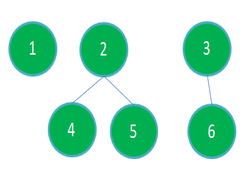
Dado un árbol con un valor de N Nodes de 1 a N y (N – 1) aristas y un número K , la tarea es eliminar la cantidad mínima de Nodes del árbol de modo que cada subárbol tenga como máximo K Nodes. Eliminar Nodes eliminará los bordes de esos Nodes a todos los demás Nodes conectados.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: N = 10, K = 3, A continuación se muestra el gráfico:
Salida:
Número de Nodes eliminados: 2
Nodes eliminados: 2 1
Explicación:
Después de eliminar los Nodes 1 y 2, aquí, ningún subárbol o árbol tiene más de 3 Nodes. A continuación se muestra el gráfico resultante:
Entrada: N = 6, K = 3, A continuación se muestra el gráfico:
Salida:
Número de Nodes eliminados: 1
Nodes eliminados: 1
Explicación:
Después de eliminar los Nodes 1, aquí, ningún subárbol o árbol tiene más de 3 Nodes. A continuación se muestra el gráfico resultante:
Enfoque: La idea es observar que el número de Nodes en el subárbol de un Node X es la suma del número de Nodes en el subárbol de sus hijos y el Node mismo. A continuación se muestran los pasos:
- Utilice Programación Dinámica y DFS para almacenar fácilmente el recuento de Nodes en el subárbol de cada Node.
- Ahora, para no tener ningún Node con un subárbol que tenga más de K Nodes, la idea es eliminar el Node cada vez que tenga más de K Nodes en su subárbol y pasar 0 a su padre.
- En el paso anterior, estamos teniendo cada Node con Nodes en su subárbol no mayor que K y minimizando el número de eliminaciones de Nodes.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 20
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
int dfs(vector<bool> &visited, int s,
int &K, int &removals,
vector<int> &removed_nodes,
vector<vector<int>> &adj)
{
// Mark the node as true
visited[s] = true;
int nodes = 1;
// Traverse adjacency list
// of child node
for(int child : adj[s])
{
// If already visited then
// omit the node
if (visited[child])
continue;
// Add number of nodes
// in subtree
nodes += dfs(visited, child, K,
removals, removed_nodes,
adj);
}
if (nodes > K)
{
// Increment the count
removals++;
removed_nodes.push_back(s);
nodes = 0;
}
// Return the nodes
return nodes;
}
// Function to add edges in graph
void addEdge(vector<vector<int>> &adj,
int a, int b)
{
adj[a].push_back(b);
adj[b].push_back(a);
}
// Function that finds the number
// of nodes to be removed such that
// every subtree has size at most K
void findRemovedNodes(vector<bool> &visited, int K,
int &removals,
vector<int> &removed_nodes,
vector<vector<int>> &adj)
{
// Function Call to find the
// number of nodes to remove
dfs(visited, 1, K, removals,
removed_nodes, adj);
// Print Removed Nodes
cout << "Number of nodes removed: "
<< removals << endl;
cout << "Removed Nodes: ";
for(int node : removed_nodes)
{
cout << node << " ";
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Variables used to store data globally
vector<bool> visited(N);
int K;
int removals = 0;
vector<int> removed_nodes;
// Adjacency list representation of tree
vector<vector<int>> adj(N);
// Insert of nodes in graph
addEdge(adj, 1, 2);
addEdge(adj, 1, 3);
addEdge(adj, 2, 4);
addEdge(adj, 2, 5);
addEdge(adj, 3, 6);
// Required subtree size
K = 3;
// Function Call
findRemovedNodes(visited, K, removals,
removed_nodes, adj);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by sanjeev2552
Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Variables used to store data globally
static final int N = 20;
static boolean visited[] = new boolean[N];
static int K;
static int removals = 0;
static ArrayList<Integer> removed_nodes
= new ArrayList<>();
// Adjacency list representation of tree
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > adj
= new ArrayList<>();
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
static int dfs(int s)
{
// Mark the node as true
visited[s] = true;
int nodes = 1;
// Traverse adjacency list
// of child node
for (Integer child : adj.get(s)) {
// If already visited then
// omit the node
if (visited[child])
continue;
// Add number of nodes
// in subtree
nodes += dfs(child);
}
if (nodes > K) {
// Increment the count
removals++;
removed_nodes.add(s);
nodes = 0;
}
// Return the nodes
return nodes;
}
// Function to add edges in graph
static void addEdge(int a, int b)
{
adj.get(a).add(b);
adj.get(b).add(a);
}
// Function that finds the number
// of nodes to be removed such that
// every subtree has size at most K
public static void findRemovedNodes(int K)
{
// Function Call to find the
// number of nodes to remove
dfs(1);
// Print Removed Nodes
System.out.println("Number of nodes"
+ " removed: "
+ removals);
System.out.print("Removed Nodes: ");
for (int node : removed_nodes)
System.out.print(node + " ");
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating list for all nodes
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
// Insert of nodes in graph
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(1, 3);
addEdge(2, 4);
addEdge(2, 5);
addEdge(3, 6);
// Required subtree size
K = 3;
// Function Call
findRemovedNodes(K);
}
}
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Variables used to store data globally
N = 20
visited = [False for i in range(N)]
K = 0
removals = 0
removed_nodes = []
# Adjacency list representation of tree
adj = [[] for i in range(N)]
# Function to perform DFS Traversal
def dfs(s):
global removals
# Mark the node as true
visited[s] = True
nodes = 1
# Traverse adjacency list
# of child node
for child in adj[s]:
# If already visited then
# omit the node
if (visited[child]):
continue
# Add number of nodes
# in subtree
nodes += dfs(child)
if (nodes > K):
# Increment the count
removals += 1
removed_nodes.append(s)
nodes = 0
# Return the nodes
return nodes
# Function to add edges in graph
def addEdge(a, b):
adj[a].append(b)
adj[b].append(a)
# Function that finds the number
# of nodes to be removed such that
# every subtree has size at most K
def findRemovedNodes(K):
# Function Call to find the
# number of nodes to remove
dfs(1)
# Print Removed Nodes
print("Number of nodes removed: ", removals)
print("Removed Nodes: ", end = ' ')
for node in removed_nodes:
print(node, end = ' ')
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Insert of nodes in graph
addEdge(1, 2)
addEdge(1, 3)
addEdge(2, 4)
addEdge(2, 5)
addEdge(3, 6)
# Required subtree size
K = 3
# Function Call
findRemovedNodes(K)
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56
C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
// Variables used to store data globally
static readonly int N = 20;
static bool []visited = new bool[N];
static int K;
static int removals = 0;
static List<int> removed_nodes
= new List<int>();
// Adjacency list representation of tree
static List<List<int> > adj
= new List<List<int>>();
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
static int dfs(int s)
{
// Mark the node as true
visited[s] = true;
int nodes = 1;
// Traverse adjacency list
// of child node
foreach (int child in adj[s])
{
// If already visited then
// omit the node
if (visited[child])
continue;
// Add number of nodes
// in subtree
nodes += dfs(child);
}
if (nodes > K)
{
// Increment the count
removals++;
removed_nodes.Add(s);
nodes = 0;
}
// Return the nodes
return nodes;
}
// Function to add edges in graph
static void addEdge(int a, int b)
{
adj[a].Add(b);
adj[b].Add(a);
}
// Function that finds the number
// of nodes to be removed such that
// every subtree has size at most K
public static void findRemovedNodes(int K)
{
// Function Call to find the
// number of nodes to remove
dfs(1);
// Print Removed Nodes
Console.WriteLine("Number of nodes" +
" removed: " +
removals);
Console.Write("Removed Nodes: ");
foreach (int node in removed_nodes)
Console.Write(node + " ");
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Creating list for all nodes
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
adj.Add(new List<int>());
// Insert of nodes in graph
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(1, 3);
addEdge(2, 4);
addEdge(2, 5);
addEdge(3, 6);
// Required subtree size
K = 3;
// Function Call
findRemovedNodes(K);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rohit_ranjan
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program for the above approach
// Variables used to store data globally
let N = 20;
let visited = new Array(N);
let K;
let removals = 0;
let removed_nodes = [];
// Adjacency list representation of tree
let adj = [];
// Function to perform DFS Traversal
function dfs(s)
{
// Mark the node as true
visited[s] = true;
let nodes = 1;
// Traverse adjacency list
// of child node
for(let child = 0; child < adj[s].length; child++)
{
// If already visited then
// omit the node
if (visited[adj[s][child]])
continue;
// Add number of nodes
// in subtree
nodes += dfs(adj[s][child]);
}
if (nodes > K)
{
// Increment the count
removals++;
removed_nodes.push(s);
nodes = 0;
}
// Return the nodes
return nodes;
}
// Function to add edges in graph
function addEdge(a, b)
{
adj[a].push(b);
adj[b].push(a);
}
// Function that finds the number
// of nodes to be removed such that
// every subtree has size at most K
function findRemovedNodes(K)
{
// Function Call to find the
// number of nodes to remove
dfs(1);
// Print Removed Nodes
document.write("Number of nodes" + " removed: " +
removals + "</br>");
document.write("Removed Nodes: ");
for(let node = 0; node < removed_nodes.length; node++)
document.write(removed_nodes[node] + " ");
}
// Creating list for all nodes
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++)
adj.push([]);
// Insert of nodes in graph
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(1, 3);
addEdge(2, 4);
addEdge(2, 5);
addEdge(3, 6);
// Required subtree size
K = 3;
// Function Call
findRemovedNodes(K);
</script>
Number of nodes removed: 1 Removed Nodes: 1
Complejidad temporal: O(N)
Espacio auxiliar: O(N)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por jrishabh99 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA