throwing(String sourceClass, String sourceMethod, Throwable throw) se utiliza para registrar el lanzamiento de una excepción. En muchos escenarios, el método se cierra lanzando una excepción, entonces este es un método muy útil para registrar que un método está terminando lanzando una excepción. El registro se realiza utilizando el registro de nivel FINER. Si el nivel del registrador está configurado para registrar el registro de nivel FINER, los argumentos proporcionados se almacenan en un registro con un mensaje THROW que se reenvía a todos los controladores de salida registrados.
Sintaxis:
public void throwing(String sourceClass,
String sourceMethod,
Throwable thrown)
Parámetros: Este método acepta tres parámetros:
- sourceClass es el nombre de la clase que emitió la solicitud de registro,
- sourceMethod es el nombre del método y
- El resultado es The Throwable que se está lanzando.
Valor devuelto: este método no devuelve nada.
Los siguientes programas ilustran el método de lanzamiento (String sourceClass, String sourceMethod, Object result):
Programa 1:
// Java program to demonstrate
// throwing(String, String, Throwable) method
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.logging.FileHandler;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import java.util.logging.SimpleFormatter;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws SecurityException, IOException
{
// Create a Logger
Logger logger
= Logger.getLogger(
GFG.class.getName());
// Create a file handler object
FileHandler handler
= new FileHandler("logs.txt");
handler.setFormatter(new SimpleFormatter());
// Add file handler as
// handler of logs
logger.addHandler(handler);
// set Logger level()
logger.setLevel(Level.FINER);
// set Logger level()
logger.setLevel(Level.FINER);
// call throwing method with class
// name = GFG and method name = main
// and IO Exception as Thrown object
logger.throwing(GFG.class.getName(),
GFG.class.getMethods()[0].getName(),
new IOException());
}
}
El resultado impreso en log.txt se muestra a continuación.
Producción: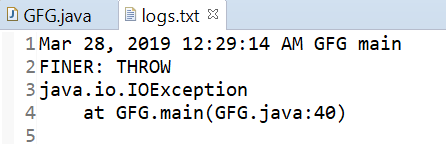
Programa 2:
// Java program to demonstrate
// throwing(String, String, Throwable) method
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.logging.FileHandler;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class GFG {
// Create a Logger
static Logger logger
= Logger.getLogger(
GFG.class.getName());
public static void main(String[] args)
throws SecurityException, IOException
{
// Create a file handler object
FileHandler handler
= new FileHandler("logs.txt");
// Add file handler as
// handler of logs
logger.addHandler(handler);
// set Logger level()
logger.setLevel(Level.FINER);
// set Logger level()
logger.setLevel(Level.FINER);
// call throwing method with string
// and ArithmeticException as Thrown object
logger.throwing(String.class.getName(),
String.class.getMethods()[0].getName(),
new ArithmeticException());
}
}
El resultado impreso en log.txt se muestra a continuación.
Producción: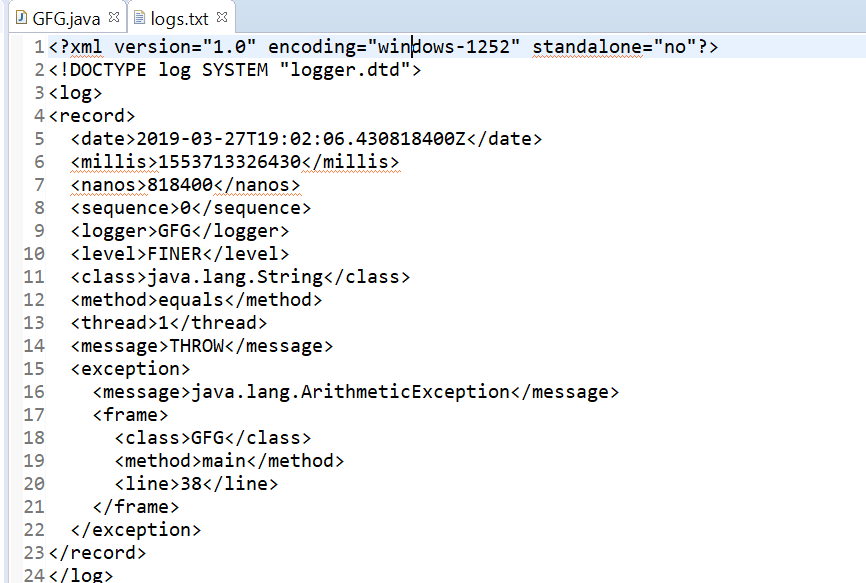
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por AmanSingh2210 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA