El método Console.SetIn() se utiliza para establecer la propiedad In del objeto StreamReader especificado, es decir, redirige la entrada estándar de la consola al archivo de entrada. Dado que la consola está configurada con este objeto StreamReader, se puede llamar al método ReadLine() para leer el contenido del archivo, línea por línea.
Sintaxis: public static void SetIn (System.IO.StreamReader newIn);
Parámetro:
newIn : Es un flujo que es la nueva entrada estándar.
Excepciones:
- ArgumentNullException: si newIn es nulo.
- SecurityException: si la persona que llama no tiene el permiso requerido.
Ejemplo: En este ejemplo, el método SetIn() se usa para configurar el objeto StreamReader en la consola, y el contenido del archivo se leerá, almacenará e imprimirá.
Archivo de texto utilizado:

// C# program to demonstrate SetIn() method
using System;
using System.IO;
class GFG {
// Main Method
static void Main()
{
// Create a string to get
// data from the file
string geeks = " ";
// creating the StreamReader object
// and set it to the desired
// text file
using(StreamReader gfg = new StreamReader("D:\\out.txt"))
{
// setting the StreamReader
// object to the Console
Console.SetIn(gfg);
string l;
// Reading the contents of the file into l
while ((l = Console.ReadLine()) != null)
{
geeks = geeks + l;
}
// Printing the file contents
// appended to "Hello "
Console.WriteLine("Hello " + geeks);
// Waiting for user input
// to exit the program
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
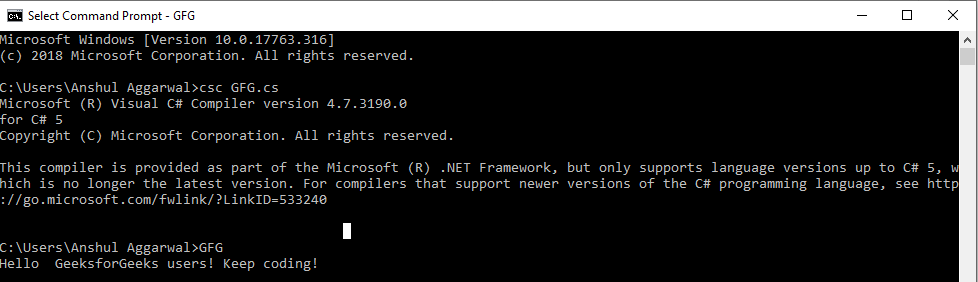
Producción:
Referencia:
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por MukkeshMckenzie y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA