Dada una permutación P (P1, P2, P3, … Pn) de los primeros n números naturales. Encuentre el número mínimo de operaciones para convertirlo en una permutación de identidad, es decir , 1, 2, 3, …, n donde cada operación se define como:
P[i] = P[P[P[i]]] ![]() i de 1 a n (1 indexación basada). Si no hay forma de convertir, imprima -1 .
i de 1 a n (1 indexación basada). Si no hay forma de convertir, imprima -1 .
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr[] = {2, 3, 1}
Salida: 1
Después de 1 operación:
P[1] = P[P[P[1]]] = P[P[2]] = P[3] = 1
P[2] = P[P[P[2]]] = P[P[3]] = P[1] = 2
P[3] = P[P[P[3]]] = P[P[ 1]] = P[2] = 3
Así después de 1 operación obtenemos una permutación de identidad.
Entrada: arr[] = {2, 1, 3}
Salida: -1
No hay forma de obtener la permutación de identidad
sin importar cuántas operaciones apliquemos.
Enfoque: Primero, encuentre todos los ciclos en la permutación dada. Aquí, un ciclo es un gráfico dirigido en el que hay una arista desde un elemento e hasta el elemento en la posición e.
Por ejemplo, aquí está el gráfico de permutación {4, 6, 5, 3, 2, 1, 8, 7}
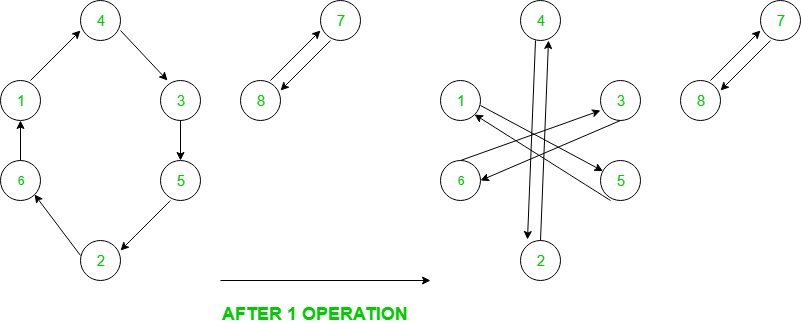
Ahora, en una operación, cada ciclo de longitud 3k se divide en 3 ciclos cada uno de longitud k mientras que los ciclos de longitud 3k+1 o 3k+2 no se dividen. Dado que al final, necesitamos todos los ciclos de longitud 1, por lo tanto, todos los ciclos deben ser una potencia de 3, de lo contrario, la respuesta no existe. La respuesta sería entonces el máximo de log (base 3) de todas las longitudes de ciclo.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int calculateCycleOperations(int len)
{
int cycle_operations = 0;
while (len) {
len /= 3;
++cycle_operations;
}
return --cycle_operations;
}
// Function to return the minimum operations required
int minimumOperations(int p[], int n)
{
// Array to keep track of visited elements
bool visited[n + 1] = { 0 };
// To store the final answer
int ans = 0;
// Looping through all the elements
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// Current element
int ele = p[i];
// If current element is not present in the
// previous cycles then only consider this
if (!visited[ele]) {
// Mark current element visited so that it
// will not be considered in other cycles
visited[ele] = 1;
// To store the length of each cycle
int len = 1;
ele = p[ele];
// Calculating cycle length
while (!visited[ele]) {
visited[ele] = 1;
++len;
ele = p[ele];
}
// Operations needed for this cycle to reduce
// to length 1 (if possible)
int operations = calculateCycleOperations(len);
// Checking cycle length to be power of 3
// if not, then return -1
int num = pow(3, operations);
if (num != len) {
return -1;
}
// Taking maximum of the operations
ans = max(ans, operations);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// 1-based indexing
int P[] = { -1, 4, 6, 5, 3, 2, 7, 8, 9, 1 };
int n = (sizeof(P) / sizeof(P[0])) - 1;
// Calling function
cout << minimumOperations(P, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int calculateCycleOperations(int len)
{
int cycle_operations = 0;
while (len > 0)
{
len /= 3;
++cycle_operations;
}
return --cycle_operations;
}
// Function to return the minimum operations required
static int minimumOperations(int p[], int n)
{
// Array to keep track of visited elements
int []visited = new int[n+1];
Arrays.fill(visited,0);
// To store the final answer
int ans = 0;
// Looping through all the elements
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// Current element
int ele = p[i];
// If current element is not present in the
// previous cycles then only consider this
if (visited[ele] == 0)
{
// Mark current element visited so that it
// will not be considered in other cycles
visited[ele] = 1;
// To store the length of each cycle
int len = 1;
ele = p[ele];
// Calculating cycle length
while (visited[ele] == 0)
{
visited[ele] = 1;
++len;
ele = p[ele];
}
// Operations needed for this cycle to reduce
// to length 1 (if possible)
int operations = calculateCycleOperations(len);
// Checking cycle length to be power of 3
// if not, then return -1
int num = (int)Math.pow(3, operations);
if (num != len) {
return -1;
}
// Taking maximum of the operations
ans = Math.max(ans, operations);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// 1-based indexing
int P[] = { -1, 4, 6, 5, 3, 2, 7, 8, 9, 1 };
int n = P.length-1;
// Calling function
System.out.println(minimumOperations(P, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// Surendra_Gangwar
Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach def calculateCycleOperations(length): cycle_operations = 0 while length > 0: length //= 3 cycle_operations += 1 return cycle_operations - 1 # Function to return the minimum # operations required def minimumOperations(p, n): # Array to keep track of visited elements visited = [0] * (n + 1) # To store the final answer ans = 0 # Looping through all the elements for i in range(1, n + 1): # Current element ele = p[i] # If current element is not present in the # previous cycles then only consider this if not visited[ele]: # Mark current element visited so that it # will not be considered in other cycles visited[ele] = 1 # To store the length of each cycle length = 1 ele = p[ele] # Calculating cycle length while not visited[ele]: visited[ele] = 1 length += 1 ele = p[ele] # Operations needed for this cycle to # reduce to length 1 (if possible) operations = calculateCycleOperations(length) # Checking cycle length to be power # of 3 if not, then return -1 num = pow(3, operations) if num != length: return -1 # Taking maximum of the operations ans = max(ans, operations) return ans # Driver code if __name__ == "__main__": # 1-based indexing P = [-1, 4, 6, 5, 3, 2, 7, 8, 9, 1] n = len(P) - 1 # Calling function print(minimumOperations(P, n)) # This code is contributed by Rituraj Jain
C#
// C# implementation of the above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
static int calculateCycleOperations(int len)
{
int cycle_operations = 0;
while (len > 0)
{
len /= 3;
++cycle_operations;
}
return --cycle_operations;
}
// Function to return the minimum operations required
static int minimumOperations(int []p, int n)
{
// Array to keep track of visited elements
int []visited = new int[n+1];
// To store the final answer
int ans = 0;
// Looping through all the elements
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// Current element
int ele = p[i];
// If current element is not present in the
// previous cycles then only consider this
if (visited[ele] == 0)
{
// Mark current element visited so that it
// will not be considered in other cycles
visited[ele] = 1;
// To store the length of each cycle
int len = 1;
ele = p[ele];
// Calculating cycle length
while (visited[ele] == 0)
{
visited[ele] = 1;
++len;
ele = p[ele];
}
// Operations needed for this cycle to reduce
// to length 1 (if possible)
int operations = calculateCycleOperations(len);
// Checking cycle length to be power of 3
// if not, then return -1
int num = (int)Math.Pow(3, operations);
if (num != len)
{
return -1;
}
// Taking maximum of the operations
ans = Math.Max(ans, operations);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
// 1-based indexing
int []P = { -1, 4, 6, 5, 3, 2, 7, 8, 9, 1 };
int n = P.Length-1;
// Calling function
Console.WriteLine(minimumOperations(P, n));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Ryuga
PHP
<?php
// PHP implementation of the approach
function calculateCycleOperations($len)
{
$cycle_operations = 0;
while ($len)
{
$len = (int)($len / 3);
++$cycle_operations;
}
return --$cycle_operations;
}
// Function to return the minimum
// operations required
function minimumOperations($p, $n)
{
// Array to keep track of visited elements
$visited[$n + 1] = array(0);
// To store the final answer
$ans = 0;
// Looping through all the elements
for ($i = 1; $i <= $n; $i++)
{
// Current element
$ele = $p[$i];
// If current element is not present in the
// previous cycles then only consider this
if (!$visited[$ele])
{
// Mark current element visited so that it
// will not be considered in other cycles
$visited[$ele] = 1;
// To store the length of each cycle
$len = 1;
$ele = $p[$ele];
// Calculating cycle length
while (!$visited[$ele])
{
$visited[$ele] = 1;
++$len;
$ele = $p[$ele];
}
// Operations needed for this cycle to reduce
// to length 1 (if possible)
$operations = calculateCycleOperations($len);
// Checking cycle length to be power of 3
// if not, then return -1
$num = pow(3, $operations);
if ($num != $len)
{
return -1;
}
// Taking maximum of the operations
$ans = max($ans, $operations);
}
}
return $ans;
}
// Driver code
// 1-based indexing
$P = array(-1, 4, 6, 5, 3, 2, 7, 8, 9, 1);
$n = sizeof($P) - 1;
// Calling function
echo minimumOperations($P, $n);
// This code is contributed by Akanksha Rai
?>
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript implementation of the approach
function calculateCycleOperations(len)
{
let cycle_operations = 0;
while (len > 0)
{
len = Math.floor(len / 3);
++cycle_operations;
}
return --cycle_operations;
}
// Function to return the minimum operations required
function minimumOperations(p, n)
{
// Array to keep track of visited elements
let visited = Array.from({length: n + 1}, (_, i) => 0);
// To store the final answer
let ans = 0;
// Looping through all the elements
for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// Current element
let ele = p[i];
// If current element is not present in the
// previous cycles then only consider this
if (visited[ele] == 0)
{
// Mark current element visited so that it
// will not be considered in other cycles
visited[ele] = 1;
// To store the length of each cycle
let len = 1;
ele = p[ele];
// Calculating cycle length
while (visited[ele] == 0)
{
visited[ele] = 1;
++len;
ele = p[ele];
}
// Operations needed for this cycle to reduce
// to length 1 (if possible)
let operations = calculateCycleOperations(len);
// Checking cycle length to be power of 3
// if not, then return -1
let num = Math.floor(Math.pow(3, operations));
if (num != len) {
return -1;
}
// Taking maximum of the operations
ans = Math.max(ans, operations);
}
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
// 1-based indexing
let P = [ -1, 4, 6, 5, 3, 2, 7, 8, 9, 1 ];
let n = P.length - 1;
// Calling function
document.write(minimumOperations(P, n));
</script>
2
Complejidad del tiempo: O(N*LogN)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por tech_mint0013 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA