Dado un entero N y una array 2D cost[][3] , donde cost[i][0] , cost[i][1] y cost[i][2] es el costo de pintar i -ésima casa con colores rojo , azul y verde respectivamente, la tarea es encontrar el costo mínimo para pintar todas las casas de modo que no haya dos casas adyacentes del mismo color.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 3, costo[][3] = {{14, 2, 11}, {11, 14, 5}, {14, 3, 10}}
Salida: 10
Explicación:
Pinte la casa 0 de azul. Costo = 2. Pintar la casa 1 de verde. Costo = 5. Pintar la casa 2 de azul. Costo = 3.
Por lo tanto, el costo total = 2 + 5 + 3 = 10.Entrada: N = 2, costo[][3] = {{1, 2, 3}, {1, 4, 6}}
Salida: 3
Enfoque ingenuo: el enfoque más simple para resolver el problema dado es generar todas las formas posibles de colorear todas las casas con los colores rojo , azul y verde y encontrar el costo mínimo entre todas las combinaciones posibles de modo que no haya dos casas adyacentes que tengan el mismo colores.
Complejidad de Tiempo: (3 N )
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
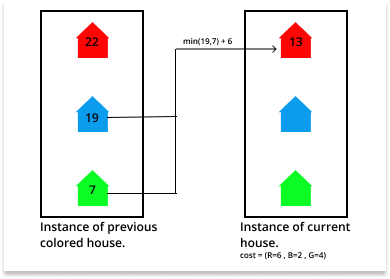
Enfoque eficiente: el enfoque anterior se puede optimizar mediante el uso de la programación dinámica , ya que hay subproblemas superpuestos que se pueden almacenar para minimizar la cantidad de llamadas recursivas . La idea es encontrar el costo mínimo de pintar la casa actual de cualquier color a partir del costo mínimo de los otros dos colores de casas coloreadas anteriormente . Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema dado:
Siga los pasos a continuación para resolver el problema:
- Cree una array 2D dp[][3] auxiliar para almacenar el costo mínimo de las casas previamente coloreadas.
- Inicialice dp[0][0] , dp[0][1] y dp[0][2] como el costo de cost[i][0] , cost[i][1] y cost[i] [2] respectivamente.
- Recorra la array dada cost[][3] sobre el rango [1, N] y actualice el costo de pintar la casa actual con los colores rojo , azul y verde con el mínimo del costo de otros dos colores en dp[i][ 0] , dp[i][1] y dp[i][2] respectivamente.
- Después de completar los pasos anteriores, imprima el mínimo de dp[N – 1][0] , dp[N – 1][1] y dp[N – 1][2] como el costo mínimo de pintar todas las casas con diferentes colores adyacentes.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the minimum cost of
// coloring the houses such that no two
// adjacent houses has the same color
int minCost(vector<vector<int> >& costs,
int N)
{
// Corner Case
if (N == 0)
return 0;
// Auxiliary 2D dp array
vector<vector<int> > dp(
N, vector<int>(3, 0));
// Base Case
dp[0][0] = costs[0][0];
dp[0][1] = costs[0][1];
dp[0][2] = costs[0][2];
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
// If current house is colored
// with red the take min cost of
// previous houses colored with
// (blue and green)
dp[i][0] = min(dp[i - 1][1],
dp[i - 1][2])
+ costs[i][0];
// If current house is colored
// with blue the take min cost of
// previous houses colored with
// (red and green)
dp[i][1] = min(dp[i - 1][0],
dp[i - 1][2])
+ costs[i][1];
// If current house is colored
// with green the take min cost of
// previous houses colored with
// (red and blue)
dp[i][2] = min(dp[i - 1][0],
dp[i - 1][1])
+ costs[i][2];
}
// Print the min cost of the
// last painted house
cout << min(dp[N - 1][0],
min(dp[N - 1][1],
dp[N - 1][2]));
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
vector<vector<int> > costs{ { 14, 2, 11 },
{ 11, 14, 5 },
{ 14, 3, 10 } };
int N = costs.size();
// Function Call
minCost(costs, N);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Function to find the minimum cost of
// coloring the houses such that no two
// adjacent houses has the same color
static void minCost(int costs[][], int N)
{
// Corner Case
if (N == 0)
return;
// Auxiliary 2D dp array
int dp[][] = new int[N][3];
// Base Case
dp[0][0] = costs[0][0];
dp[0][1] = costs[0][1];
dp[0][2] = costs[0][2];
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
// If current house is colored
// with red the take min cost of
// previous houses colored with
// (blue and green)
dp[i][0] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][2])
+ costs[i][0];
// If current house is colored
// with blue the take min cost of
// previous houses colored with
// (red and green)
dp[i][1] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][2])
+ costs[i][1];
// If current house is colored
// with green the take min cost of
// previous houses colored with
// (red and blue)
dp[i][2] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1])
+ costs[i][2];
}
// Print the min cost of the
// last painted house
System.out.println(
Math.min(dp[N - 1][0],
Math.min(dp[N - 1][1], dp[N - 1][2])));
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int costs[][] = { { 14, 2, 11 },
{ 11, 14, 5 },
{ 14, 3, 10 } };
int N = costs.length;
// Function Call
minCost(costs, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Kingash.
Python3
# Python 3 program for the above approach # Function to find the minimum cost of # coloring the houses such that no two # adjacent houses has the same color def minCost(costs, N): # Corner Case if (N == 0): return 0 # Auxiliary 2D dp array dp = [[0 for i in range(3)] for j in range(3)] # Base Case dp[0][0] = costs[0][0] dp[0][1] = costs[0][1] dp[0][2] = costs[0][2] for i in range(1, N, 1): # If current house is colored # with red the take min cost of # previous houses colored with # (blue and green) dp[i][0] = min(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][2]) + costs[i][0] # If current house is colored # with blue the take min cost of # previous houses colored with # (red and green) dp[i][1] = min(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][2]) + costs[i][1] # If current house is colored # with green the take min cost of # previous houses colored with # (red and blue) dp[i][2] = min(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1]) + costs[i][2] # Print the min cost of the # last painted house print(min(dp[N - 1][0], min(dp[N - 1][1],dp[N - 1][2]))) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': costs = [[14, 2, 11], [11, 14, 5], [14, 3, 10]] N = len(costs) # Function Call minCost(costs, N) # This code is contributed by ipg2016107.
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Function to find the minimum cost of
// coloring the houses such that no two
// adjacent houses has the same color
static int minCost(List<List<int>>costs,
int N)
{
// Corner Case
if (N == 0)
return 0;
// Auxiliary 2D dp array
List<int> temp = new List<int>();
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
temp.Add(0);
List<List<int>> dp = new List<List<int>>();
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
dp.Add(temp);
// Base Case
dp[0][0] = costs[0][0];
dp[0][1] = costs[0][1];
dp[0][2] = costs[0][2];
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
// If current house is colored
// with red the take min cost of
// previous houses colored with
// (blue and green)
dp[i][0] = Math.Min(dp[i - 1][1],
dp[i - 1][2])
+ costs[i][0];
// If current house is colored
// with blue the take min cost of
// previous houses colored with
// (red and green)
dp[i][1] = Math.Min(dp[i - 1][0],
dp[i - 1][2])
+ costs[i][1];
// If current house is colored
// with green the take min cost of
// previous houses colored with
// (red and blue)
dp[i][2] = Math.Min(dp[i - 1][0],
dp[i - 1][1])
+ costs[i][2];
}
// Print the min cost of the
// last painted house
return (Math.Min(dp[N - 1][0], Math.Min(dp[N - 1][1],dp[N - 1][2])))-11;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main()
{
List<List<int>>costs = new List<List<int>>();
costs.Add(new List<int>(){14, 2, 11});
costs.Add(new List<int>(){11, 14, 5 });
costs.Add(new List<int>(){14, 3, 10 });
int N = 3;
// Function Call
Console.WriteLine((int)(minCost(costs, N)));
}
}
// This code is contributed by bgangwar59.
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript program for the above approach
// Function to find the minimum cost of
// coloring the houses such that no two
// adjacent houses has the same color
function minCost(costs, N)
{
// Corner Case
if (N == 0)
return 0;
// Auxiliary 2D dp array
let dp = new Array(N);
for(let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
dp[i] = new Array(3);
for(let j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// Base Case
dp[0][0] = costs[0][0];
dp[0][1] = costs[0][1];
dp[0][2] = costs[0][2];
for(let i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
// If current house is colored
// with red the take min cost of
// previous houses colored with
// (blue and green)
dp[i][0] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][2]) + costs[i][0];
// If current house is colored
// with blue the take min cost of
// previous houses colored with
// (red and green)
dp[i][1] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][2]) + costs[i][1];
// If current house is colored
// with green the take min cost of
// previous houses colored with
// (red and blue)
dp[i][2] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1]) + costs[i][2];
}
// Print the min cost of the
// last painted house
document.write(Math.min(dp[N - 1][0], Math.min(dp[N - 1][1],dp[N - 1][2])));
}
let costs = [[14, 2, 11],
[11, 14, 5],
[14, 3, 10]];
let N = costs.length;
// Function Call
minCost(costs, N);
// This code is contributed by decode2207.
</script>
10
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por rutvikchandla3 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA