Java.util.Vector .setSize() es un método de la clase Vector que se utiliza para establecer el nuevo tamaño del vector. Si el nuevo tamaño del vector es mayor que el tamaño actual, se agregan elementos nulos al vector; si el nuevo tamaño es menor que el tamaño actual, se eliminan todos los elementos de orden superior.
Este método modificó el tamaño del Vector a newSize y no devuelve nada.
Sintaxis:
public void setSize(int newSize)
Parámetros: Este método acepta un parámetro obligatorio newSize del vector.
Tipo de devolución: NA
Excepciones: ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
Nota: si el nuevo tamaño es negativo, arrojará un error de tiempo de ejecución
Ejemplo 1:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate setSize() method
// of Vector class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of Vector class
// Declaring object of string type
Vector<String> v = new Vector<String>();
// Inserting elements into the vector
// using add() method
// Custom input elements
v.add("Geeks");
v.add("for");
v.add("Geeks");
v.add("Computer");
v.add("Science");
v.add("Portal");
// Printing vector before calling setSize() method
System.out.println("Initially");
System.out.println("Vector: " + v);
System.out.println("Size: " + v.size());
// Setting new custom size
v.setSize(8);
// Printing vector after calling setSize()
System.out.println("\nAfter using setSize()");
System.out.println("Vector: " + v);
System.out.println("Size: " + v.size());
}
}
Initially Vector: [Geeks, for, Geeks, Computer, Science, Portal] Size: 6 After using setSize() Vector: [Geeks, for, Geeks, Computer, Science, Portal, null, null] Size: 8
Ejemplo 2: cuando el nuevo tamaño es positivo
Java
// Java program to Illustrate setSize() method
// of Vector class
// Where size is positive
// Importing utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// amin driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating vector object of string type
Vector<String> v = new Vector<String>();
// Inserting elements into the vector
//. using add() method
// Custom input elements
v.add("Geeks");
v.add("for");
v.add("Geeks");
v.add("Computer");
v.add("Science");
v.add("Portal");
// Printing vector before calling setSize()
System.out.println("Initially");
System.out.println("Vector: " + v);
System.out.println("Size: " + v.size());
// Setting new size
v.setSize(4);
// Printing vector after calling setSize()
System.out.println("\nAfter using setSize()");
System.out.println("Vector: " + v);
System.out.println("Size: " + v.size());
}
}
Initially Vector: [Geeks, for, Geeks, Computer, Science, Portal] Size: 6 After using setSize() Vector: [Geeks, for, Geeks, Computer] Size: 4
Ejemplo 3: cuando el nuevo tamaño es negativo
Java
// Java program to Illustrate setSize() method
// of vector class
// Where size is negative
// Importing utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating Vector class object of string type
Vector<String> v = new Vector<String>();
// Inserting elements into the vector
// using add() method
v.add("Geeks");
v.add("for");
v.add("Geeks");
v.add("Computer");
v.add("Science");
v.add("Portal");
// Printing vector before calling setSize()
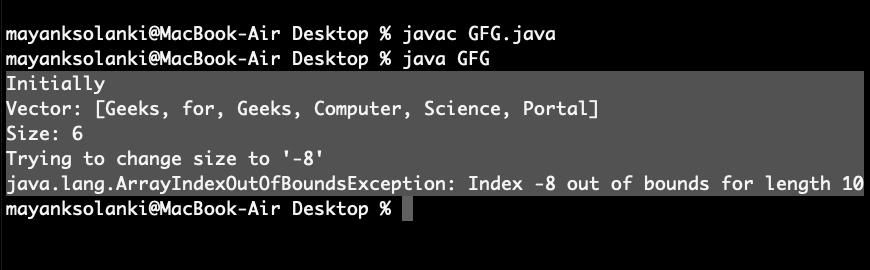
System.out.println("Initially");
System.out.println("Vector: " + v);
System.out.println("Size: " + v.size());
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Setting new size
v.setSize(-8);
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (Exception e) {
// Display message when exceptions occurred
System.out.println("Trying to change "
+ "size to '-8'\n" + e);
}
}
}
Producción:
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por ankit15697 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA