Acerca de:
la clase java.lang.Boolean envuelve el valor booleano de tipo primitivo en un objeto.
Declaración de clase
public final class Boolean
extends Object
implements Serializable, Comparable
Constructores :
Boolean(boolean val) : Assigning Boolean object representing the val argument.
Boolean(String str) : Assigning Boolean object representing the value true or false
according to the string.
Métodos :
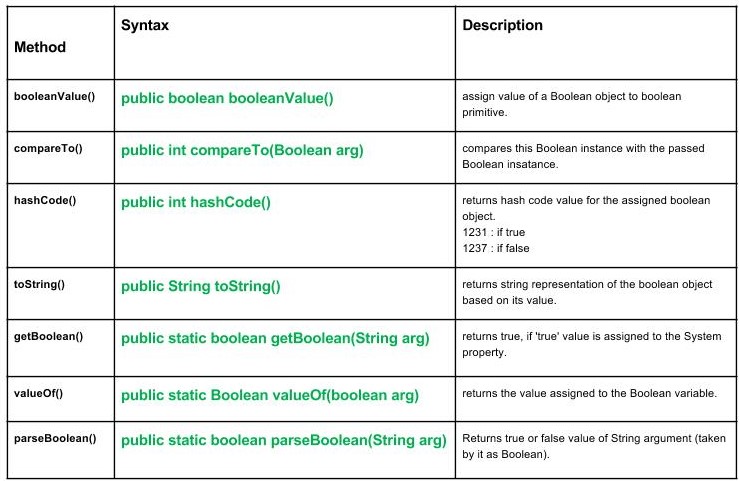
- booleanValue() : java.lang.Boolean.booleanValue() se usa para asignar el valor de un objeto booleano a una primitiva booleana.
Sintaxis:
public boolean booleanValue() Returns : primitive boolean value of the boolean object.
- compareTo() : java.lang.Boolean.compareTo(Boolean arg) compara esta instancia booleana con la instancia booleana pasada.
Sintaxis:
public int compareTo(Boolean arg) Parameter : arg : boolean instance to be compared with this instance. Returns : 0 : if this instance = argumented instance. +ve value : if this instance > argumented instance. -ve value : if this instance < argumented instance.
- hashCode() : java.lang.Boolean.hashCode() devuelve el valor del código hash para el objeto booleano asignado.
Sintaxis:
public int hashCode() Returns : 1231 : if the boolean value of object is true. 1237 : if the boolean value of object is false.
- toString() : java.lang.Boolean.toString() devuelve una representación de string del objeto booleano en función de su valor.
Sintaxis:
public String toString() Returns : string value - 'true' if boolean object is true, else false.
Implementación:
Java
// Java program illustrating Boolean class methods
// booleanValue(), compareTo(), hashCode(), toString()
import java.lang.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a boolean object and assigning value to it.
Boolean bool1 = new Boolean(true);
Boolean bool2 = new Boolean(false);
System.out.println("Boolean object - bool1 : "+bool1);
System.out.println("Boolean object - bool2 : "+bool2);
// Creating a boolean primitive bool2
boolean bool3, bool4 ;
// Use of booleanValue()
// Assigning object value to primitive variable.
bool3 = bool1.booleanValue();
System.out.println("Primitive value of object i.e. bool3 : "+bool3);
bool4 = bool2.booleanValue();
System.out.println("Primitive value of object i.e. bool4 : "+bool4);
System.out.println("");
// Comparing two boolean instances bool1 and bool2
// Use of compareTo() method
int comp = bool1.compareTo(bool2);
if (comp > 0)
System.out.println("bool1 is greater than bool2 as comp = "+comp);
if (comp == 0)
System.out.println("bool1 is equal to bool2 as comp = "+comp);
if (comp < 0)
System.out.println("bool1 is less than bool2 as comp = "+comp);
System.out.println("");
// HashCode value of the boolean object.
// use of hashCode() method
int h1 = bool1.hashCode();
int h2 = bool2.hashCode();
System.out.println("Hash Code value of bool1 : " + h1);
System.out.println("Hash Code value of bool2 : " + h2);
System.out.println("");
// String representation of the boolean object
// Use of toString() method.
String s1, s2;
s1 = bool1.toString();
s2 = bool2.toString();
System.out.println("String value of bool1 : " + s1);
System.out.println("String value of bool2 : " + s2);
}
}
Producción:
Boolean object - bool1 : true Boolean object - bool2 : false Primitive value of object i.e. bool3 : true Primitive value of object i.e. bool4 : false bool1 is greater than bool2 as comp = 1 Hash Code value of bool1 : 1231 Hash Code value of bool2 : 1237 String value of bool1 : true String value of bool2 : false
- getBoolean() : java.lang.Boolean.getBoolean(String arg) devuelve verdadero, si el valor ‘verdadero’ se asigna a la propiedad Sistema.
Para asignar cualquier valor a la propiedad, estamos usando el método setProperty() de la clase System.
Sintaxis:
public static boolean getBoolean(String arg) Parameters : arg - name of the property Returns : true : if 'true' value is assigned to the System property. false : if no such property exists or if exists then no value is assigned to it.
Implementación:
Java
// Java program illustrating getBoolean() method
import java.lang.*; // Using Boolean and System classes
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Use of getBoolean() to check whether
any value is assigned to Property - p1, p2 or not */
boolean b1 = Boolean.getBoolean("p1");
boolean b2 = Boolean.getBoolean("p2");
System.out.println("Bool Value of p1 : "+b1);
System.out.println("Bool Value of p2 : "+b2);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("Since, no value assigned to p1, p2, Bool value is false");
System.out.println("Assign value to p1,p2 using java.lang.System.setProperty()");
System.out.println("");
System.setProperty("p1","true");
System.setProperty("p2","Cool");
boolean b3 = Boolean.getBoolean("p1");
boolean b4 = Boolean.getBoolean("p2");
System.out.println("Bool Value of p1 : " + b3);
System.out.println("Bool Value of p2 : " + b4);
}
}
Producción:
Bool Value of p1 : false Bool Value of p2 : false Since, no value assigned to p1, p2, Bool value is false Assign value to p1,p2 using java.lang.System.setProperty() Bool Value of p1 : true Bool Value of p2 : false
- valueOf() : java.java.lang.Boolean.valueOf(boolean arg) devuelve el valor asignado a la variable booleana.
Si se asigna el valor verdadero, se devuelve verdadero, de lo contrario, falso.
Para asignar cualquier valor a la propiedad, estamos usando el método setProperty() de la clase System.
Sintaxis:
public static Boolean valueOf(boolean arg) Parameters : arg - boolean variable Returns : True : if true value is assigned to the boolean variable, else false
- parseBoolean() : java.lang.Boolean.parseBoolean(String s) devuelve el valor verdadero o falso del argumento String (tomado por él como booleano).
Es un método que no distingue entre mayúsculas y minúsculas.
Sintaxis:
public static boolean parseBoolean(String arg) Parameters : arg - String argument taken as Boolean Returns : Boolean value of a String argument
Implementación:
Java
// Java program illustrating parseBoolean() and valueOf() method
import java.lang.*;
public class NewClass
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
boolean b1 = false;
boolean b2 = true;
// Use of valueOf() method
boolean val1 = Boolean.valueOf(b1);
boolean val2 = Boolean.valueOf(b2);
System.out.println("Value of b1 : "+ val1);
System.out.println("Value of b2 : " +val2);
System.out.println("");
// Use of parseBoolean() method
String st1, st2, st3;
st1 = "True";
st2 = "yes";
st3 = "true"; // Case insensitive
boolean p1 = Boolean.parseBoolean(st1);
boolean p2 = Boolean.parseBoolean(st2);
boolean p3 = Boolean.parseBoolean(st3);
System.out.println("Value of String st1 as Boolean : "+p1);
System.out.println("Value of String st2 as Boolean : "+p2);
System.out.println("Value of String st3 as Boolean : "+p3);
}
}
Producción:
Value of b1 : false Value of b2 : true Value of String st1 as Boolean : true Value of String st2 as Boolean : false Value of String st3 as Boolean : true
Este artículo es aportado por. Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA