Dado un grafo no dirigido con N vértices y M aristas, la tarea es imprimir todos los Nodes del grafo dado cuyo grado sea un Número Primo .
Ejemplos:
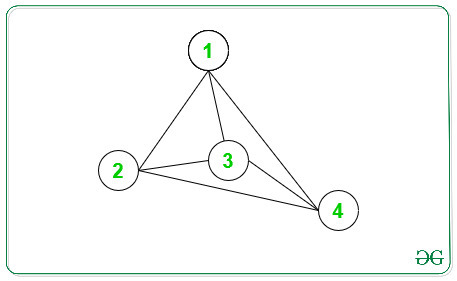
Entrada: N = 4, arr[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 }, { 1, 4 }, { 2, 3 }, { 2, 4 }, { 3, 4 } }
Salida : 1 2 3 4
Explicación:
A continuación se muestra el gráfico de la información anterior:
El grado del Node según el gráfico anterior es:
Node -> Grado
1 -> 3
2 -> 3
3 -> 3
4 -> 3
Por lo tanto, los Nodes con grado primo son 1 2 3 4
Entrada: N = 5, arr [][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 }, { 2, 4 }, { 2, 5 } }
Salida: 1
Acercarse:
- Usa la criba de Eratóstenes para calcular los números primos hasta el 10 5 .
- Para cada vértice, el grado se puede calcular por la longitud de la Lista de Adyacencia del gráfico dado en el vértice correspondiente.
- Imprime aquellos vértices de la gráfica dada cuyo grado sea un Número Primo .
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n = 10005;
// To store Prime Numbers
vector<bool> Prime(n + 1, true);
// Function to find the prime numbers
// till 10^5
void SieveOfEratosthenes()
{
int i, j;
Prime[0] = Prime[1] = false;
for (i = 2; i * i <= 10005; i++) {
// Traverse all multiple of i
// and make it false
if (Prime[i]) {
for (j = 2 * i; j < 10005; j += i) {
Prime[j] = false;
}
}
}
}
// Function to print the nodes having
// prime degree
void primeDegreeNodes(int N, int M,
int edges[][2])
{
// To store Adjacency List of
// a Graph
vector<int> Adj[N + 1];
// Make Adjacency List
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int x = edges[i][0];
int y = edges[i][1];
Adj[x].push_back(y);
Adj[y].push_back(x);
}
// To precompute prime numbers
// till 10^5
SieveOfEratosthenes();
// Traverse each vertex
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
// Find size of Adjacency List
int x = Adj[i].size();
// If length of Adj[i] is Prime
// then print it
if (Prime[x])
cout << i << ' ';
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Vertices and Edges
int N = 4, M = 6;
// Edges
int edges[M][2] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 },
{ 1, 4 }, { 2, 3 },
{ 2, 4 }, { 3, 4 } };
// Function Call
primeDegreeNodes(N, M, edges);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int n = 10005;
// To store Prime Numbers
static boolean []Prime = new boolean[n + 1];
// Function to find the prime numbers
// till 10^5
static void SieveOfEratosthenes()
{
int i, j;
Prime[0] = Prime[1] = false;
for (i = 2; i * i <= 10005; i++)
{
// Traverse all multiple of i
// and make it false
if (Prime[i])
{
for (j = 2 * i; j < 10005; j += i)
{
Prime[j] = false;
}
}
}
}
// Function to print the nodes having
// prime degree
static void primeDegreeNodes(int N, int M,
int edges[][])
{
// To store Adjacency List of
// a Graph
Vector<Integer> []Adj = new Vector[N + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < Adj.length; i++)
Adj[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
// Make Adjacency List
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
int x = edges[i][0];
int y = edges[i][1];
Adj[x].add(y);
Adj[y].add(x);
}
// To precompute prime numbers
// till 10^5
SieveOfEratosthenes();
// Traverse each vertex
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
// Find size of Adjacency List
int x = Adj[i].size();
// If length of Adj[i] is Prime
// then print it
if (Prime[x])
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Vertices and Edges
int N = 4, M = 6;
// Edges
int edges[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 },
{ 1, 4 }, { 2, 3 },
{ 2, 4 }, { 3, 4 } };
Arrays.fill(Prime, true);
// Function Call
primeDegreeNodes(N, M, edges);
}
}
// This code is contributed by sapnasingh4991
Python3
# Python3 implementation of # the above approach n = 10005; # To store Prime Numbers Prime = [True for i in range(n + 1)] # Function to find # the prime numbers # till 10^5 def SieveOfEratosthenes(): i = 2 Prime[0] = Prime[1] = False; while i * i <= 10005: # Traverse all multiple # of i and make it false if (Prime[i]): for j in range(2 * i, 10005): Prime[j] = False i += 1 # Function to print the # nodes having prime degree def primeDegreeNodes(N, M, edges): # To store Adjacency # List of a Graph Adj = [[] for i in range(N + 1)]; # Make Adjacency List for i in range(M): x = edges[i][0]; y = edges[i][1]; Adj[x].append(y); Adj[y].append(x); # To precompute prime # numbers till 10^5 SieveOfEratosthenes(); # Traverse each vertex for i in range(N + 1): # Find size of Adjacency List x = len(Adj[i]); # If length of Adj[i] is Prime # then print it if (Prime[x]): print(i, end = ' ') # Driver code if __name__ == "__main__": # Vertices and Edges N = 4 M = 6 # Edges edges = [[1, 2], [1, 3], [1, 4], [2, 3], [2, 4], [3, 4]]; # Function Call primeDegreeNodes(N, M, edges); # This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int n = 10005;
// To store Prime Numbers
static bool []Prime = new bool[n + 1];
// Function to find the prime numbers
// till 10^5
static void SieveOfEratosthenes()
{
int i, j;
Prime[0] = Prime[1] = false;
for(i = 2; i * i <= 10005; i++)
{
// Traverse all multiple of i
// and make it false
if (Prime[i])
{
for(j = 2 * i; j < 10005; j += i)
{
Prime[j] = false;
}
}
}
}
// Function to print the nodes having
// prime degree
static void primeDegreeNodes(int N, int M,
int [,]edges)
{
// To store Adjacency List of
// a Graph
List<int> []Adj = new List<int>[N + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < Adj.Length; i++)
Adj[i] = new List<int>();
// Make Adjacency List
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
int x = edges[i, 0];
int y = edges[i, 1];
Adj[x].Add(y);
Adj[y].Add(x);
}
// To precompute prime numbers
// till 10^5
SieveOfEratosthenes();
// Traverse each vertex
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
// Find size of Adjacency List
int x = Adj[i].Count;
// If length of Adj[i] is Prime
// then print it
if (Prime[x])
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Vertices and Edges
int N = 4, M = 6;
// Edges
int [,]edges = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 },
{ 1, 4 }, { 2, 3 },
{ 2, 4 }, { 3, 4 } };
for(int i = 0; i < Prime.Length; i++)
Prime[i] = true;
// Function Call
primeDegreeNodes(N, M, edges);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript implementation of the approach
let n = 10005;
// To store Prime Numbers
let Prime = new Array(n + 1).fill(true);
// Function to find the prime numbers
// till 10^5
function SieveOfEratosthenes()
{
let i, j;
Prime[0] = Prime[1] = false;
for (i = 2; i * i <= 10005; i++) {
// Traverse all multiple of i
// and make it false
if (Prime[i]) {
for (j = 2 * i; j < 10005; j += i) {
Prime[j] = false;
}
}
}
}
// Function to print the nodes having
// prime degree
function primeDegreeNodes(N, M, edges)
{
// To store Adjacency List of
// a Graph
let Adj = new Array();
for(let i = 0; i < N + 1; i++){
Adj.push(new Array())
}
// Make Adjacency List
for (let i = 0; i < M; i++) {
let x = edges[i][0];
let y = edges[i][1];
Adj[x].push(y);
Adj[y].push(x);
}
// To precompute prime numbers
// till 10^5
SieveOfEratosthenes();
// Traverse each vertex
for (let i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
// Find size of Adjacency List
let x = Adj[i].length;
// If length of Adj[i] is Prime
// then print it
if (Prime[x])
document.write(i + ' ');
}
}
// Driver code
// Vertices and Edges
let N = 4, M = 6;
// Edges
let edges = [ [ 1, 2 ], [ 1, 3 ],
[ 1, 4 ], [ 2, 3 ],
[ 2, 4 ], [ 3, 4 ] ];
// Function Call
primeDegreeNodes(N, M, edges);
// This code is contributed by gfgking
</script>
1 2 3 4
Complejidad temporal: O(N + M) , donde N es el número de vértices y M es el número de aristas.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por muskan_garg y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA