Dado un árbol binario con N Nodes y un número entero K , la tarea es imprimir los Nodes del K -ésimo nivel de un árbol binario sin duplicados.
Ejemplos:
Input:
60 --- Level 0
/ \
50 30 --- Level 1
/ \ /
80 10 40 --- Level 2
K = 1
Output: 30 50
Input:
50 --- Level 0
/ \
60 70 --- Level 1
/ \ / \
90 40 40 20 --- Level 2
K = 2
Output: 20 40 90
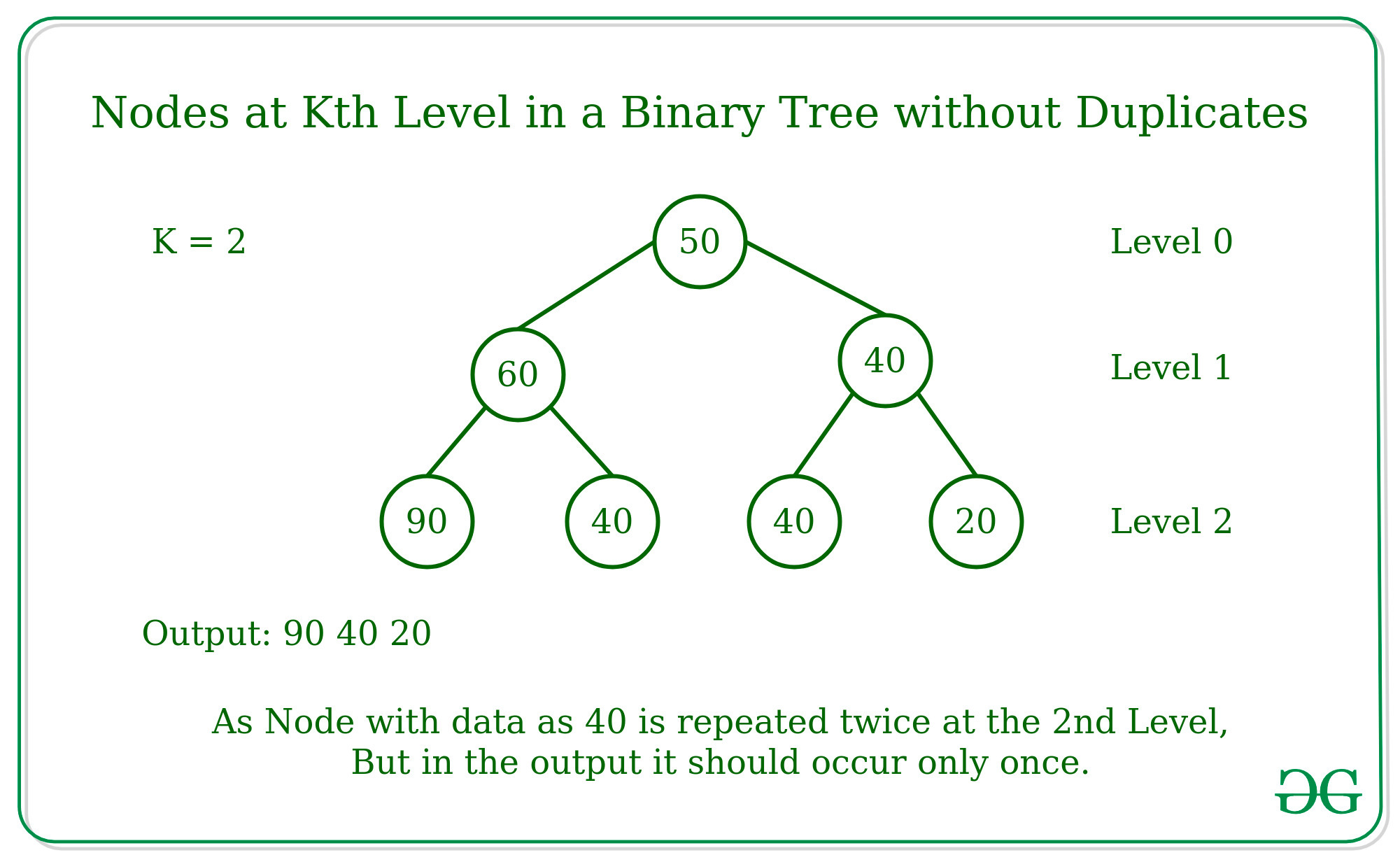
Enfoque: la idea es atravesar el árbol binario utilizando el recorrido de orden de niveles con la ayuda de la cola y, si el nivel del recorrido es K, almacenar todos los Nodes de ese nivel en un conjunto de modo que no haya Nodes duplicados en ese nivel. .
Algoritmo:
- Inicialice una cola vacía para almacenar los Nodes en un nivel.
- Ponga en cola el Node raíz del árbol binario en la cola.
- Inicialice el nivel como 0, ya que se supone que el primer nivel del árbol es 0 aquí.
- Inicialice la bandera como 0 para comprobar si se alcanza o no el nivel K.
- Iterar usando un bucle while hasta que la cola no esté vacía.
- Encuentre el tamaño de la cola y guárdelo en un tamaño variable para visitar solo los Nodes de un nivel actual.
- Iterar con otro bucle while hasta que la variable de tamaño no sea 0
- Quitar un Node de la cola y poner en cola sus hijos izquierdo y derecho en la cola.
- Si el nivel actual es igual a K, agregue los datos del Node al conjunto y también establezca la bandera .
- Si la bandera está configurada, rompa el bucle para no visitar más niveles; de lo contrario, incremente el nivel actual en 1.
- Imprime los elementos del conjunto con la ayuda de iterator .
Explicación con ejemplo:
Binary Tree -
50 --- Level 0
/ \
60 70 --- Level 1
/ \ / \
90 40 40 20 --- Level 2
K = 2
Initialize Queue and Set and append Root in queue
Step 1:
Queue = [50], Set = {}, Level = 0
As current Level is not equal to K,
Deque nodes from the queue and enqueue its child
Step 2:
Queue = [60, 70], Set = {}, Level = 1
As current level is not equal to K
Deque nodes one by one from the queue and enqueue its child
Step 3:
Queue = [90, 40, 40, 20], Set = {}, Level = 2
As the current level is equal to K
Deque all the nodes from the queue and add to the set
Set = {90, 40, 20}
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque:
C++
// C++ implementation to print the
// nodes of Kth Level without duplicates
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Structure of Binary Tree node
struct node {
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
// Function to create new
// Binary Tree node
struct node* newNode(int data)
{
struct node* temp = new struct node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = nullptr;
temp->right = nullptr;
return temp;
};
// Function to print the nodes
// of Kth Level without duplicates
void nodesAtKthLevel(struct node* root,
int k){
// Condition to check if current
// node is None
if (root == nullptr)
return;
// Create Queue
queue<struct node*> que;
// Enqueue the root node
que.push(root);
// Create a set
set<int> s;
// Level to track
// the current level
int level = 0;
int flag = 0;
// Iterate the queue till its not empty
while (!que.empty()) {
// Calculate the number of nodes
// in the current level
int size = que.size();
// Process each node of the current
// level and enqueue their left
// and right child to the queue
while (size--) {
struct node* ptr = que.front();
que.pop();
// If the current level matches the
// required level then add into set
if (level == k) {
// Flag initialized to 1
flag = 1;
// Inserting node data in set
s.insert(ptr->data);
}
else {
// Traverse to the left child
if (ptr->left)
que.push(ptr->left);
// Traverse to the right child
if (ptr->right)
que.push(ptr->right);
}
}
// Increment the variable level
// by 1 for each level
level++;
// Break out from the loop
// if the Kth Level is reached
if (flag == 1)
break;
}
set<int>::iterator it;
for (it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct node* root = new struct node;
// Tree Construction
root = newNode(60);
root->left = newNode(20);
root->right = newNode(30);
root->left->left = newNode(80);
root->left->right = newNode(10);
root->right->left = newNode(40);
int level = 1;
nodesAtKthLevel(root, level);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation to print the
// nodes of Kth Level without duplicates
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Structure of Binary Tree node
static class node {
int data;
node left;
node right;
};
// Function to create new
// Binary Tree node
static node newNode(int data)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
};
// Function to print the nodes
// of Kth Level without duplicates
static void nodesAtKthLevel(node root,
int k){
// Condition to check if current
// node is None
if (root == null)
return;
// Create Queue
Queue<node> que = new LinkedList<node>();
// Enqueue the root node
que.add(root);
// Create a set
HashSet<Integer> s = new HashSet<Integer>();
// Level to track
// the current level
int level = 0;
int flag = 0;
// Iterate the queue till its not empty
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
// Calculate the number of nodes
// in the current level
int size = que.size();
// Process each node of the current
// level and enqueue their left
// and right child to the queue
while (size-- > 0) {
node ptr = que.peek();
que.remove();
// If the current level matches the
// required level then add into set
if (level == k) {
// Flag initialized to 1
flag = 1;
// Inserting node data in set
s.add(ptr.data);
}
else {
// Traverse to the left child
if (ptr.left!=null)
que.add(ptr.left);
// Traverse to the right child
if (ptr.right!=null)
que.add(ptr.right);
}
}
// Increment the variable level
// by 1 for each level
level++;
// Break out from the loop
// if the Kth Level is reached
if (flag == 1)
break;
}
for (int it : s) {
System.out.print(it+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
node root = new node();
// Tree Construction
root = newNode(60);
root.left = newNode(20);
root.right = newNode(30);
root.left.left = newNode(80);
root.left.right = newNode(10);
root.right.left = newNode(40);
int level = 1;
nodesAtKthLevel(root, level);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992
Python3
# Python3 implementation to print the # nodes of Kth Level without duplicates from collections import deque # A binary tree node has key, pointer to # left child and a pointer to right child class Node: def __init__(self, key): self.data = key self.left = None self.right = None # Function to print the nodes # of Kth Level without duplicates def nodesAtKthLevel(root: Node, k: int): # Condition to check if current # node is None if root is None: return # Create Queue que = deque() # Enqueue the root node que.append(root) # Create a set s = set() # Level to track # the current level level = 0 flag = 0 # Iterate the queue till its not empty while que: # Calculate the number of nodes # in the current level size = len(que) # Process each node of the current # level and enqueue their left # and right child to the queue while size: ptr = que[0] que.popleft() # If the current level matches the # required level then add into set if level == k: # Flag initialized to 1 flag = 1 # Inserting node data in set s.add(ptr.data) else: # Traverse to the left child if ptr.left: que.append(ptr.left) # Traverse to the right child if ptr.right: que.append(ptr.right) size -= 1 # Increment the variable level # by 1 for each level level += 1 # Break out from the loop # if the Kth Level is reached if flag == 1: break for it in s: print(it, end = " ") print() # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": # Tree Construction root = Node(60) root.left = Node(20) root.right = Node(30) root.left.left = Node(80) root.left.right = Node(10) root.right.left = Node(40) level = 1 nodesAtKthLevel(root, level) # This code is contributed by sanjeev2552
C#
// C# implementation to print the
// nodes of Kth Level without duplicates
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Structure of Binary Tree node
class node {
public int data;
public node left;
public node right;
};
// Function to create new
// Binary Tree node
static node newNode(int data)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to print the nodes
// of Kth Level without duplicates
static void nodesAtKthLevel(node root,
int k){
// Condition to check if current
// node is None
if (root == null)
return;
// Create Queue
List<node> que = new List<node>();
// Enqueue the root node
que.Add(root);
// Create a set
HashSet<int> s = new HashSet<int>();
// Level to track
// the current level
int level = 0;
int flag = 0;
// Iterate the queue till its not empty
while (que.Count != 0) {
// Calculate the number of nodes
// in the current level
int size = que.Count;
// Process each node of the current
// level and enqueue their left
// and right child to the queue
while (size-- > 0) {
node ptr = que[0];
que.RemoveAt(0);
// If the current level matches the
// required level then add into set
if (level == k) {
// Flag initialized to 1
flag = 1;
// Inserting node data in set
s.Add(ptr.data);
}
else {
// Traverse to the left child
if (ptr.left != null)
que.Add(ptr.left);
// Traverse to the right child
if (ptr.right != null)
que.Add(ptr.right);
}
}
// Increment the variable level
// by 1 for each level
level++;
// Break out from the loop
// if the Kth Level is reached
if (flag == 1)
break;
}
foreach (int it in s) {
Console.Write(it+ " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
node root = new node();
// Tree Construction
root = newNode(60);
root.left = newNode(20);
root.right = newNode(30);
root.left.left = newNode(80);
root.left.right = newNode(10);
root.right.left = newNode(40);
int level = 1;
nodesAtKthLevel(root, level);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript implementation to print the
// nodes of Kth Level without duplicates
// Structure of Binary Tree node
class node {
constructor()
{
this.data = 0;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
};
// Function to create new
// Binary Tree node
function newNode(data)
{
var temp = new node();
temp.data = data;
temp.left = null;
temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to print the nodes
// of Kth Level without duplicates
function nodesAtKthLevel(root, k){
// Condition to check if current
// node is None
if (root == null)
return;
// Create Queue
var que = [];
// Enqueue the root node
que.push(root);
// Create a set
var s = new Set();
// Level to track
// the current level
var level = 0;
var flag = 0;
// Iterate the queue till its not empty
while (que.length != 0) {
// Calculate the number of nodes
// in the current level
var size = que.length;
// Process each node of the current
// level and enqueue their left
// and right child to the queue
while (size-- > 0) {
var ptr = que[0];
que.shift();
// If the current level matches the
// required level then add into set
if (level == k) {
// Flag initialized to 1
flag = 1;
// Inserting node data in set
s.add(ptr.data);
}
else {
// Traverse to the left child
if (ptr.left != null)
que.push(ptr.left);
// Traverse to the right child
if (ptr.right != null)
que.push(ptr.right);
}
}
// Increment the variable level
// by 1 for each level
level++;
// Break out from the loop
// if the Kth Level is reached
if (flag == 1)
break;
}
for(var it of s) {
document.write(it+ " ");
}
document.write("<br>");
}
// Driver code
var root = new node();
// Tree Construction
root = newNode(60);
root.left = newNode(20);
root.right = newNode(30);
root.left.left = newNode(80);
root.left.right = newNode(10);
root.right.left = newNode(40);
var level = 1;
nodesAtKthLevel(root, level);
</script>
Producción:
20 30
Análisis de rendimiento:
- Complejidad de tiempo: como en el enfoque anterior, en el peor de los casos se visitan todos los N Nodes del árbol, por lo que la complejidad de tiempo será O (N)
- Complejidad espacial: como en el peor de los casos, en el nivel más inferior del árbol puede tener el número máximo de Nodes que es 2 H-1 donde H es la altura del árbol binario, entonces la complejidad espacial del árbol binario será O( 2H-1 )
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por iam__manish y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA