CURRENT_TIMESTAMP()
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(precision)
Analicemos la sintaxis anterior:
- precisión
- CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() MARCA DE TIEMPO CON ZONA HORARIA
FECHA Y HORA ACTUAL()
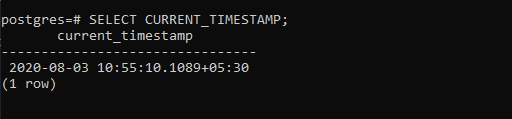
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP;
Producción:
Ejemplo 2:
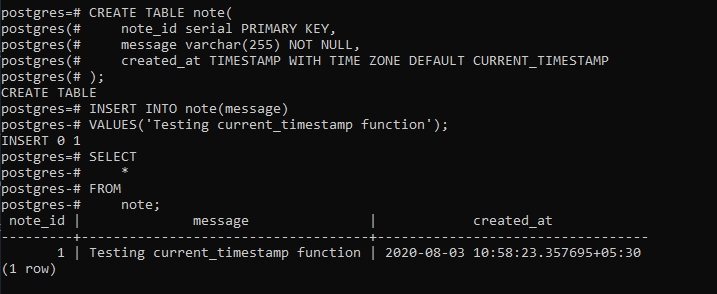
Primero cree una nota de tabla created_at TIMESTAMP CON ZONA HORARIA
CREATE TABLE note(
note_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
message varchar(255) NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
creado_enCURRENT_TIMESTAMP()
INSERT INTO note(message)
VALUES('Testing current_timestamp function');
SELECT
*
FROM
note;
Producción:
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por RajuKumar19 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA