Dada una cuadrícula que consta de 4 tipos de caracteres: ‘B’ ‘.’ ‘S’ y ‘D’. Necesitamos llegar a D comenzando desde S, en cada paso podemos ir a las celdas vecinas, es decir, arriba, abajo, izquierda y derecha. Las celdas que tienen el carácter ‘B’ están bloqueadas, es decir, en cualquier paso no podemos movernos a la celda que tiene ‘B’. La cuadrícula dada tiene puntos de tal manera que solo hay una forma de llegar a cualquier celda desde cualquier otra celda. Necesitamos decir cuántas veces debemos elegir nuestro camino entre más de una opción, es decir, decidir el camino para llegar a D.
Ejemplos:
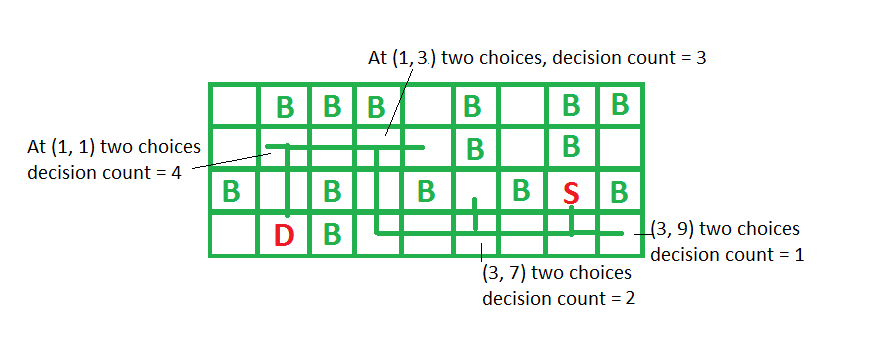
Input : Grid = [".BBB.B.BB"
".....B.B."
"B.B.B.BSB"
".DB......"]
Output : 4
In above shown grid we have to decide 4
times to reach destination at (3, 7),
(3, 5), (1, 3) and (1, 1).
Podemos resolver este problema usando DFS . En la ruta desde el origen hasta el destino, podemos ver que cada vez que tenemos más de 1 vecinos, debemos decidir nuestra ruta, por lo que primero hacemos un DFS y almacenamos la ruta desde el origen hasta el destino en términos de array padre-hijo y luego nos movemos desde el destino hasta el origen, celda por celda usando la array principal y en cada celda donde tengamos más de 1 vecinos, aumentaremos nuestra respuesta en 1.
Consulte el código a continuación para una mejor comprensión.
C++
// C++ program to find decision taken to
// reach destination from source
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Utility dfs method to fill parent array
void dfs(int u, vector<int> g[], int prt[], bool visit[])
{
visit[u] = true;
// loop over all unvisited neighbors
for (int i = 0; i < g[u].size(); i++)
{
int v = g[u][i];
if (!visit[v])
{
prt[v] = u;
dfs(v, g, prt, visit);
}
}
}
// method returns decision taken to reach destination
// from source
int turnsToReachDestination(string grid[], int M)
{
int N = grid[0].length();
// storing direction for neighbors
int dx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int dy[] = {0, -1, 0, 1};
vector<int> g[M*N];
bool visit[M*N] = {0};
int prt[M*N];
int start, dest;
/* initialize start and dest and
store neighbours vector g
If cell index is (i, j), then we can convert
it to 1D as (i*N + j) */
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if (grid[i][j] == 'D')
dest = i*N + j;
if (grid[i][j] == 'S')
start = i*N + j;
g[i*N + j].clear();
if (grid[i][j] != 'B')
{
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int u = i + dx[k];
int v = j + dy[k];
// if neighboring cell is in boundary
// and doesn't have 'B'
if (u >= 0 && u < M && v >= 0 &&
v < N && grid[u][v] != 'B')
g[i*N + j].push_back(u*N + v);
}
}
}
}
// call dfs from start and fill up parent array
dfs(start, g, prt, visit);
int curr = dest;
int res = 0;
// loop from destination cell back to start cell
while (curr != start)
{
/* if current cell has more than 2 neighbors,
then we need to decide our path to reach S
from D, so increase result by 1 */
if (g[curr].size() > 2)
res++;
curr = prt[curr];
}
return res;
}
// Driver code to test above methods
int main()
{
string grid[] =
{
".BBB.B.BB",
".....B.B.",
"B.B.B.BSB",
".DB......"
};
int M = sizeof(grid)/sizeof(grid[0]);
cout << turnsToReachDestination(grid, M) << endl;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to find decision taken to
// reach destination from source
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// Utility dfs method to fill parent array
static void dfs(int u, Vector<Integer> g[],
int prt[], boolean visit[])
{
visit[u] = true;
// loop over all unvisited neighbors
for (int i = 0; i < g[u].size(); i++)
{
int v = g[u].get(i);
if (!visit[v])
{
prt[v] = u;
dfs(v, g, prt, visit);
}
}
}
// method returns decision taken to reach destination
// from source
static int turnsToReachDestination(String grid[], int M)
{
int N = grid[0].length();
// storing direction for neighbors
int dx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int dy[] = {0, -1, 0, 1};
Vector<Integer> []g = new Vector[M*N];
for (int i = 0; i < M*N; i++)
g[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
boolean []visit = new boolean[M*N];
int []prt = new int[M*N];
int start = -1, dest = -1;
/* initialize start and dest and
store neighbours vector g
If cell index is (i, j), then we can convert
it to 1D as (i*N + j) */
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if (grid[i].charAt(j) == 'D')
dest = i * N + j;
if (grid[i].charAt(j) == 'S')
start = i * N + j;
g[i * N + j].clear();
if (grid[i].charAt(j) != 'B')
{
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int u = i + dx[k];
int v = j + dy[k];
// if neighboring cell is in boundary
// and doesn't have 'B'
if (u >= 0 && u < M && v >= 0 &&
v < N && grid[u].charAt(v) != 'B')
g[i * N + j].add(u * N + v);
}
}
}
}
// call dfs from start and fill up parent array
dfs(start, g, prt, visit);
int curr = dest;
int res = 0;
// loop from destination cell back to start cell
while (curr != start)
{
/* if current cell has more than 2 neighbors,
then we need to decide our path to reach S
from D, so increase result by 1 */
if (g[curr].size() > 2)
res++;
curr = prt[curr];
}
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String grid[] =
{
".BBB.B.BB",
".....B.B.",
"B.B.B.BSB",
".DB......"
};
int M = grid.length;
System.out.print(turnsToReachDestination(grid, M) +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Python3
# Python3 program to find decision taken
# to reach destination from source
# Utility dfs method to fill parent array
def dfs(u, g, prt, visit):
visit[u] = True
# Loop over all unvisited neighbors
for i in range(len(g[u])):
v = g[u][i]
if (not visit[v]):
prt[v] = u
dfs(v, g, prt, visit)
# Method returns decision taken to
# reach destination from source
def turnsToReachDestination(grid, M):
N = len(grid[0])
# Storing direction for neighbors
dx = [ -1, 0, 1, 0 ]
dy = [ 0, -1, 0, 1 ]
g = {}
visit = [0 for i in range(M * N)]
prt = [0 for i in range(M * N)]
start = -1
dest = -1
# Initialize start and dest and
# store neighbours vector g
# If cell index is (i, j), then
# we can convert
# it to 1D as (i*N + j)
for i in range(M):
for j in range(N):
if (grid[i][j] == 'D'):
dest = i * N + j
if (grid[i][j] == 'S'):
start = i * N + j
if (grid[i][j] != 'B'):
for k in range(4):
u = i + dx[k]
v = j + dy[k]
# If neighboring cell is in
# boundary and doesn't have 'B'
if (u >= 0 and u < M and
v >= 0 and v < N and
grid[u][v] != 'B'):
if (i * N +j) not in g:
g[i * N + j] = []
g[i * N + j].append(u * N + v)
else:
g[i * N + j].append(u * N + v)
# Call dfs from start and fill up parent array
dfs(start, g, prt, visit)
curr = dest
res = 0
# Loop from destination cell back to start cell
while(curr != start):
# If current cell has more than 2 neighbors,
# then we need to decide our path to reach S
# from D, so increase result by 1 */
if (len(g[curr]) > 2):
res += 1
curr = prt[curr]
return res
# Driver code
grid = [ ".BBB.B.BB", ".....B.B.",
"B.B.B.BSB", ".DB......" ]
M = len(grid)
print(turnsToReachDestination(grid, M))
# This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
C#
// C# program to find decision taken to
// reach destination from source
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// Utility dfs method to fill parent array
static void dfs(int u, List<int> []g,
int []prt, bool []visit)
{
visit[u] = true;
// loop over all unvisited neighbors
for (int i = 0; i < g[u].Count; i++)
{
int v = g[u][i];
if (!visit[v])
{
prt[v] = u;
dfs(v, g, prt, visit);
}
}
}
// method returns decision taken to reach destination
// from source
static int turnsToReachDestination(String []grid, int M)
{
int N = grid[0].Length;
// storing direction for neighbors
int []dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int []dy = {0, -1, 0, 1};
List<int> []g = new List<int>[M*N];
for (int i = 0; i < M*N; i++)
g[i] = new List<int>();
bool []visit = new bool[M*N];
int []prt = new int[M*N];
int start = -1, dest = -1;
/* initialize start and dest and
store neighbours vector g
If cell index is (i, j), then we can convert
it to 1D as (i*N + j) */
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if (grid[i][j] == 'D')
dest = i * N + j;
if (grid[i][j] == 'S')
start = i * N + j;
g[i * N + j].Clear();
if (grid[i][j] != 'B')
{
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int u = i + dx[k];
int v = j + dy[k];
// if neighboring cell is in boundary
// and doesn't have 'B'
if (u >= 0 && u < M && v >= 0 &&
v < N && grid[u][v] != 'B')
g[i * N + j].Add(u * N + v);
}
}
}
}
// call dfs from start and fill up parent array
dfs(start, g, prt, visit);
int curr = dest;
int res = 0;
// loop from destination cell back to start cell
while (curr != start)
{
/* if current cell has more than 2 neighbors,
then we need to decide our path to reach S
from D, so increase result by 1 */
if (g[curr].Count > 2)
res++;
curr = prt[curr];
}
return res;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
String []grid =
{
".BBB.B.BB",
".....B.B.",
"B.B.B.BSB",
".DB......"
};
int M = grid.Length;
Console.Write(turnsToReachDestination(grid, M) +"\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to find decision taken to
// reach destination from source
// Utility dfs method to fill parent array
function dfs(u,g,prt,visit)
{
visit[u] = true;
// loop over all unvisited neighbors
for (let i = 0; i < g[u].length; i++)
{
let v = g[u][i];
if (!visit[v])
{
prt[v] = u;
dfs(v, g, prt, visit);
}
}
}
// method returns decision taken to reach destination
// from source
function turnsToReachDestination(grid,M)
{
let N = grid[0].length;
// storing direction for neighbors
let dx = [-1, 0, 1, 0];
let dy = [0, -1, 0, 1];
let g = new Array(M*N);
for (let i = 0; i < M*N; i++)
g[i] = [];
let visit = new Array(M*N);
let prt = new Array(M*N);
let start = -1, dest = -1;
/* initialize start and dest and
store neighbours vector g
If cell index is (i, j), then we can convert
it to 1D as (i*N + j) */
for (let i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
for (let j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
if (grid[i][j] == 'D')
dest = i * N + j;
if (grid[i][j] == 'S')
start = i * N + j;
g[i * N + j]=[];
if (grid[i][j] != 'B')
{
for (let k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
let u = i + dx[k];
let v = j + dy[k];
// if neighboring cell is in boundary
// and doesn't have 'B'
if (u >= 0 && u < M && v >= 0 &&
v < N && grid[u][v] != 'B')
g[i * N + j].push(u * N + v);
}
}
}
}
// call dfs from start and fill up parent array
dfs(start, g, prt, visit);
let curr = dest;
let res = 0;
// loop from destination cell back to start cell
while (curr != start)
{
/* if current cell has more than 2 neighbors,
then we need to decide our path to reach S
from D, so increase result by 1 */
if (g[curr].length > 2)
res++;
curr = prt[curr];
}
return res;
}
// Driver code
let grid=[".BBB.B.BB",
".....B.B.",
"B.B.B.BSB",
".DB......"];
let M = grid.length;
document.write(turnsToReachDestination(grid, M) +"<br>");
// This code is contributed by rag2127
</script>
Producción:
4
Este artículo es una contribución de Utkarsh Trivedi . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA