Dada una array de n enteros donde cada valor representa la cantidad de chocolates en un paquete. Cada paquete puede tener un número variable de bombones. Hay m estudiantes, la tarea es distribuir paquetes de chocolate de tal manera que:
- Cada estudiante recibe un paquete.
- La diferencia entre la cantidad de chocolates en el paquete con el máximo de chocolates y el paquete con el mínimo de chocolates que se les da a los estudiantes es mínima.
Ejemplos:
Entrada: arr[] = {7, 3, 2, 4, 9, 12, 56} , m = 3
Salida: La diferencia mínima es 2
Explicación:
Tenemos siete paquetes de chocolates y
necesitamos elegir tres paquetes para 3 estudiantes
Si elegimos 2, 3 y 4, obtenemos la
diferencia mínima entre los tamaños de paquete máximo y mínimo
.Entrada: arr[] = {3, 4, 1, 9, 56, 7, 9, 12}, m = 5
Salida: La diferencia mínima es 6
Explicación:
El conjunto va como 3,4,7,9,9 y el la salida
es 9-3 = 6Entrada: arr[] = {12, 4, 7, 9, 2, 23, 25, 41, 30, 40, 28, 42, 30, 44, 48,
43
, 50}, m = 7
Salida: La diferencia mínima es 10
Explicación:
Necesitamos recoger 7 paquetes. Elegimos 40, 41,
42, 44, 48, 43 y 50 para minimizar la diferencia
entre el máximo y el mínimo.
Fuente: Experiencia de entrevista Flipkart
Una solución simple es generar todos los subconjuntos de tamaño m de arr[0..n-1]. Para cada subconjunto, encuentre la diferencia entre los elementos máximo y mínimo en él. Finalmente, devuelva la diferencia mínima.
Una solución eficiente se basa en la observación de que para minimizar la diferencia, debemos elegir elementos consecutivos de un paquete ordenado. Primero ordenamos el arreglo arr[0..n-1], luego encontramos el subarreglo de tamaño m con la diferencia mínima entre el último y el primer elemento.
La imagen de abajo es una ejecución en seco del enfoque anterior:
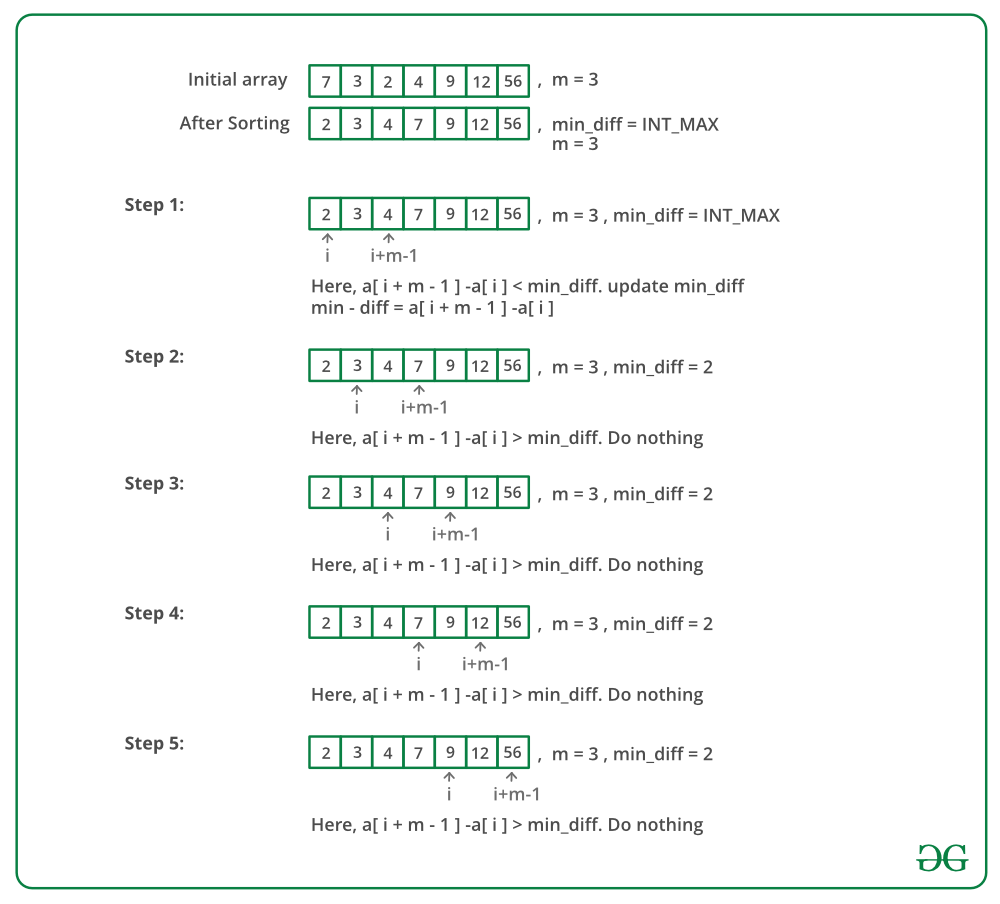
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to solve chocolate distribution
// problem
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// arr[0..n-1] represents sizes of packets
// m is number of students.
// Returns minimum difference between maximum
// and minimum values of distribution.
int findMinDiff(int arr[], int n, int m)
{
// if there are no chocolates or number
// of students is 0
if (m == 0 || n == 0)
return 0;
// Sort the given packets
sort(arr, arr + n);
// Number of students cannot be more than
// number of packets
if (n < m)
return -1;
// Largest number of chocolates
int min_diff = INT_MAX;
// Find the subarray of size m such that
// difference between last (maximum in case
// of sorted) and first (minimum in case of
// sorted) elements of subarray is minimum.
for (int i = 0; i + m - 1 < n; i++) {
int diff = arr[i + m - 1] - arr[i];
if (diff < min_diff)
min_diff = diff;
}
return min_diff;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 4, 7, 9, 2, 23, 25, 41, 30,
40, 28, 42, 30, 44, 48, 43, 50 };
int m = 7; // Number of students
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << "Minimum difference is "
<< findMinDiff(arr, n, m);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
C
// C program to solve chocolate distribution problem
#include <limits.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Compare function for qsort
int cmpfunc(const void* a, const void* b)
{
return (*(int*)a - *(int*)b);
}
// arr[0..n-1] represents sizes of packets
// m is number of students.
// Returns minimum difference between maximum
// and minimum values of distribution.
int findMinDiff(int arr[], int n, int m)
{
// if there are no chocolates or number
// of students is 0
if (m == 0 || n == 0)
return 0;
// Sort the given packets
qsort(arr, n, sizeof(int), cmpfunc);
// Number of students cannot be more than
// number of packets
if (n < m)
return -1;
// Largest number of chocolates
int min_diff = INT_MAX;
// Find the subarray of size m such that
// difference between last (maximum in case
// of sorted) and first (minimum in case of
// sorted) elements of subarray is minimum.
for (int i = 0; i + m - 1 < n; i++) {
int diff = arr[i + m - 1] - arr[i];
if (diff < min_diff)
min_diff = diff;
}
return min_diff;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 4, 7, 9, 2, 23, 25, 41, 30,
40, 28, 42, 30, 44, 48, 43, 50 };
int m = 7; // Number of students
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Minimum difference is %d",
findMinDiff(arr, n, m));
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
Java
// JAVA Code For Chocolate Distribution
// Problem
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// arr[0..n-1] represents sizes of
// packets. m is number of students.
// Returns minimum difference between
// maximum and minimum values of
// distribution.
static int findMinDiff(int arr[], int n,
int m)
{
// if there are no chocolates or
// number of students is 0
if (m == 0 || n == 0)
return 0;
// Sort the given packets
Arrays.sort(arr);
// Number of students cannot be
// more than number of packets
if (n < m)
return -1;
// Largest number of chocolates
int min_diff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// Find the subarray of size m
// such that difference between
// last (maximum in case of
// sorted) and first (minimum in
// case of sorted) elements of
// subarray is minimum.
for (int i = 0; i + m - 1 < n; i++)
{
int diff = arr[i+m-1] - arr[i];
if (diff < min_diff)
min_diff = diff;
}
return min_diff;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = {12, 4, 7, 9, 2, 23,
25, 41, 30, 40, 28,
42, 30, 44, 48, 43,
50};
int m = 7; // Number of students
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println("Minimum difference is "
+ findMinDiff(arr, n, m));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnav Kr. Mandal.
Python3
# Python3 program to solve
# chocolate distribution
# problem
# arr[0..n-1] represents sizes of packets
# m is number of students.
# Returns minimum difference between maximum
# and minimum values of distribution.
def findMinDiff(arr, n, m):
# if there are no chocolates or number
# of students is 0
if (m==0 or n==0):
return 0
# Sort the given packets
arr.sort()
# Number of students cannot be more than
# number of packets
if (n < m):
return -1
# Largest number of chocolates
min_diff = arr[n-1] - arr[0]
# Find the subarray of size m such that
# difference between last (maximum in case
# of sorted) and first (minimum in case of
# sorted) elements of subarray is minimum.
for i in range(len(arr) - m + 1):
min_diff = min(min_diff , arr[i + m - 1] - arr[i])
return min_diff
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [12, 4, 7, 9, 2, 23, 25, 41,
30, 40, 28, 42, 30, 44, 48,
43, 50]
m = 7 # Number of students
n = len(arr)
print("Minimum difference is", findMinDiff(arr, n, m))
#This code is contributed by Smitha
C#
// C# Code For Chocolate Distribution
// Problem
using System;
class GFG {
// arr[0..n-1] represents sizes of
// packets. m is number of students.
// Returns minimum difference between
// maximum and minimum values of
// distribution.
static int findMinDiff(int []arr, int n,
int m)
{
// if there are no chocolates or
// number of students is 0
if (m == 0 || n == 0)
return 0;
// Sort the given packets
Array.Sort(arr);
// Number of students cannot be
// more than number of packets
if (n < m)
return -1;
// Largest number of chocolates
int min_diff = int.MaxValue;
// Find the subarray of size m
// such that difference between
// last (maximum in case of
// sorted) and first (minimum in
// case of sorted) elements of
// subarray is minimum.
for (int i = 0; i + m - 1 < n; i++)
{
int diff = arr[i+m-1] - arr[i];
if (diff < min_diff)
min_diff = diff;
}
return min_diff;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
public static void Main()
{
int []arr = {12, 4, 7, 9, 2, 23,
25, 41, 30, 40, 28,
42, 30, 44, 48, 43,
50};
int m = 7; // Number of students
int n = arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine("Minimum difference is "
+ findMinDiff(arr, n, m));
}
}
// This code is contributed by vt_m.
PHP
<?php
// PHP program to solve
// chocolate distribution
// problem
// arr[0..n-1] represents
// sizes of packets m is
// number of students.
// Returns minimum difference
// between maximum and minimum
// values of distribution.
function findMinDiff($arr, $n, $m)
{
// if there are no
// chocolates or number
// of students is 0
if ($m == 0 || $n == 0)
return 0;
// Sort the given packets
sort($arr);
// Number of students
// cannot be more than
// number of packets
if ($n < $m)
return -1;
// Largest number
// of chocolates
$min_diff = PHP_INT_MAX;
// Find the subarray of size
// m such that difference
// between last (maximum in
// case of sorted) and first
// (minimum in case of sorted)
// elements of subarray is minimum.
for ($i = 0;
$i + $m - 1 < $n; $i++)
{
$diff = $arr[$i + $m - 1] -
$arr[$i];
if ($diff < $min_diff)
$min_diff = $diff;
}
return $min_diff;
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(12, 4, 7, 9, 2, 23,
25, 41, 30, 40, 28,
42, 30, 44, 48, 43, 50);
$m = 7; // Number of students
$n = sizeof($arr);
echo "Minimum difference is ",
findMinDiff($arr, $n, $m);
// This code is contributed by ajit
?>
Javascript
<script>
// Javascript Code For Chocolate
// Distribution Problem
// arr[0..n-1] represents sizes of
// packets. m is number of students.
// Returns minimum difference between
// maximum and minimum values of
// distribution.
function findMinDiff(arr, n, m)
{
// If there are no chocolates or
// number of students is 0
if (m == 0 || n == 0)
return 0;
// Sort the given packets
arr.sort(function(a, b){return a - b});
// Number of students cannot be
// more than number of packets
if (n < m)
return -1;
// Largest number of chocolates
let min_diff = Number.MAX_VALUE;
// Find the subarray of size m
// such that difference between
// last (maximum in case of
// sorted) and first (minimum in
// case of sorted) elements of
// subarray is minimum.
for(let i = 0; i + m - 1 < n; i++)
{
let diff = arr[i + m - 1] - arr[i];
if (diff < min_diff)
min_diff = diff;
}
return min_diff;
}
// Driver code
let arr = [ 12, 4, 7, 9, 2, 23, 25,
41, 30, 40, 28, 42, 30,
44, 48, 43, 50 ];
// Number of students
let m = 7;
let n = arr.length;
document.write("Minimum difference is " +
findMinDiff(arr, n, m));
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019
</script>
Minimum difference is 10
Complejidad de tiempo: O (n Log n) ya que aplicamos la clasificación antes de la búsqueda de subarreglo.
Espacio Auxiliar : O(1)
Este artículo es una contribución de Roshni Agarwal . Si te gusta GeeksforGeeks y te gustaría contribuir, también puedes escribir un artículo usando write.geeksforgeeks.org o enviar tu artículo por correo a review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. Vea su artículo que aparece en la página principal de GeeksforGeeks y ayude a otros Geeks.
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA
