting in pq gets done by first value of pair
pq.add(new edge(source, -1));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int x = pq.poll().v;
// Displaying the path having lowest cost
System.out.print(x + " ");
if (target == x) {
break;
}
for (edge adjacentNodeEdge : adj.get(x)) {
if (!visited[adjacentNodeEdge.v]) {
visited[adjacentNodeEdge.v] = true;
pq.add(adjacentNodeEdge);
}
}
}
}
void addedge(int u, int v, int cost)
{
adj.get(u).add(new edge(v, cost));
adj.get(v).add(new edge(u, cost));
}
// Driver code to test above methods
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No. of Nodes
int v = 14;
// The nodes shown in above example(by alphabets) are
// implemented using integers addedge(x,y,cost);
GFG graph = new GFG(v);
graph.addedge(0, 1, 3);
graph.addedge(0, 2, 6);
graph.addedge(0, 3, 5);
graph.addedge(1, 4, 9);
graph.addedge(1, 5, 8);
graph.addedge(2, 6, 12);
graph.addedge(2, 7, 14);
graph.addedge(3, 8, 7);
graph.addedge(8, 9, 5);
graph.addedge(8, 10, 6);
graph.addedge(9, 11, 1);
graph.addedge(9, 12, 10);
graph.addedge(9, 13, 2);
int source = 0;
int target = 9;
// Function call
best_first_search(source, target, v);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Prithi_Dey
Python3
from queue import PriorityQueue v = 14 graph = [[] for i in range(v)] # Function For Implementing Best First Search # Gives output path having lowest cost def best_first_search(actual_Src, target, n): visited = [False] * n pq = PriorityQueue() pq.put((0, actual_Src)) visited[actual_Src] = True while pq.empty() == False: u = pq.get()[1] # Displaying the path having lowest cost print(u, end=" ") if u == target: break for v, c in graph[u]: if visited[v] == False: visited[v] = True pq.put((c, v)) print() # Function for adding edges to graph def addedge(x, y, cost): graph[x].append((y, cost)) graph[y].append((x, cost)) # The nodes shown in above example(by alphabets) are # implemented using integers addedge(x,y,cost); addedge(0, 1, 3) addedge(0, 2, 6) addedge(0, 3, 5) addedge(1, 4, 9) addedge(1, 5, 8) addedge(2, 6, 12) addedge(2, 7, 14) addedge(3, 8, 7) addedge(8, 9, 5) addedge(8, 10, 6) addedge(9, 11, 1) addedge(9, 12, 10) addedge(9, 13, 2) source = 0 target = 9 best_first_search(source, target, v) # This code is contributed by Jyotheeswar Ganne
0 1 3 2 8 9
Análisis :
- La complejidad de tiempo en el peor de los casos para Best First Search es O(n * log n) donde n es el número de Nodes. En el peor de los casos, es posible que tengamos que visitar todos los Nodes antes de alcanzar el objetivo. Tenga en cuenta que la cola de prioridad se implementa utilizando Min (o Max) Heap, y las operaciones de inserción y eliminación toman tiempo O (log n).
- El rendimiento del algoritmo depende de qué tan bien esté diseñada la función de costo o evaluación.
Casos especiales de Mejor primera búsqueda:
- Greedy Best primer algoritmo de búsqueda
- Algoritmo de búsqueda A*
Este artículo es una contribución de Shambhavi Singh . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA