El muestreo es el método en el que se puede tomar un subconjunto (Muestra) de los datos proporcionados e investigar en la muestra sin investigar cada elemento individual de los datos. Por ejemplo, supongamos que en una universidad, alguien quiere verificar la altura promedio de los estudiantes que estudian en la universidad. Una forma es recopilar datos de todos los estudiantes y los calculará, pero esta tarea lleva mucho tiempo. Por lo tanto, se utiliza el muestreo. Entonces, la solución es que durante el recreo, elija al azar a los estudiantes de la cantina y mida su altura y calculará la altura promedio de ese subconjunto de estudiantes.

Tipos de muestreo:
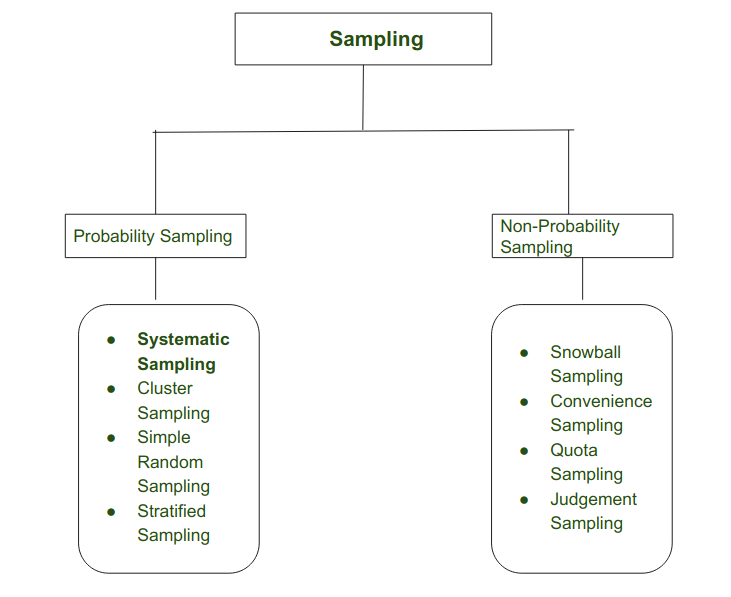
Muestreo
Muestreo Sistemático
El muestreo sistemático se define como el tipo de muestreo de probabilidad en el que un investigador puede investigar datos específicos de un gran conjunto de datos. Los datos objetivo se eligen seleccionando un punto de inicio aleatorio y, después de cierto intervalo, se elige el siguiente elemento para la muestra. En este se extrae un pequeño subconjunto (muestra) de grandes datos.
Supongamos que el tamaño de los datos es D y N será el tamaño de la muestra que queremos seleccionar. Entonces, de acuerdo con el muestreo sistemático:
Intervalo = (D/N)
Supongamos (D/N) = J
Entonces, cuando elegimos el primer elemento aleatorio E de Data, el siguiente elemento para Sample sería (E+J)
Ejemplo: tamaño total de los datos = 50 (1 a 50)
Queremos elementos en Muestra = 5
Intervalo = 50/5 = 10 .
Significa que en una muestra queremos espacios de 10 elementos sistemáticamente.
Supongamos que elijo al azar el elemento primero Elemento de muestra = 5
Entonces el próximo sería 5+10 = 15
15+10= 25
25+ 10 =35
35+10 = 45
Asi que,
Muestra = { 5,15,25,35,45 }
Esquemáticamente,

Acercarse:
- Toma datos.
- Extraiga muestras sistemáticas de grandes datos.
- Imprima el promedio de datos de muestra.
Programa:
Python3
# Import in order to use inbuilt functions
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Define total number of students
number_of_students = 15
# Create data dictionary
data = {'Id': np.arange(1, number_of_students+1).tolist(),
'height': [159, 171, 158, 162, 162, 177, 160, 175,
168, 171, 178, 178, 173, 177, 164]}
# Transform dictionary into a data frame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
display(df)
# Define systematic sampling function
def systematic_sampling(df, step):
indexes = np.arange(0, len(df), step=step)
systematic_sample = df.iloc[indexes]
return systematic_sample
# Obtain a systematic sample and save it in a new variable
systematic_sample = systematic_sampling(df, 3)
# View sampled data frame
display(systematic_sample)
Producción:


Ejemplo: Promedio de impresión de datos de muestra
Python3
# Import in order to use inbuilt functions
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Define total number of students
number_of_students = 15
# Create data dictionary
data = {'Id': np.arange(1, number_of_students+1).tolist(),
'height': [159, 171, 158, 162, 162, 177, 160, 175,
168, 171, 178, 178, 173, 177, 164]}
# Transform dictionary into a data frame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Define systematic sampling function
def systematic_sampling(df, step):
indexes = np.arange(0, len(df), step=step)
systematic_sample = df.iloc[indexes]
return systematic_sample
# Obtain a systematic sample and save it in a new variable
systematic_sample = systematic_sampling(df, 3)
# View sampled data frame
display(systematic_sample)
# Empty Print Statement for new line
print()
# Save the sample data in a separate variable
systematic_data = round(systematic_sample['height'].mean())
print("Average Height in cm: ", systematic_data)
Producción:

Tipos de muestreo sistemático
El muestreo sistemático es de tres tipos, como se muestra a continuación:
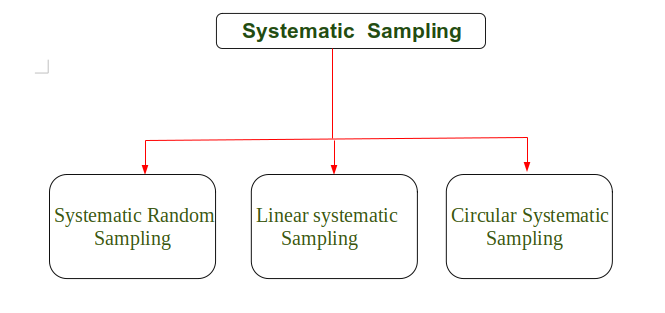
Tipos de muestreo sistemático
Muestreo aleatorio sistemático:
En el muestreo aleatorio sistemático, se elige un punto de inicio aleatorio y, a partir de ese punto de inicio aleatorio, se aplica el muestreo sistemático.
Acercarse:
- Obtener datos
- Elija un punto de partida aleatorio
- Aplicar un enfoque sistemático a los datos.
- Realizar operaciones según lo previsto
Ejemplo:
Python3
# Import in order to use inbuilt functions
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import random
# Define total number of house
number_of_house = 30
# Create data dictionary
data = {'house_number': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13,
14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30],
'number_of_children': [2, 2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 4, 1, 3, 5, 4, 3, 5,
3, 2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 3, 4, 5, 2, 2, 2,
2, 3, 2, 1]}
# Transform dictionary into a data frame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Defining Size of Systematic Sample
size_of_systematic_sample = 6
# Defining Interval(gap) in order to get required data.
interval = (number_of_house // size_of_systematic_sample)
# Choosing Random Number
random_number = random.randint(1, 30)
# Define systematic sampling function
def systematic_sampling(df, step):
indexes = np.arange(random_number, len(df), step=step)
systematic_sample = df.iloc[indexes]
return systematic_sample
# Obtain a systematic sample and save it in a new variable
systematic_sample = systematic_sampling(df, interval)
# View sampled data frame
display(systematic_sample)
# Empty Print Statement for new line
print()
# Save the sample data in a separate variable
systematic_data = round(systematic_sample['number_of_children'].mean())
# Printing Average Number of Children
print("Average Number Of Childrens in Locality: ", systematic_data)
Producción:

Muestreo Sistemático Lineal:
El muestreo sistemático lineal es un tipo de muestreo sistemático en el que la muestra se selecciona mediante un enfoque lineal. Enfoque lineal en el sentido de que después de un intervalo particular, la muestra se selecciona de los datos grandes y luego se realizan operaciones en la muestra seleccionada.
Los elementos se eligen entre el rango número_aleatorio_inicial a último_elemento -1.
Acercarse:
- Obtener datos
- Seleccionar datos del conjunto de datos después de un intervalo particular
- Realizar operaciones según lo previsto
Ejemplo:
Python3
# Import in order to use inbuilt functions
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import random
# Define total number of boxes
number_of_boxes = 30
# Create data dictionary
data = {'Box_Number': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14,
15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26,
27, 28, 29, 30],
'Defective_Bulbs': [2, 2, 1, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 3, 5, 4, 3, 5, 3,
0, 1, 2, 0, 4, 5, 3, 4, 5, 2, 0, 3, 2, 0,
5, 4]}
# Transform dictionary into a data frame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Size of Systematic Sample
size_systematic_sample = 5
# Interval (Gap) taken
interval = (number_of_boxes // size_systematic_sample)
# Choosing Random Starting Point
random_number = random.randint(1, 30)
# Define systematic sampling function
def systematic_sampling(df, step):
indexes = np.arange(random_number, len(df)-1, step=step)
systematic_sample = df.iloc[indexes]
return systematic_sample
# Obtain a systematic sample and save it in a new variable
systematic_sample = systematic_sampling(df, interval)
# View sampled data frame
display(systematic_sample)
# Empty Print Statement for new line
print()
# Save the sample data in a separate variable
systematic_data = round(systematic_sample['Defective_Bulbs'].mean())
# Printing Average Number of Defective Bulbs
print("Average Number Of Defective Bulbs: ", systematic_data)
Producción:

Muestreo Sistemático Circular
En el muestreo sistemático circular, una muestra comienza nuevamente desde el mismo punto después de finalizar. Básicamente, mientras se seleccionan las muestras sistemáticamente y cuando se alcanza el elemento final, una vez más, la selección de la muestra comenzará desde el principio hasta que se seleccionen todos los elementos de la muestra. Significa que las operaciones se realizan sobre todos los datos que se seleccionan mediante muestreo sistemático circular.
Acercarse:
- Obtener datos
- Seleccionar muestras sistemáticamente
- Una vez que se alcanza el final, reinicie
- Realizar operaciones según lo previsto
Programa:
Python3
# Import in order to use inbuilt functions
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import random
# Define total number of house
number_of_house = 30
# Create data dictionary
data = {'house_number': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13,
14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23,
24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30],
'number_of_Adults': [2, 2, 5, 3, 2, 8, 4, 7, 8, 5, 4, 9, 5,
4, 2, 3, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 4, 5, 4, 2, 6,
2, 3, 2, 2]}
# Transform dictionary into a data frame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Defining Size of Systematic Sample
size_of_systematic_sample = 6
# Defining Interval(gap) in order to get required data.
interval = (number_of_house // size_of_systematic_sample)
# Define systematic sampling function
def systematic_sampling(df, step):
indexes = np.arange(0, len(df), step=step)
systematic_sample = df.iloc[indexes]
return systematic_sample
# Obtain a systematic sample and save it in a new variable
systematic_sample = systematic_sampling(df, interval)
# View sampled data frame
display(systematic_sample)
# Empty Print Statement for new line
print()
# Save the sample data in a separate variable
systematic_data = round(systematic_sample['number_of_Adults'].mean())
# Printing Average Number of Children
print("Average Number Of Adults in Locality: ", systematic_data)
Producción:

Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por jagroopofficial y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA