Dada una barra de oro de longitud N con N marcas iguales, la tarea es encontrar el número mínimo de cortes necesarios para pagar el salario en N días , de modo que en cualquier i- ésimo día el trabajador tenga i partes de la barra de oro.
Ejemplos:
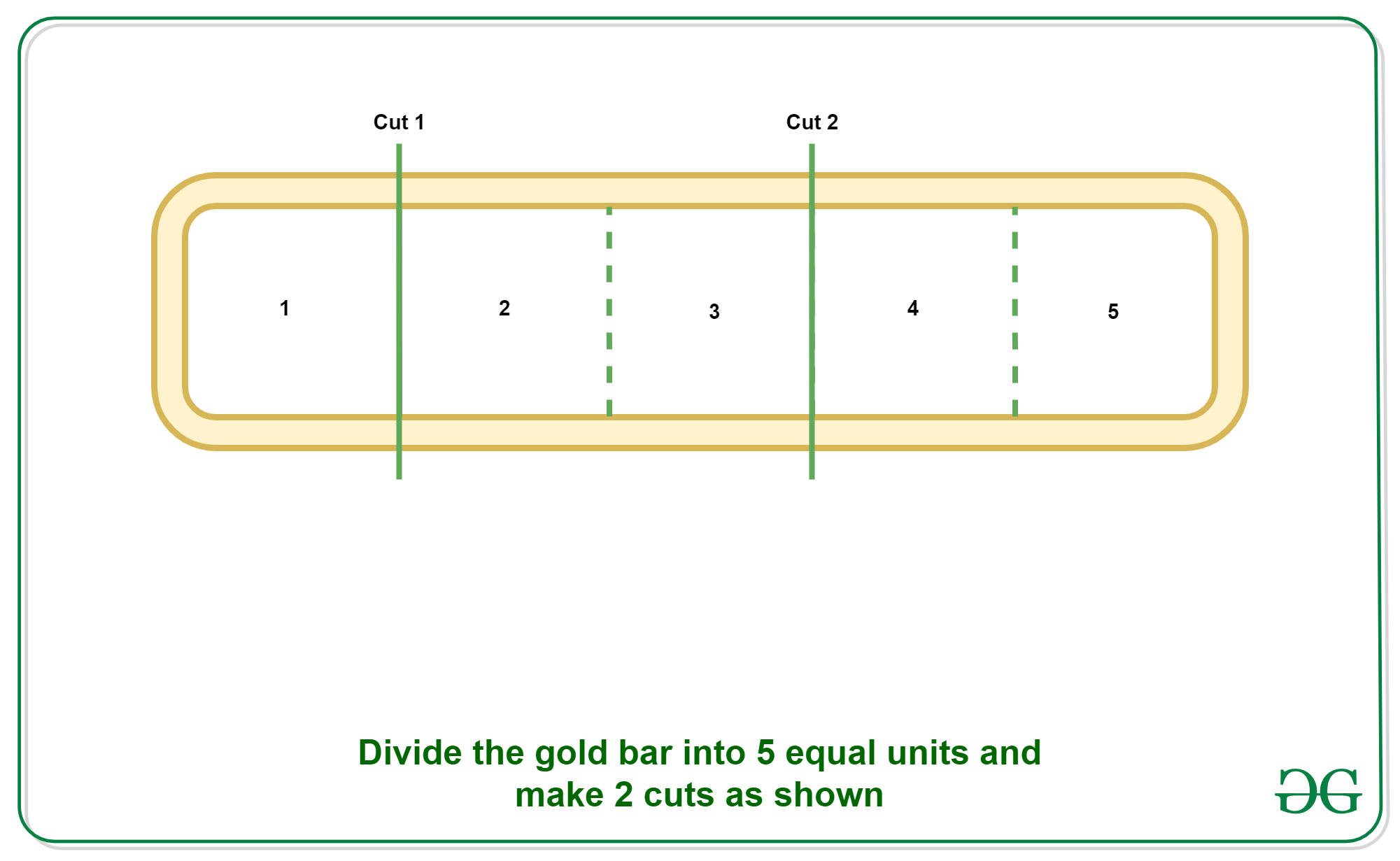
Entrada: N = 5
Salida: 2
Explicación:
Divida la barra de oro de 5 longitudes en 3 partes de longitud 1, 2, 2 haciendo 2 cortes. Entonces el salario para cada día será como:
Para el Día 1 = 1 (Dé 1 barra de longitud)
Para el Día 2 = 2 – 1 = 1 (Dé 2 barras de longitud y recupere 1 barra de longitud)
Para el Día 3 = 1 (Dé 1 barra de longitud) barra)
Para el Día 4 = 2 – 1 = 1 (Dar 2 barras de longitud y retirar 1 barra de longitud)
Para el Día 5 = 1 (Dar 1 barra de longitud)
Entrada: N = 15
Salida: 3
Explicación:
Divida la barra de oro de 15 longitudes en 4 partes de longitud 1, 2, 4, 8 haciendo 3 cortes. Entonces el salario para cada día será como:
Para el Día 1 = 1 (Dé 1 barra de longitud)
Para el Día 2 = 2 – 1 = 1 (Dé 2 barras de longitud y recupere 1 barra de longitud)
Para el Día 3 = 1 (Dé 1 barra de longitud) barra)
Para el día 4 = 4 – 2 – 1 = 1 (dar 4 barras de longitud y quitar 1 y 2 barras de longitud)
Para el día 5 = 1 (dar 1 barra de longitud)
Para el día 6 = 2 – 1 = 1 (dar 2 barras) barra de longitud y retirar 1 barra de longitud)
Para el día 7 = 1 (dar 1 barra de longitud)
Para el día 8 = 8 – 4 – 2 – 1 = 1 (dar 8 barras de longitud y retirar 1, 2 y 4 barras de longitud)
Para Día 9 = 1 (Dé 1 barra de longitud)
Para el día 10 = 2 – 1 = 1 (dar 2 barras de longitud y quitar 1 barra de longitud)
Para el día 11 = 1 (dar 1 barra de longitud)
Para el día 12 = 4 – 2 – 1 = 1 (dar 4 barras de longitud y quitar atrás 1 y 2 barra de largo)
Para el día 13 = 1 (dar 1 barra de largo)
Para el día 14 = 2 – 1 = 1 (dar 2 barras de largo y retirar 1 barra de largo)
Para el día 15 = 1 (dar 1 barra de largo)
Planteamiento:
Como sabemos cualquier número se puede representar con la ayuda de los números en forma de potencias de 2 . Entonces, si cortamos la longitud de la barra de oro en el entero más cercano a log 2 (N), entonces podemos representar cualquier número hasta N.
Por ejemplo: cuando N = 15, podemos dividir el número en las partes 1, 2, 4 , 8 y usando estos números podemos representar cualquier número del 1 al 15, como se muestra a continuación:
For 1 - 1 For 2 - 2 For 3 - 2 + 1 For 4 - 4 For 5 - 4 + 1 For 6 - 4 + 2 For 7 - 4 + 2 + 1 For 8 - 8 For 9 - 8 + 1 For 10 - 8 + 2 For 11 - 8 + 2 + 1 For 12 - 8 + 4 For 13 - 8 + 4 + 1 For 14 - 8 + 4 + 2 For 15 - 8 + 4 + 2 + 1
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior.
C++
// CPP Implementation to find
// the minimum number of cuts to
// pay the worker.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the minimum
// number of cuts to pay the worker.
int pay(int n)
{
// Nearest Integer to the Log
// value of the number N
int cuts = int(log(n)/log(2));
return cuts;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 5;
int cuts = pay(n);
cout << cuts << endl;
// Cuts Required in the
// Length of 15
n = 15;
cuts = pay(n);
cout<<(cuts);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
Java
// JAVA Implementation to find
// the minimum number of cuts to
// pay the worker.
class GFG
{
// Function to find the minimum
// number of cuts to pay the worker.
static int pay(int n)
{
// Nearest Integer to the Log
// value of the number N
int cuts = (int) (Math.log(n)/Math.log(2));
return cuts;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
int cuts = pay(n);
System.out.print(cuts +"\n");
// Cuts Required in the
// Length of 15
n = 15;
cuts = pay(n);
System.out.print(cuts);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Python
# Python Implementation to find # the minimum number of cuts to # pay the worker. import math # Function to find the minimum # number of cuts to pay the worker. def pay(n): # Nearest Integer to the Log # value of the number N cuts = int(math.log(n, 2)) return cuts # Driver Code if __name__ == "__main__": n = 5 cuts = pay(n) print(cuts) # Cuts Required in the # Length of 15 n = 15 cuts = pay(n) print(cuts)
C#
// C# Implementation to find
// the minimum number of cuts to
// pay the worker.
using System;
class GFG
{
// Function to find the minimum
// number of cuts to pay the worker.
static int pay(int n)
{
// Nearest int to the Log
// value of the number N
int cuts = (int) (Math.Log(n)/Math.Log(2));
return cuts;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
int cuts = pay(n);
Console.Write(cuts +"\n");
// Cuts Required in the
// Length of 15
n = 15;
cuts = pay(n);
Console.Write(cuts);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript Implementation to find
// the minimum number of cuts to
// pay the worker.
// Function to find the minimum
// number of cuts to pay the worker.
function pay(n)
{
// Nearest Integer to the Log
// value of the number N
let cuts = parseInt(Math.log(n)/Math.log(2));
return cuts;
}
// Driver code
let n = 5;
let cuts = pay(n);
document.write(cuts + "<br>");
// Cuts Required in the
// Length of 15
n = 15;
cuts = pay(n);
document.write(cuts + "<br>");
</script>
2 3
Complejidad de tiempo: O(1)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(1)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por gadamsettykarthikeya y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA