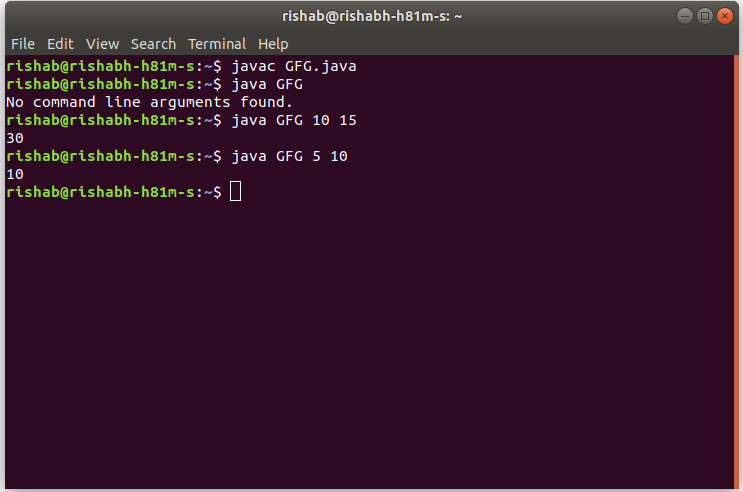
Dados dos números, la tarea es encontrar el MCM de dos números usando argumentos de línea de comando . MCM (Mínimo común múltiplo) de dos números es el número más pequeño que se puede dividir entre ambos números. Por ejemplo, MCM de 15 y 20 es 60 y MCM de 5 y 7 es 35. Ejemplos:
Input: n1 = 10, n2 = 15 Output: 30 Input: n1 = 5, n2 = 10 Output: 10
Acercarse:
- Dado que los números se ingresan como argumentos de línea de comando , no hay necesidad de una línea de entrada dedicada
- Extraiga los números de entrada del argumento de la línea de comando
- Estos números extraídos estarán en tipo de string.
- Convierta estos números en tipo entero y guárdelos en variables, digamos num1 y num2
- Encuentra el MCM de los números. Una solución eficiente se basa en la siguiente fórmula para MCM de dos números ‘a’ y ‘b’.
a x b = LCM(a, b) * GCD (a, b) LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
- Para encontrar el GCD o HCF, una solución eficiente es utilizar el algoritmo euclidiano, que es el principal algoritmo utilizado para este propósito. La idea es que el MCD de dos números no cambia si se resta un número más pequeño de un número más grande.
- Imprima o devuelva el LCM
Programa:
C
// C program to compute the LCM of two numbers
// using command line arguments
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> /* atoi */
// Function to compute the GCD of two numbers
int GCD(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
return GCD(b, a % b);
}
// Function to find the LCM
int LCM(int a, int b)
{
return (a * b) / GCD(a, b);
}
// Driver code
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int num1, num2;
// Check if the length of args array is 1
if (argc == 1)
printf("No command line arguments found.\n");
else {
// Get the command line argument and
// Convert it from string type to integer type
// using function "atoi( argument)"
num1 = atoi(argv[1]);
num2 = atoi(argv[2]);
// Find the LCM and print it
printf("%d\n", LCM(num1, num2));
}
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to compute the LCM of two numbers
// using command line arguments
class GFG {
// Function to compute the GCD of two numbers
static int GCD(int a, int b)
{
if (b == 0)
return a;
return GCD(b, a % b);
}
// Function to find the LCM
static int LCM(int a, int b)
{
return (a * b) / GCD(a, b);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Check if length of args array is
// greater than 0
if (args.length > 0) {
// Get the command line argument and
// Convert it from string type to integer type
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
// Find the LCM
int res = LCM(num1, num2);
// Print the LCM
System.out.println(res);
}
else
System.out.println("No command line "
+ "arguments found.");
}
}
Producción:
Complejidad de tiempo: O (logN)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(logN)
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por RishabhPrabhu y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA