Dada una expresión booleana con los siguientes símbolos.
Symbols
'T' ---> true
'F' ---> false
Y los siguientes operadores rellenos entre símbolos
Operators
& ---> boolean AND
| ---> boolean OR
^ ---> boolean XOR
Cuente la cantidad de formas en que podemos poner entre paréntesis la expresión para que el valor de expresión se evalúe como verdadero.
Deje que la entrada esté en forma de dos arrays, una contiene los símbolos (T y F) en orden y la otra contiene los operadores (&, | y ^}
Ejemplos:
Input: symbol[] = {T, F, T}
operator[] = {^, &}
Output: 2
The given expression is "T ^ F & T", it evaluates true
in two ways "((T ^ F) & T)" and "(T ^ (F & T))"
Input: symbol[] = {T, F, F}
operator[] = {^, |}
Output: 2
The given expression is "T ^ F | F", it evaluates true
in two ways "( (T ^ F) | F )" and "( T ^ (F | F) )".
Input: symbol[] = {T, T, F, T}
operator[] = {|, &, ^}
Output: 4
The given expression is "T | T & F ^ T", it evaluates true
in 4 ways ((T|T)&(F^T)), (T|(T&(F^T))), (((T|T)&F)^T)
and (T|((T&F)^T)).
Solución:
Sea T(i, j) la cantidad de formas de poner entre paréntesis los símbolos entre i y j (ambos inclusive) de modo que la subexpresión entre i y j se evalúe como verdadera.
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com T(i,j)=\sum_{k=i}^{j-1}\begin{Bmatrix} T(i,k)*T(k+1,j) & if&operator&[k]is '\&'\\ Total(i,k)*Total(k+1,j)-F(i,k)*F(k+1,j) &if&operator&[k]&is'|' \\ T(i,k)*F(k+1,j)+F(i,k)*T(k+1,j) &if&operator&[k]&is '\oplus' \end{Bmatrix} Total(i,j)= T(i,j)+F(i,j)](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2c3532cf5fe1e00d5f358bb49773e154_l3.png)

Sea F(i, j) la cantidad de formas de poner entre paréntesis los símbolos entre i y j (inclusive) de modo que la subexpresión entre i y j se evalúe como falsa.![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com F(i,j)=\sum_{k=i}^{j-1} \begin{Bmatrix} Total(i,k)*Total(k+1,j)-T(i,k)*T(k+1,j) & if&operator[k]&is'\&'\\ F(i,k)*F(k+1,j) &if&operator[k] &is'|' \\ T(i,k)*T(k+1,j)+F(i,k)*F(k+1,j) &if&operator[k]&is'\oplus' \end{Bmatrix} Total(i,j)=T(i,j)+F(i,j)](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-bf692c3a737b1bd5b5fedfc5c5889c02_l3.png)
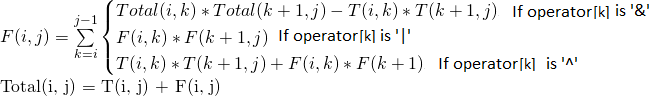
Casos básicos:
T(i, i) = 1 if symbol[i] = 'T' T(i, i) = 0 if symbol[i] = 'F' F(i, i) = 1 if symbol[i] = 'F' F(i, i) = 0 if symbol[i] = 'T'
Si dibujamos el árbol recursivo de la solución recursiva anterior, podemos observar que tiene muchos subproblemas superpuestos. Al igual que otros problemas de programación dinámica , se puede resolver llenando una tabla de forma ascendente. A continuación se muestra la implementación de una solución de programación dinámica.
C++
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Returns count of all possible
// parenthesizations that lead
// to result true for a boolean
// expression with symbols like
// true and false and operators
// like &, | and ^ filled
// between symbols
int countParenth(char symb[], char oper[], int n)
{
int F[n][n], T[n][n];
// Fill diagonal entries first
// All diagonal entries in
// T[i][i] are 1 if symbol[i]
// is T (true). Similarly,
// all F[i][i] entries are 1 if
// symbol[i] is F (False)
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
F[i][i] = (symb[i] == 'F') ? 1 : 0;
T[i][i] = (symb[i] == 'T') ? 1 : 0;
}
// Now fill T[i][i+1],
// T[i][i+2], T[i][i+3]... in order
// And F[i][i+1], F[i][i+2],
// F[i][i+3]... in order
for (int gap = 1; gap < n; ++gap)
{
for (int i = 0, j = gap;
j < n; ++i, ++j)
{
T[i][j] = F[i][j] = 0;
for (int g = 0;
g < gap; g++)
{
// Find place of parenthesization using
// current value of gap
int k = i + g;
// Store Total[i][k]
// and Total[k+1][j]
int tik = T[i][k] + F[i][k];
int tkj = T[k + 1][j]
+ F[k + 1][j];
// Follow the recursive formulas
// according
// to the current operator
if (oper[k] == '&') {
T[i][j] += T[i][k]
* T[k + 1][j];
F[i][j] += (tik * tkj
- T[i][k]
* T[k + 1][j]);
}
if (oper[k] == '|') {
F[i][j] += F[i][k]
* F[k + 1][j];
T[i][j] += (tik * tkj
- F[i][k]
* F[k + 1][j]);
}
if (oper[k] == '^') {
T[i][j] += F[i][k]
* T[k + 1][j]
+ T[i][k]
* F[k + 1][j];
F[i][j] += T[i][k]
* T[k + 1][j]
+ F[i][k] * F[k + 1][j];
}
}
}
}
return T[0][n - 1];
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
char symbols[] = "TTFT";
char operators[] = "|&^";
int n = strlen(symbols);
// There are 4 ways
// ((T|T)&(F^T)), (T|(T&(F^T))), (((T|T)&F)^T) and
// (T|((T&F)^T))
cout << countParenth(symbols, operators, n);
return 0;
}
Java
class GFG {
// Returns count of all possible
// parenthesizations that lead to
// result true for a boolean
// expression with symbols like true
// and false and operators like &, |
// and ^ filled between symbols
static int countParenth(char symb[],
char oper[],
int n)
{
int F[][] = new int[n][n];
int T[][] = new int[n][n];
// Fill diagonal entries first
// All diagonal entries in T[i][i]
// are 1 if symbol[i] is T (true).
// Similarly, all F[i][i] entries
// are 1 if symbol[i] is F (False)
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
F[i][i] = (symb[i] == 'F') ? 1 : 0;
T[i][i] = (symb[i] == 'T') ? 1 : 0;
}
// Now fill T[i][i+1], T[i][i+2],
// T[i][i+3]... in order And F[i][i+1],
// F[i][i+2], F[i][i+3]... in order
for (int gap = 1; gap < n; ++gap)
{
for (int i = 0,
j = gap; j < n;
++i, ++j)
{
T[i][j] = F[i][j] = 0;
for (int g = 0; g < gap; g++)
{
// Find place of parenthesization
// using current value of gap
int k = i + g;
// Store Total[i][k]
// and Total[k+1][j]
int tik = T[i][k]
+ F[i][k];
int tkj = T[k + 1][j]
+ F[k + 1][j];
// Follow the recursive formulas
// according to the current operator
if (oper[k] == '&')
{
T[i][j] += T[i][k]
* T[k + 1][j];
F[i][j]
+= (tik * tkj
- T[i][k]
* T[k + 1][j]);
}
if (oper[k] == '|')
{
F[i][j] += F[i][k]
* F[k + 1][j];
T[i][j]
+= (tik * tkj
- F[i][k]
* F[k + 1][j]);
}
if (oper[k] == '^')
{
T[i][j] += F[i][k]
* T[k + 1][j]
+ T[i][k]
* F[k + 1][j];
F[i][j] += T[i][k]
* T[k + 1][j]
+ F[i][k]
* F[k + 1][j];
}
}
}
}
return T[0][n - 1];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
char symbols[] = "TTFT".toCharArray();
char operators[] = "|&^".toCharArray();
int n = symbols.length;
// There are 4 ways
// ((T|T)&(F^T)), (T|(T&(F^T))),
// (((T|T)&F)^T) and (T|((T&F)^T))
System.out.println(
countParenth(symbols, operators, n));
}
}
// This code has been contributed
// by 29AjayKumar
Python
# Returns count of all possible # parenthesizations that lead to # result true for a boolean # expression with symbols like # true and false and operators # like &, | and ^ filled between symbols def countParenth(symb, oper, n): F = [[0 for i in range(n + 1)] for i in range(n + 1)] T = [[0 for i in range(n + 1)] for i in range(n + 1)] # Fill diagonal entries first # All diagonal entries in # T[i][i] are 1 if symbol[i] # is T (true). Similarly, all # F[i][i] entries are 1 if # symbol[i] is F (False) for i in range(n): if symb[i] == 'F': F[i][i] = 1 else: F[i][i] = 0 if symb[i] == 'T': T[i][i] = 1 else: T[i][i] = 0 # Now fill T[i][i+1], T[i][i+2], # T[i][i+3]... in order And # F[i][i+1], F[i][i+2], # F[i][i+3]... in order for gap in range(1, n): i = 0 for j in range(gap, n): T[i][j] = F[i][j] = 0 for g in range(gap): # Find place of parenthesization # using current value of gap k = i + g # Store Total[i][k] and Total[k+1][j] tik = T[i][k] + F[i][k] tkj = T[k + 1][j] + F[k + 1][j] # Follow the recursive formulas # according to the current operator if oper[k] == '&': T[i][j] += T[i][k] * T[k + 1][j] F[i][j] += (tik * tkj - T[i][k] * T[k + 1][j]) if oper[k] == '|': F[i][j] += F[i][k] * F[k + 1][j] T[i][j] += (tik * tkj - F[i][k] * F[k + 1][j]) if oper[k] == '^': T[i][j] += (F[i][k] * T[k + 1][j] + T[i][k] * F[k + 1][j]) F[i][j] += (T[i][k] * T[k + 1][j] + F[i][k] * F[k + 1][j]) i += 1 return T[0][n - 1] # Driver Code symbols = "TTFT" operators = "|&^" n = len(symbols) # There are 4 ways # ((T|T)&(F^T)), (T|(T&(F^T))), # (((T|T)&F)^T) and (T|((T&F)^T)) print(countParenth(symbols, operators, n)) # This code is contributed by # sahil shelangia
C#
// C# program of above approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// Returns count of all possible
// parenthesizations that lead to
// result true for a boolean
// expression with symbols like true
// and false and operators like &, |
// and ^ filled between symbols
static int countParenth(char []symb,
char []oper, int n)
{
int [,]F = new int[n, n];
int [,]T = new int[n, n];
// Fill diagonal entries first
// All diagonal entries in T[i,i]
// are 1 if symbol[i] is T (true).
// Similarly, all F[i,i] entries
// are 1 if symbol[i] is F (False)
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
F[i,i] = (symb[i] == 'F') ? 1 : 0;
T[i,i] = (symb[i] == 'T') ? 1 : 0;
}
// Now fill T[i,i+1], T[i,i+2],
// T[i,i+3]... in order And F[i,i+1],
// F[i,i+2], F[i,i+3]... in order
for (int gap = 1; gap < n; ++gap)
{
for (int i = 0, j = gap; j < n; ++i, ++j)
{
T[i, j] = F[i, j] = 0;
for (int g = 0; g < gap; g++)
{
// Find place of parenthesization
// using current value of gap
int k = i + g;
// Store Total[i,k] and Total[k+1,j]
int tik = T[i, k] + F[i, k];
int tkj = T[k + 1, j] + F[k + 1, j];
// Follow the recursive formulas
// according to the current operator
if (oper[k] == '&')
{
T[i, j] += T[i, k]
* T[k + 1, j];
F[i, j] += (tik * tkj
- T[i, k] * T[k + 1, j]);
}
if (oper[k] == '|')
{
F[i,j] += F[i, k]
* F[k + 1, j];
T[i,j] += (tik
* tkj - F[i, k]
* F[k + 1, j]);
}
if (oper[k] == '^')
{
T[i, j] += F[i, k] * T[k + 1, j] +
T[i, k] * F[k + 1, j];
F[i, j] += T[i, k] * T[k + 1, j] +
F[i, k] * F[k + 1, j];
}
}
}
}
return T[0,n - 1];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
char []symbols = "TTFT".ToCharArray();
char []operators = "|&^".ToCharArray();
int n = symbols.Length;
// There are 4 ways
// ((T|T)&(F^T)), (T|(T&(F^T))),
// (((T|T)&F)^T) and (T|((T&F)^T))
Console.WriteLine(countParenth(symbols,
operators, n));
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */
Javascript
<script>
// Returns count of all possible
// parenthesizations that lead to
// result true for a boolean
// expression with symbols like true
// and false and operators like &, |
// and ^ filled between symbols
function countParenth(symb, oper, n)
{
let F = new Array(n);
let T = new Array(n);
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
F[i] = new Array(n);
T[i] = new Array(n);
for(let j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
F[i][j] = 0;
T[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// Fill diagonal entries first
// All diagonal entries in T[i][i]
// are 1 if symbol[i] is T (true).
// Similarly, all F[i][i] entries
// are 1 if symbol[i] is F (False)
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
F[i][i] = (symb[i] == 'F') ? 1 : 0;
T[i][i] = (symb[i] == 'T') ? 1 : 0;
}
// Now fill T[i][i+1], T[i][i+2],
// T[i][i+3]... in order And F[i][i+1],
// F[i][i+2], F[i][i+3]... in order
for (let gap = 1; gap < n; ++gap)
{
for (let i = 0,
j = gap; j < n;
++i, ++j)
{
T[i][j] = F[i][j] = 0;
for (let g = 0; g < gap; g++)
{
// Find place of parenthesization
// using current value of gap
let k = i + g;
// Store Total[i][k]
// and Total[k+1][j]
let tik = T[i][k]
+ F[i][k];
let tkj = T[k + 1][j]
+ F[k + 1][j];
// Follow the recursive formulas
// according to the current operator
if (oper[k] == '&')
{
T[i][j] += T[i][k]
* T[k + 1][j];
F[i][j]
+= (tik * tkj
- T[i][k]
* T[k + 1][j]);
}
if (oper[k] == '|')
{
F[i][j] += F[i][k]
* F[k + 1][j];
T[i][j]
+= (tik * tkj
- F[i][k]
* F[k + 1][j]);
}
if (oper[k] == '^')
{
T[i][j] += F[i][k]
* T[k + 1][j]
+ T[i][k]
* F[k + 1][j];
F[i][j] += T[i][k]
* T[k + 1][j]
+ F[i][k]
* F[k + 1][j];
}
}
}
}
return T[0][n - 1];
}
let symbols = "TTFT".split('');
let operators = "|&^".split('');
let n = symbols.length;
// There are 4 ways
// ((T|T)&(F^T)), (T|(T&(F^T))),
// (((T|T)&F)^T) and (T|((T&F)^T))
document.write(countParenth(symbols, operators, n));
// This code is contributed by mukesh07.
</script>
Producción:
4
Complejidad de tiempo: O(n 3 ), ya que estamos usando bucles anidados para atravesar n 3 veces. Donde n es la longitud de la string de símbolos.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(n 2 ), ya que estamos usando espacio extra para la array DP. Donde n es la longitud de la string de símbolos.
Enfoque 2:
También podemos usar el enfoque recursivo (Top-Down DP), este enfoque usa la memorización.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int dp[101][101][2];
int parenthesis_count(string s,
int i,
int j,
int isTrue)
{
// Base Condition
if (i > j)
return false;
if (i == j) {
if (isTrue == 1)
return s[i] == 'T';
else
return s[i] == 'F';
}
if (dp[i][j][isTrue] != -1)
return dp[i][j][isTrue];
int ans = 0;
for (int k = i + 1
; k <= j - 1; k = k + 2)
{
int leftF, leftT, rightT, rightF;
if (dp[i][k - 1][1] == -1)
{
leftT = parenthesis_count(s, i, k - 1, 1);
} // Count no. of T in left partition
else {
leftT = dp[i][k - 1][1];
}
if (dp[k + 1][j][1] == -1)
{
rightT = parenthesis_count(s, k + 1, j, 1);
} // Count no. of T in right partition
else
{
rightT = dp[k + 1][j][1];
}
if (dp[i][k - 1][0] == -1)
{
// Count no. of F in left partition
leftF = parenthesis_count(s, i, k - 1, 0);
}
else
{
leftF = dp[i][k - 1][0];
}
if (dp[k + 1][j][0] == -1)
{
// Count no. of F in right partition
rightF = parenthesis_count(s, k + 1, j, 0);
}
else
{
rightF = dp[k + 1][j][0];
}
if (s[k] == '&')
{
if (isTrue == 1)
ans += leftT * rightT;
else
ans += leftF * rightF + leftT * rightF
+ leftF * rightT;
}
else if (s[k] == '|')
{
if (isTrue == 1)
ans += leftT * rightT + leftT * rightF
+ leftF * rightT;
else
ans = ans + leftF * rightF;
}
else if (s[k] == '^')
{
if (isTrue == 1)
ans = ans + leftF * rightT + leftT * rightF;
else
ans = ans + leftT * rightT + leftF * rightF;
}
dp[i][j][isTrue] = ans;
}
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
string symbols = "TTFT";
string operators = "|&^";
string s;
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < symbols.length(); i++)
{
s.push_back(symbols[i]);
if (j < operators.length())
s.push_back(operators[j++]);
}
// We obtain the string T|T&F^T
int n = s.length();
// There are 4 ways
// ((T|T)&(F^T)), (T|(T&(F^T))), (((T|T)&F)^T) and
// (T|((T&F)^T))
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
cout << parenthesis_count(s, 0, n - 1, 1);
return 0;
}
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static int countWays(int N, String S)
{
int dp[][][] = new int[N + 1][N + 1][2];
for (int row[][] : dp)
for (int col[] : row)
Arrays.fill(col, -1);
return parenthesis_count(S, 0, N - 1, 1, dp);
}
public static int parenthesis_count(String str, int i,
int j, int isTrue,
int[][][] dp)
{
if (i > j)
return 0;
if (i == j)
{
if (isTrue == 1)
{
return (str.charAt(i) == 'T') ? 1 : 0;
}
else
{
return (str.charAt(i) == 'F') ? 1 : 0;
}
}
if (dp[i][j][isTrue] != -1)
return dp[i][j][isTrue];
int temp_ans = 0;
int leftTrue, rightTrue, leftFalse, rightFalse;
for (int k = i + 1; k <= j - 1; k = k + 2)
{
if (dp[i][k - 1][1] != -1)
leftTrue = dp[i][k - 1][1];
else
{
// Count number of True in left Partition
leftTrue = parenthesis_count(str, i, k - 1,
1, dp);
}
if (dp[i][k - 1][0] != -1)
leftFalse = dp[i][k - 1][0];
else
{
// Count number of False in left Partition
leftFalse = parenthesis_count(str, i, k - 1,
0, dp);
}
if (dp[k + 1][j][1] != -1)
rightTrue = dp[k + 1][j][1];
else
{
// Count number of True in right Partition
rightTrue = parenthesis_count(str, k + 1, j,
1, dp);
}
if (dp[k + 1][j][0] != -1)
rightFalse = dp[k + 1][j][0];
else
{
// Count number of False in right Partition
rightFalse = parenthesis_count(str, k + 1,
j, 0, dp);
}
// Evaluate AND operation
if (str.charAt(k) == '&')
{
if (isTrue == 1)
{
temp_ans
= temp_ans + leftTrue * rightTrue;
}
else
{
temp_ans = temp_ans
+ leftTrue * rightFalse
+ leftFalse * rightTrue
+ leftFalse * rightFalse;
}
}
// Evaluate OR operation
else if (str.charAt(k) == '|')
{
if (isTrue == 1)
{
temp_ans = temp_ans
+ leftTrue * rightTrue
+ leftTrue * rightFalse
+ leftFalse * rightTrue;
}
else
{
temp_ans
= temp_ans + leftFalse * rightFalse;
}
}
// Evaluate XOR operation
else if (str.charAt(k) == '^')
{
if (isTrue == 1)
{
temp_ans = temp_ans
+ leftTrue * rightFalse
+ leftFalse * rightTrue;
}
else
{
temp_ans = temp_ans
+ leftTrue * rightTrue
+ leftFalse * rightFalse;
}
}
dp[i][j][isTrue] = temp_ans;
}
return temp_ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String symbols = "TTFT";
String operators = "|&^";
StringBuilder S = new StringBuilder();
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < symbols.length(); i++)
{
S.append(symbols.charAt(i));
if (j < operators.length())
S.append(operators.charAt(j++));
}
// We obtain the string T|T&F^T
int N = S.length();
// There are 4 ways
// ((T|T)&(F^T)), (T|(T&(F^T))), (((T|T)&F)^T) and
// (T|((T&F)^T))
System.out.println(countWays(N, S.toString()));
}
}
// This code is contributed by farheenbano.
Python3
def parenthesis_count(Str, i, j, isTrue, dp) : if (i > j) : return 0 if (i == j) : if (isTrue == 1) : return 1 if Str[i] == 'T' else 0 else : return 1 if Str[i] == 'F' else 0 if (dp[i][j][isTrue] != -1) : return dp[i][j][isTrue] temp_ans = 0 for k in range(i + 1, j, 2) : if (dp[i][k - 1][1] != -1) : leftTrue = dp[i][k - 1][1] else : # Count number of True in left Partition leftTrue = parenthesis_count(Str, i, k - 1, 1, dp) if (dp[i][k - 1][0] != -1) : leftFalse = dp[i][k - 1][0] else : # Count number of False in left Partition leftFalse = parenthesis_count(Str, i, k - 1, 0, dp) if (dp[k + 1][j][1] != -1) : rightTrue = dp[k + 1][j][1] else : # Count number of True in right Partition rightTrue = parenthesis_count(Str, k + 1, j, 1, dp) if (dp[k + 1][j][0] != -1) : rightFalse = dp[k + 1][j][0] else : # Count number of False in right Partition rightFalse = parenthesis_count(Str, k + 1, j, 0, dp) # Evaluate AND operation if (Str[k] == '&') : if (isTrue == 1) : temp_ans = temp_ans + leftTrue * rightTrue else : temp_ans = temp_ans + leftTrue * rightFalse + leftFalse * rightTrue + leftFalse * rightFalse # Evaluate OR operation elif (Str[k] == '|') : if (isTrue == 1) : temp_ans = temp_ans + leftTrue * rightTrue + leftTrue * rightFalse + leftFalse * rightTrue else : temp_ans = temp_ans + leftFalse * rightFalse # Evaluate XOR operation elif (Str[k] == '^') : if (isTrue == 1) : temp_ans = temp_ans + leftTrue * rightFalse + leftFalse * rightTrue else : temp_ans = temp_ans + leftTrue * rightTrue + leftFalse * rightFalse dp[i][j][isTrue] = temp_ans return temp_ans def countWays(N, S) : dp = [[[-1 for k in range(2)] for i in range(N + 1)] for j in range(N + 1)] return parenthesis_count(S, 0, N - 1, 1, dp) symbols = "TTFT" operators = "|&^" S = "" j = 0 for i in range(len(symbols)) : S = S + symbols[i] if (j < len(operators)) : S = S + operators[j] j += 1 # We obtain the string T|T&F^T N = len(S) # There are 4 ways # ((T|T)&(F^T)), (T|(T&(F^T))), (((T|T)&F)^T) and # (T|((T&F)^T)) print(countWays(N, S)) # This code is contributed by divyesh072019
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int parenthesis_count(string str, int i,
int j, int isTrue,
int[,,] dp)
{
if (i > j)
return 0;
if (i == j)
{
if (isTrue == 1)
{
return (str[i] == 'T') ? 1 : 0;
}
else
{
return (str[i] == 'F') ? 1 : 0;
}
}
if (dp[i, j, isTrue] != -1)
return dp[i, j, isTrue];
int temp_ans = 0;
int leftTrue, rightTrue, leftFalse, rightFalse;
for (int k = i + 1; k <= j - 1; k = k + 2)
{
if (dp[i, k - 1, 1] != -1)
leftTrue = dp[i, k - 1, 1];
else
{
// Count number of True in left Partition
leftTrue = parenthesis_count(str, i, k - 1, 1, dp);
}
if (dp[i, k - 1, 0] != -1)
leftFalse = dp[i, k - 1, 0];
else
{
// Count number of False in left Partition
leftFalse = parenthesis_count(str, i, k - 1, 0, dp);
}
if (dp[k + 1, j, 1] != -1)
rightTrue = dp[k + 1, j, 1];
else
{
// Count number of True in right Partition
rightTrue = parenthesis_count(str, k + 1, j,
1, dp);
}
if (dp[k + 1, j, 0] != -1)
rightFalse = dp[k + 1, j, 0];
else
{
// Count number of False in right Partition
rightFalse = parenthesis_count(str, k + 1,
j, 0, dp);
}
// Evaluate AND operation
if (str[k] == '&')
{
if (isTrue == 1)
{
temp_ans
= temp_ans + leftTrue * rightTrue;
}
else
{
temp_ans = temp_ans
+ leftTrue * rightFalse
+ leftFalse * rightTrue
+ leftFalse * rightFalse;
}
}
// Evaluate OR operation
else if (str[k] == '|')
{
if (isTrue == 1)
{
temp_ans = temp_ans
+ leftTrue * rightTrue
+ leftTrue * rightFalse
+ leftFalse * rightTrue;
}
else
{
temp_ans
= temp_ans + leftFalse * rightFalse;
}
}
// Evaluate XOR operation
else if (str[k] == '^')
{
if (isTrue == 1)
{
temp_ans = temp_ans
+ leftTrue * rightFalse
+ leftFalse * rightTrue;
}
else
{
temp_ans = temp_ans
+ leftTrue * rightTrue
+ leftFalse * rightFalse;
}
}
dp[i, j, isTrue] = temp_ans;
}
return temp_ans;
}
static int countWays(int N, string S)
{
int[,,] dp = new int[N + 1, N + 1, 2];
for(int i = 0; i < (N + 1); i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < (N + 1); j++)
{
for(int k = 0; k < 2; k++)
{
dp[i, j, k] = -1;
}
}
}
return parenthesis_count(S, 0, N - 1, 1, dp);
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
string symbols = "TTFT";
string operators = "|&^";
string S = "";
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < symbols.Length; i++)
{
S = S + symbols[i];
if (j < operators.Length)
S = S + operators[j++];
}
// We obtain the string T|T&F^T
int N = S.Length;
// There are 4 ways
// ((T|T)&(F^T)), (T|(T&(F^T))), (((T|T)&F)^T) and
// (T|((T&F)^T))
Console.WriteLine(countWays(N, S));
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07.
Javascript
<script>
function countWays(N, S)
{
let dp = new Array(N + 1);
for(let i = 0; i < N + 1; i++)
{
dp[i] = new Array(N+1);
for(let j = 0; j < N + 1;j++)
{
dp[i][j] = new Array(2);
for(let k = 0; k < 2; k++)
dp[i][j][k] = -1;
}
}
return parenthesis_count(S, 0, N - 1, 1, dp);
}
function parenthesis_count(str, i, j, isTrue, dp)
{
if (i > j)
return 0;
if (i == j)
{
if (isTrue == 1)
{
return (str[i] == 'T') ? 1 : 0;
}
else
{
return (str[i] == 'F') ? 1 : 0;
}
}
if (dp[i][j][isTrue] != -1)
return dp[i][j][isTrue];
let temp_ans = 0;
let leftTrue, rightTrue, leftFalse, rightFalse;
for (let k = i + 1; k <= j - 1; k = k + 2)
{
if (dp[i][k - 1][1] != -1)
leftTrue = dp[i][k - 1][1];
else
{
// Count number of True in left Partition
leftTrue = parenthesis_count(str, i, k - 1,
1, dp);
}
if (dp[i][k - 1][0] != -1)
leftFalse = dp[i][k - 1][0];
else
{
// Count number of False in left Partition
leftFalse = parenthesis_count(str, i, k - 1,
0, dp);
}
if (dp[k + 1][j][1] != -1)
rightTrue = dp[k + 1][j][1];
else
{
// Count number of True in right Partition
rightTrue = parenthesis_count(str, k + 1, j,
1, dp);
}
if (dp[k + 1][j][0] != -1)
rightFalse = dp[k + 1][j][0];
else
{
// Count number of False in right Partition
rightFalse = parenthesis_count(str, k + 1,
j, 0, dp);
}
// Evaluate AND operation
if (str[k] == '&')
{
if (isTrue == 1)
{
temp_ans
= temp_ans + leftTrue * rightTrue;
}
else
{
temp_ans = temp_ans
+ leftTrue * rightFalse
+ leftFalse * rightTrue
+ leftFalse * rightFalse;
}
}
// Evaluate OR operation
else if (str[k] == '|')
{
if (isTrue == 1)
{
temp_ans = temp_ans
+ leftTrue * rightTrue
+ leftTrue * rightFalse
+ leftFalse * rightTrue;
}
else
{
temp_ans
= temp_ans + leftFalse * rightFalse;
}
}
// Evaluate XOR operation
else if (str[k] == '^')
{
if (isTrue == 1)
{
temp_ans = temp_ans
+ leftTrue * rightFalse
+ leftFalse * rightTrue;
}
else
{
temp_ans = temp_ans
+ leftTrue * rightTrue
+ leftFalse * rightFalse;
}
}
dp[i][j][isTrue] = temp_ans;
}
return temp_ans;
}
// Driver code
let symbols = "TTFT";
let operators = "|&^";
let S = [];
let j = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < symbols.length; i++)
{
S.push(symbols[i]);
if (j < operators.length)
S.push(operators[j++]);
}
// We obtain the string T|T&F^T
let N = S.length;
// There are 4 ways
// ((T|T)&(F^T)), (T|(T&(F^T))), (((T|T)&F)^T) and
// (T|((T&F)^T))
document.write(countWays(N, S.join("")));
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
4
Complejidad de tiempo: O(n 3 ), ya que estamos usando un bucle para atravesar, n veces y estamos haciendo llamadas recursivas que costarán n 2 veces. Donde n es la longitud de la string de símbolos.
Espacio Auxiliar: O(n 2 ), ya que estamos usando espacio extra para la array DP. Donde n es la longitud de la string de símbolos.
Referencias:
http://people.cs.clemson.edu/~bcdean/dp_practice/dp_9.swf
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA