El problema de partición es determinar si un conjunto dado se puede dividir en dos subconjuntos de manera que la suma de los elementos en ambos subconjuntos sea la misma.
Ejemplos:
arr[] = {1, 5, 11, 5}
Output: true
The array can be partitioned as {1, 5, 5} and {11}
arr[] = {1, 5, 3}
Output: false
The array cannot be partitioned into equal sum sets.
Le recomendamos encarecidamente que haga clic aquí y lo practique antes de pasar a la solución.
Los siguientes son los dos pasos principales para resolver este problema:
1) Calcular la suma de la array. Si la suma es impar, no puede haber dos subconjuntos con la misma suma, por lo que devuelve falso.
2) Si la suma de los elementos del arreglo es par, calcule sum/2 y encuentre un subconjunto del arreglo con sum igual a sum/2.
El primer paso es simple. El segundo paso es crucial, se puede resolver usando recursividad o Programación Dinámica.
Solución recursiva
A continuación se muestra la propiedad recursiva del segundo paso mencionado anteriormente.
Let isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum/2) be the function that returns true if
there is a subset of arr[0..n-1] with sum equal to sum/2
The isSubsetSum problem can be divided into two subproblems
a) isSubsetSum() without considering last element
(reducing n to n-1)
b) isSubsetSum considering the last element
(reducing sum/2 by arr[n-1] and n to n-1)
If any of the above subproblems return true, then return true.
isSubsetSum (arr, n, sum/2) = isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum/2) ||
isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum/2 - arr[n-1])
A continuación se muestra la implementación del código anterior:
C++
// A recursive C++ program for partition problem
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A utility function that returns true if there is
// a subset of arr[] with sum equal to given sum
bool isSubsetSum(int arr[], int n, int sum)
{
// Base Cases
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
// If last element is greater than sum, then
// ignore it
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum);
/* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element
*/
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1]);
}
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
// Calculate sum of the elements in array
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
// If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
// with equal sum
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
// Find if there is subset with sum equal to
// half of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
cout << "Can be divided into two subsets "
"of equal sum";
else
cout << "Can not be divided into two subsets"
" of equal sum";
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
// A recursive C program for partition problem
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
// A utility function that returns true if there is
// a subset of arr[] with sum equal to given sum
bool isSubsetSum(int arr[], int n, int sum)
{
// Base Cases
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
// If last element is greater than sum, then
// ignore it
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum);
/* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element
*/
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1]);
}
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
// Calculate sum of the elements in array
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
// If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
// with equal sum
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
// Find if there is subset with sum equal to
// half of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
printf("Can be divided into two subsets "
"of equal sum");
else
printf("Can not be divided into two subsets"
" of equal sum");
return 0;
}
Java
// A recursive Java solution for partition problem
import java.io.*;
class Partition {
// A utility function that returns true if there is a
// subset of arr[] with sum equal to given sum
static boolean isSubsetSum(int arr[], int n, int sum)
{
// Base Cases
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
// If last element is greater than sum, then ignore
// it
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum);
/* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element
*/
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1]);
}
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
static boolean findPartition(int arr[], int n)
{
// Calculate sum of the elements in array
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
// If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
// with equal sum
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
// Find if there is subset with sum equal to half
// of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = arr.length;
// Function call
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
System.out.println("Can be divided into two "
+ "subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println(
"Can not be divided into "
+ "two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Devesh Agrawal */
Python3
# A recursive Python3 program for
# partition problem
# A utility function that returns
# true if there is a subset of
# arr[] with sum equal to given sum
def isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum):
# Base Cases
if sum == 0:
return True
if n == 0 and sum != 0:
return False
# If last element is greater than sum, then
# ignore it
if arr[n-1] > sum:
return isSubsetSum(arr, n-1, sum)
''' else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element'''
return isSubsetSum(arr, n-1, sum) or isSubsetSum(arr, n-1, sum-arr[n-1])
# Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
# subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
def findPartion(arr, n):
# Calculate sum of the elements in array
sum = 0
for i in range(0, n):
sum += arr[i]
# If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
# with equal sum
if sum % 2 != 0:
return false
# Find if there is subset with sum equal to
# half of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum // 2)
# Driver code
arr = [3, 1, 5, 9, 12]
n = len(arr)
# Function call
if findPartion(arr, n) == True:
print("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
else:
print("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
# This code is contributed by shreyanshi_arun.
C#
// A recursive C# solution for partition problem
using System;
class GFG {
// A utility function that returns true if there is a
// subset of arr[] with sum equal to given sum
static bool isSubsetSum(int[] arr, int n, int sum)
{
// Base Cases
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
// If last element is greater than sum, then ignore
// it
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum);
/* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element
*/
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1]);
}
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
static bool findPartition(int[] arr, int n)
{
// Calculate sum of the elements in array
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
// If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
// with equal sum
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
// Find if there is subset with sum equal to half
// of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = arr.Length;
// Function call
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
Console.Write("Can be divided into two "
+ "subsets of equal sum");
else
Console.Write("Can not be divided into "
+ "two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007
PHP
<?php
// A recursive PHP solution for partition problem
// A utility function that returns true if there is
// a subset of arr[] with sum equal to given sum
function isSubsetSum ($arr, $n, $sum)
{
// Base Cases
if ($sum == 0)
return true;
if ($n == 0 && $sum != 0)
return false;
// If last element is greater than
// sum, then ignore it
if ($arr[$n - 1] > $sum)
return isSubsetSum ($arr, $n - 1, $sum);
/* else, check if sum can be obtained
by any of the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element
*/
return isSubsetSum ($arr, $n - 1, $sum) ||
isSubsetSum ($arr, $n - 1,
$sum - $arr[$n - 1]);
}
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
function findPartiion ($arr, $n)
{
// Calculate sum of the elements
// in array
$sum = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
$sum += $arr[$i];
// If sum is odd, there cannot be
// two subsets with equal sum
if ($sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
// Find if there is subset with sum
// equal to half of total sum
return isSubsetSum ($arr, $n, $sum / 2);
}
// Driver Code
$arr = array(3, 1, 5, 9, 12);
$n = count($arr);
// Function call
if (findPartiion($arr, $n) == true)
echo "Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum";
else
echo "Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum";
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
?>
Javascript
<script>
// A recursive Javascript solution for partition problem
// A utility function that returns true if there is a
// subset of arr[] with sum equal to given sum
function isSubsetSum(arr,n,sum)
{
// Base Cases
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
// If last element is greater than sum, then ignore
// it
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum);
/* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element
*/
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1]);
}
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
function findPartition(arr,n)
{
// Calculate sum of the elements in array
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
// If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
// with equal sum
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
// Find if there is subset with sum equal to half
// of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, Math.floor(sum / 2));
}
// Driver code
let arr=[3, 1, 5, 9, 12 ];
let n = arr.length;
// Function call
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
document.write("Can be divided into two "
+ "subsets of equal sum");
else
document.write(
"Can not be divided into "
+ "two subsets of equal sum");
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum
Complejidad temporal: O(2^n) En el peor de los casos, esta solución prueba dos posibilidades (ya sea incluir o excluir) para cada elemento.
Solución de Programación Dinámica
1. Top-Down: Memoización
Podemos evitar el trabajo repetido realizado en el método 1 almacenando el resultado calculado hasta ahora.
Solo necesitamos almacenar todos los valores en una array.
C++
// A recursive C++ program for partition problem
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A utility function that returns true if there is
// a subset of arr[] with sun equal to given sum
bool isSubsetSum(int arr[], int n, int sum,
vector<vector<int> >& dp)
{
// Base Cases
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
// return solved subproblem
if (dp[n][sum] != -1) {
return dp[n][sum];
}
// If last element is greater than sum, then
// ignore it
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp);
/* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element
*/
// also store the subproblem in dp matrix
return dp[n][sum]
= isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1],
dp);
}
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
// Calculate sum of the elements in array
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
// If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
// with equal sum
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
// To store overlapping subproblems
vector<vector<int> > dp(n + 1,
vector<int>(sum + 1, -1));
// Find if there is subset with sum equal to
// half of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2, dp);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
cout << "Can be divided into two subsets "
"of equal sum";
else
cout << "Can not be divided into two subsets"
" of equal sum";
int arr2[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 14 };
int n2 = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]);
if (findPartiion(arr2, n2) == true)
cout << endl
<< "Can be divided into two subsets "
"of equal sum";
else
cout << endl
<< "Can not be divided into two subsets"
" of equal sum";
return 0;
}
Python3
# A recursive JavaScript program for partition problem
# A utility function that returns true if there is
# a subset of arr[] with sun equal to given sum
def isSubsetSum(arr,n,sum,dp):
# Base Cases
if (sum == 0):
return True
if (n == 0 and sum != 0):
return False
# return solved subproblem
if (dp[n][sum] != -1):
return dp[n][sum]
# If last element is greater than sum, then
# ignore it
if (arr[n - 1] > sum):
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp)
# else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
# the following
# (a) including the last element
# (b) excluding the last element
# also store the subproblem in dp matrix
dp[n][sum] = isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp) or isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1], dp)
return dp[n][sum]
# Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
# subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
def findPartiion(arr, n):
# Calculate sum of the elements in array
sum = 0
for i in range(n):
sum += arr[i]
# If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
# with equal sum
if (sum % 2 != 0):
return False
# To store overlapping subproblems
dp = [[-1]*(sum+1)]*(n+1)
# Find if there is subset with sum equal to
# half of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum // 2, dp)
# Driver code
arr = [ 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 ]
n = len(arr)
# Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == True):
print("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
else:
print("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
arr2 = [ 3, 1, 5, 9, 14 ]
n2 = len(arr2)
if (findPartiion(arr2, n2) == True):
print("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
else:
print("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
# This code is contributed by shinjanpatra.
Javascript
<script>
// A recursive JavaScript program for partition problem
// A utility function that returns true if there is
// a subset of arr[] with sun equal to given sum
function isSubsetSum(arr,n,sum,dp)
{
// Base Cases
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
// return solved subproblem
if (dp[n][sum] != -1) {
return dp[n][sum];
}
// If last element is greater than sum, then
// ignore it
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp);
/* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element
*/
// also store the subproblem in dp matrix
return dp[n][sum]
= isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp)
|| isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1],
dp);
}
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
function findPartiion(arr, n)
{
// Calculate sum of the elements in array
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
// If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
// with equal sum
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
// To store overlapping subproblems
let dp = new Array(n + 1).fill(new Array(sum+1).fill(-1));
// Find if there is subset with sum equal to
// half of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2, dp);
}
// Driver code
let arr = [ 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 ];
let n = arr.length;
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
document.write("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else document.write("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
let arr2 = [ 3, 1, 5, 9, 14 ];
let n2 = arr2.length;
if (findPartiion(arr2, n2) == true)
document.write("</br>","Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else document.write("</br>","Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
// This code is contributed by shinjanpatra.
</script>
Java
// Java program for partition problem
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// A utility function that returns true if there is
// a subset of arr[] with sum equal to given sum
static boolean isSubsetSum(int arr[], int n, int sum, int[][] dp)
{
// Base Cases
if (sum == 0)
return true;
if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
return false;
// return solved subproblem
if (dp[n][sum] != -1) {
return dp[n][sum] == 1;
}
// If last element is greater than sum, then
// ignore it
if (arr[n - 1] > sum)
return isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp);
/* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
the following
(a) including the last element
(b) excluding the last element
*/
// also store the subproblem in dp matrix
if (isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp) || isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1], dp))
return true;
return false;
//return dp[n][sum] = isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum, dp) || isSubsetSum(arr, n - 1, sum - arr[n - 1], dp);
}
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
static boolean findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
// Calculate sum of the elements in array
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
// If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
// with equal sum
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
// To store overlapping subproblems
int dp[][] = new int[n+1][sum+1];
for (int row[] : dp)
Arrays.fill(row,-1);
// Find if there is subset with sum equal to
// half of total sum
return isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum / 2, dp);
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 12 };
int n = arr.length;
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
System.out.println("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
int arr2[] = { 3, 1, 5, 9, 14 };
int n2 = arr2.length;
if (findPartiion(arr2, n2) == true)
System.out.println("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum
Complejidad del tiempo: O(suma*n)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(suma*n)
2. De abajo hacia arriba: tabulación
El problema se puede resolver mediante programación dinámica cuando la suma de los elementos no es demasiado grande. Podemos crear una array 2D part[][] de tamaño (sum/2 + 1)*(n+1). Y podemos construir la solución de forma ascendente de modo que cada entrada completa tenga la siguiente propiedad
part[i][j] = true if a subset of {arr[0], arr[1], ..arr[j-1]} has sum
equal to i, otherwise false
C++
// A Dynamic Programming based
// C++ program to partition problem
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool part[sum / 2 + 1][n + 1];
// initialize top row as true
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0][i] = true;
// initialize leftmost column,
// except part[0][0], as 0
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i][0] = false;
// Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i][j] = part[i][j]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
/* // uncomment this part to print table
for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
cout<<part[i][j];
cout<<endl;
} */
return part[sum / 2][n];
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
cout << "Can be divided into two subsets of equal "
"sum";
else
cout << "Can not be divided into"
<< " two subsets of equal sum";
return 0;
}
C
// A Dynamic Programming based C program to partition
// problem
#include <stdio.h>
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two subsets
// of equal sum, otherwise false
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool part[sum / 2 + 1][n + 1];
// initialize top row as true
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0][i] = true;
// initialize leftmost column, except part[0][0], as 0
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i][0] = false;
// Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i][j] = part[i][j]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
/* // uncomment this part to print table
for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
printf ("%4d", part[i][j]);
printf("\n");
} */
return part[sum / 2][n];
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
printf(
"Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
else
printf("Can not be divided into two subsets of "
"equal sum");
getchar();
return 0;
}
Java
// A dynamic programming based Java program for partition
// problem
import java.io.*;
class Partition {
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
static boolean findPartition(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
boolean part[][] = new boolean[sum / 2 + 1][n + 1];
// initialize top row as true
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0][i] = true;
// initialize leftmost column, except part[0][0], as
// 0
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i][0] = false;
// Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i][j]
= part[i][j]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
/* // uncomment this part to print table
for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
printf ("%4d", part[i][j]);
printf("\n");
} */
return part[sum / 2][n];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.length;
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
System.out.println(
"Can be divided into two " "subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println(
"Can not be divided into" " two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Devesh Agrawal */
Python3
# Dynamic Programming based python
# program to partition problem
# Returns true if arr[] can be
# partitioned in two subsets of
# equal sum, otherwise false
def findPartition(arr, n):
sum = 0
i, j = 0, 0
# calculate sum of all elements
for i in range(n):
sum += arr[i]
if sum % 2 != 0:
return false
part = [[True for i in range(n + 1)]
for j in range(sum // 2 + 1)]
# initialize top row as true
for i in range(0, n + 1):
part[0][i] = True
# initialize leftmost column,
# except part[0][0], as 0
for i in range(1, sum // 2 + 1):
part[i][0] = False
# fill the partition table in
# bottom up manner
for i in range(1, sum // 2 + 1):
for j in range(1, n + 1):
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1]
if i >= arr[j - 1]:
part[i][j] = (part[i][j] or
part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1])
return part[sum // 2][n]
# Driver Code
arr = [3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1]
n = len(arr)
# Function call
if findPartition(arr, n) == True:
print("Can be divided into two",
"subsets of equal sum")
else:
print("Can not be divided into ",
"two subsets of equal sum")
# This code is contributed
# by mohit kumar 29
C#
// A dynamic programming based C# program
// for partition problem
using System;
class GFG {
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise
// false
static bool findPartition(int[] arr, int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool[, ] part = new bool[sum / 2 + 1, n + 1];
// initialize top row as true
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0, i] = true;
// initialize leftmost column, except
// part[0][0], as 0
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++)
part[i, 0] = false;
// Fill the partition table in bottom
// up manner
for (i = 1; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i, j] = part[i, j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i, j]
= part[i, j - 1]
|| part[i - arr[j - 1], j - 1];
}
}
/* // uncomment this part to print table
for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
printf ("%4d", part[i][j]);
printf("\n");
} */
return part[sum / 2, n];
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 };
int n = arr.Length;
// Function call
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
Console.Write("Can be divided"
+ " into two subsets of"
+ " equal sum");
else
Console.Write("Can not be "
+ "divided into two subsets"
+ " of equal sum");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007.
Javascript
<script>
// A dynamic programming based javascript
// program for partition
// problemclass Partition
// Returns true if arr can be partitioned in two
// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
function findPartition(arr , n)
{
var sum = 0;
var i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
var part = Array(parseInt(sum / 2) + 1).
fill().map(()=>Array(n + 1).fill(0));
// initialize top row as true
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
part[0][i] = true;
// initialize leftmost column,
// except part[0][0], as
// 0
for (i = 1; i <= parseInt(sum / 2); i++)
part[i][0] = false;
// Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for (i = 1; i <= parseInt(sum / 2); i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1];
if (i >= arr[j - 1])
part[i][j] = part[i][j] ||
part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
/*
uncomment this part to print table
for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
{ for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
printf ("%4d", part[i][j]); printf("\n"); }
*/
return part[parseInt(sum / 2)][n];
}
// Driver code
var arr = [ 3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1 ];
var n = arr.length;
if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
document.write(
"Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum"
);
else
document.write(
"Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum"
);
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum
El siguiente diagrama muestra los valores en la tabla de particiones.
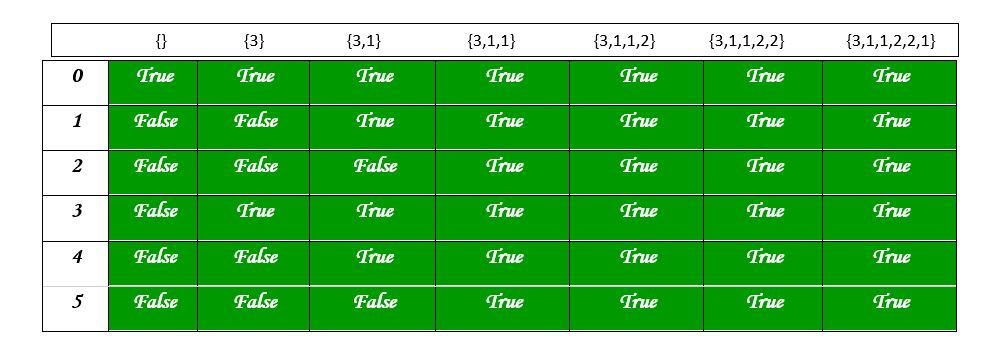
Complejidad de Tiempo: O(suma*n)
Espacio Auxiliar: O(suma*n)
Tenga en cuenta que esta solución no será factible para arrays con una gran suma.
Solución de programación dinámica (complejidad espacial optimizada)
En lugar de crear una array 2-D de tamaño (sum/2 + 1)*(n + 1), podemos resolver este problema utilizando únicamente una array de tamaño (sum/2 + 1).
parte[j] = verdadero si hay un subconjunto con suma igual a j, de lo contrario falso.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// A Dynamic Programming based
// C++ program to partition problem
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
bool findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool part[sum / 2 + 1];
// Initialize the part array
// as 0
for (i = 0; i <= sum / 2; i++) {
part[i] = 0;
}
// Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// the element to be included
// in the sum cannot be
// greater than the sum
for (j = sum / 2; j >= arr[i];
j--) { // check if sum - arr[i]
// could be formed
// from a subset
// using elements
// before index i
if (part[j - arr[i]] == 1 || j == arr[i])
part[j] = 1;
}
}
return part[sum / 2];
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
cout << "Can be divided into two subsets of equal "
"sum";
else
cout << "Can not be divided into"
<< " two subsets of equal sum";
return 0;
}
Java
// A Dynamic Programming based
// Java program to partition problem
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
public static boolean findPartiion(int arr[], int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
boolean[] part = new boolean[sum / 2 + 1];
// Initialize the part array
// as 0
for(i = 0; i <= sum / 2; i++)
{
part[i] = false;
}
// Fill the partition table in
// bottom up manner
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// The element to be included
// in the sum cannot be
// greater than the sum
for(j = sum / 2; j >= arr[i]; j--)
{
// Check if sum - arr[i] could be
// formed from a subset using elements
// before index i
if (part[j - arr[i]] == true || j == arr[i])
part[j] = true;
}
}
return part[sum / 2];
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 };
int n = 6;
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
System.out.println("Can be divided into two " +
"subsets of equal sum");
else
System.out.println("Can not be divided into " +
"two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
// This code is contributed by RohitOberoi
Python3
# A Dynamic Programming based
# Python3 program to partition problem
# Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
# in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
def findPartiion(arr, n) :
Sum = 0
# Calculate sum of all elements
for i in range(n) :
Sum += arr[i]
if (Sum % 2 != 0) :
return 0
part = [0] * ((Sum // 2) + 1)
# Initialize the part array as 0
for i in range((Sum // 2) + 1) :
part[i] = 0
# Fill the partition table in bottom up manner
for i in range(n) :
# the element to be included
# in the sum cannot be
# greater than the sum
for j in range(Sum // 2, arr[i] - 1, -1) :
# check if sum - arr[i]
# could be formed
# from a subset
# using elements
# before index i
if (part[j - arr[i]] == 1 or j == arr[i]) :
part[j] = 1
return part[Sum // 2]
# Drive code
arr = [ 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 ]
n = len(arr)
# Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == 1) :
print("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
else :
print("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
# This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07
C#
// A Dynamic Programming based
// C# program to partition problem
using System;
class GFG
{
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
static bool findPartiion(int[] arr, int n)
{
int sum = 0;
int i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
bool[] part = new bool[sum / 2 + 1];
// Initialize the part array
// as 0
for(i = 0; i <= sum / 2; i++)
{
part[i] = false;
}
// Fill the partition table in
// bottom up manner
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// The element to be included
// in the sum cannot be
// greater than the sum
for(j = sum / 2; j >= arr[i]; j--)
{
// Check if sum - arr[i] could be
// formed from a subset using elements
// before index i
if (part[j - arr[i]] == true || j == arr[i])
part[j] = true;
}
}
return part[sum / 2];
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 };
int n = 6;
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
Console.WriteLine("Can be divided into two " +
"subsets of equal sum");
else
Console.WriteLine("Can not be divided into " +
"two subsets of equal sum");
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyesh072019
Javascript
<script>
// A Dynamic Programming based Javascript
// program to partition problem
// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
function findPartiion(arr, n)
{
let sum = 0;
let i, j;
// Calculate sum of all elements
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
sum += arr[i];
if (sum % 2 != 0)
return false;
let part = new Array(parseInt(sum / 2 + 1, 10));
// Initialize the part array
// as 0
for(i = 0; i <= parseInt(sum / 2, 10); i++)
{
part[i] = false;
}
// Fill the partition table in
// bottom up manner
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// The element to be included
// in the sum cannot be
// greater than the sum
for(j = parseInt(sum / 2, 10);
j >= arr[i];
j--)
{
// Check if sum - arr[i] could be
// formed from a subset using
// elements before index i
if (part[j - arr[i]] == true ||
j == arr[i])
part[j] = true;
}
}
return part[parseInt(sum / 2, 10)];
}
// Driver code
let arr = [ 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2 ];
let n = arr.length;
// Function call
if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
document.write("Can be divided into two " +
"subsets of equal sum");
else
document.write("Can not be divided into " +
"two subsets of equal sum");
// This code is contributed by suresh07
</script>
Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum
Complejidad de Tiempo: O(suma * n)
Espacio Auxiliar : O(suma)
Tenga en cuenta que esta solución no será factible para arrays con una gran suma.
Referencias:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Partition_problem
Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA