Dada una string de entrada y un diccionario de palabras, averigüe si la string de entrada se puede segmentar en una secuencia de palabras del diccionario separadas por espacios. Consulte los siguientes ejemplos para obtener más detalles.
Esta es una famosa pregunta de la entrevista de Google, que también hacen muchas otras empresas en la actualidad.
Consider the following dictionary
{ i, like, sam, sung, samsung, mobile, ice,
cream, icecream, man, go, mango}
Input: ilike
Output: Yes
The string can be segmented as "i like".
Input: ilikesamsung
Output: Yes
The string can be segmented as "i like samsung"
or "i like sam sung".
Implementación recursiva:
La idea es simple, consideramos cada prefijo y lo buscamos en el diccionario. Si el prefijo está presente en el diccionario, recurrimos al resto de la string (o sufijo).
Python3
def wordBreak(wordList, word): if word == '': return True else: wordLen = len(word) return any([(word[:i] in wordList) and wordBreak(wordList, word[i:]) for i in range(1, wordLen+1)])
Si la llamada recursiva del sufijo devuelve verdadero, devolvemos verdadero; de lo contrario, intentamos con el siguiente prefijo. Si hemos probado todos los prefijos y ninguno de ellos resultó en una solución, devolvemos falso.
Recomendamos enfáticamente ver la función substr que se usa ampliamente en las siguientes implementaciones.
C++
// A recursive program to test whether a given
// string can be segmented into space separated
// words in dictionary
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/* A utility function to check whether a word is
present in dictionary or not. An array of strings
is used for dictionary. Using array of strings for
dictionary is definitely not a good idea. We have
used for simplicity of the program*/
int dictionaryContains(string word)
{
string dictionary[] = {"mobile","samsung","sam","sung",
"man","mango","icecream","and",
"go","i","like","ice","cream"};
int size = sizeof(dictionary)/sizeof(dictionary[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (dictionary[i].compare(word) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// returns true if string can be segmented into space
// separated words, otherwise returns false
bool wordBreak(string str)
{
int size = str.size();
// Base case
if (size == 0) return true;
// Try all prefixes of lengths from 1 to size
for (int i=1; i<=size; i++)
{
// The parameter for dictionaryContains is
// str.substr(0, i) which is prefix (of input
// string) of length 'i'. We first check whether
// current prefix is in dictionary. Then we
// recursively check for remaining string
// str.substr(i, size-i) which is suffix of
// length size-i
if (dictionaryContains( str.substr(0, i) ) &&
wordBreak( str.substr(i, size-i) ))
return true;
}
// If we have tried all prefixes and
// none of them worked
return false;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
wordBreak("ilikesamsung")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("iiiiiiii")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmango")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmangok")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.*;
// Recursive implementation of
// word break problem in java
public class WordBreakProblem
{
// set to hold dictionary values
private static Set<String> dictionary = new HashSet<>();
public static void main(String []args)
{
// array of strings to be added in dictionary set.
String temp_dictionary[] = {"mobile","samsung","sam","sung",
"man","mango","icecream","and",
"go","i","like","ice","cream"};
// loop to add all strings in dictionary set
for (String temp :temp_dictionary)
{
dictionary.add(temp);
}
// sample input cases
System.out.println(wordBreak("ilikesamsung"));
System.out.println(wordBreak("iiiiiiii"));
System.out.println(wordBreak(""));
System.out.println(wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii"));
System.out.println(wordBreak("samsungandmango"));
System.out.println(wordBreak("samsungandmangok"));
}
// returns true if the word can be segmented into parts such
// that each part is contained in dictionary
public static boolean wordBreak(String word)
{
int size = word.length();
// base case
if (size == 0)
return true;
//else check for all words
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++)
{
// Now we will first divide the word into two parts ,
// the prefix will have a length of i and check if it is
// present in dictionary ,if yes then we will check for
// suffix of length size-i recursively. if both prefix and
// suffix are present the word is found in dictionary.
if (dictionary.contains(word.substring(0,i)) &&
wordBreak(word.substring(i,size)))
return true;
}
// if all cases failed then return false
return false;
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sparsh Singhal
Python3
# Recursive implementation of
# word break problem in Python
# returns True if the word can be segmented into parts such
# that each part is contained in dictionary
def wordBreak(word):
global dictionary
size = len(word)
# base case
if (size == 0):
return True
# else check for all words
for i in range(1,size + 1):
# Now we will first divide the word into two parts ,
# the prefix will have a length of i and check if it is
# present in dictionary ,if yes then we will check for
# suffix of length size-i recursively. if both prefix and
# suffix are present the word is found in dictionary.
if (word[0:i] in dictionary and wordBreak(word[i: size])):
return True
# if all cases failed then return False
return False
# set to hold dictionary values
dictionary = set()
# array of strings to be added in dictionary set.
temp_dictionary = [ "mobile", "samsung", "sam", "sung", "man", "mango", "icecream", "and", "go", "i","like", "ice", "cream" ]
# loop to add all strings in dictionary set
for temp in temp_dictionary:
dictionary.add(temp)
# sample input cases
print("Yes" if wordBreak("ilikesamsung") else "No")
print("Yes" if wordBreak("iiiiiiii") else "No")
print("Yes" if wordBreak("") else "No")
print("Yes" if wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii") else "No")
print("Yes" if wordBreak("samsungandmango") else "No")
print("Yes" if wordBreak("samsungandmangok") else "No")
# This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
Javascript
<script>
// Recursive implementation of
// word break problem in java
// set to hold dictionary values
var dictionary = new Set();
// array of strings to be added in dictionary set.
var temp_dictionary = [ "mobile", "samsung", "sam", "sung", "man", "mango", "icecream", "and", "go", "i",
"like", "ice", "cream" ];
// loop to add all strings in dictionary set
for (var temp of temp_dictionary) {
dictionary.add(temp);
}
// sample input cases
document.write(((wordBreak("ilikesamsung"))?"Yes":"No")+"<br/>");
document.write(((wordBreak("iiiiiiii"))?"Yes":"No")+"<br/>");
document.write(((wordBreak(""))?"Yes":"No")+"<br/>");
document.write(((wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii"))?"Yes":"No")+"<br/>");
document.write(((wordBreak("samsungandmango"))?"Yes":"No")+"<br/>");
document.write(((wordBreak("samsungandmangok"))?"Yes":"No")+"<br/>");
// returns true if the word can be segmented into parts such
// that each part is contained in dictionary
function wordBreak( word) {
var size = word.length;
// base case
if (size == 0)
return true;
// else check for all words
for (var i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
// Now we will first divide the word into two parts ,
// the prefix will have a length of i and check if it is
// present in dictionary ,if yes then we will check for
// suffix of length size-i recursively. if both prefix and
// suffix are present the word is found in dictionary.
if (dictionary.has(word.substring(0, i)) && wordBreak(word.substring(i, size)))
return true;
}
// if all cases failed then return false
return false;
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Programación
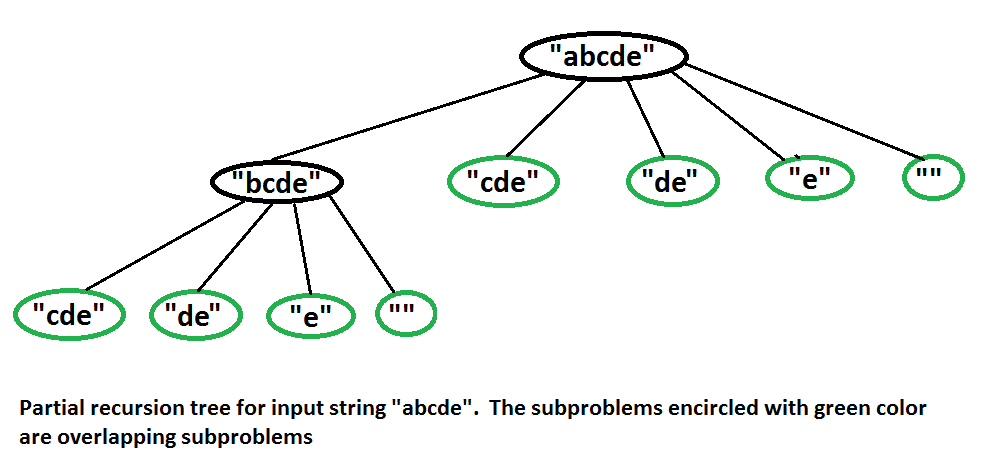
Dinámica ¿Por qué Programación Dinámica? El problema anterior exhibe subproblemas superpuestos. Por ejemplo, vea el siguiente árbol de recurrencia parcial para la string «abcde» en el peor de los casos.
CPP
// A Dynamic Programming based program to test whether a given string can
// be segmented into space separated words in dictionary
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
/* A utility function to check whether a word is present in dictionary or not.
An array of strings is used for dictionary. Using array of strings for
dictionary is definitely not a good idea. We have used for simplicity of
the program*/
int dictionaryContains(string word)
{
string dictionary[] = {"mobile","samsung","sam","sung","man","mango",
"icecream","and","go","i","like","ice","cream"};
int size = sizeof(dictionary)/sizeof(dictionary[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (dictionary[i].compare(word) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// Returns true if string can be segmented into space separated
// words, otherwise returns false
bool wordBreak(string str)
{
int size = str.size();
if (size == 0) return true;
// Create the DP table to store results of subproblems. The value wb[i]
// will be true if str[0..i-1] can be segmented into dictionary words,
// otherwise false.
bool wb[size+1];
memset(wb, 0, sizeof(wb)); // Initialize all values as false.
for (int i=1; i<=size; i++)
{
// if wb[i] is false, then check if current prefix can make it true.
// Current prefix is "str.substr(0, i)"
if (wb[i] == false && dictionaryContains( str.substr(0, i) ))
wb[i] = true;
// wb[i] is true, then check for all substrings starting from
// (i+1)th character and store their results.
if (wb[i] == true)
{
// If we reached the last prefix
if (i == size)
return true;
for (int j = i+1; j <= size; j++)
{
// Update wb[j] if it is false and can be updated
// Note the parameter passed to dictionaryContains() is
// substring starting from index 'i' and length 'j-i'
if (wb[j] == false && dictionaryContains( str.substr(i, j-i) ))
wb[j] = true;
// If we reached the last character
if (j == size && wb[j] == true)
return true;
}
}
}
/* Uncomment these lines to print DP table "wb[]"
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++)
cout << " " << wb[i]; */
// If we have tried all prefixes and none of them worked
return false;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
wordBreak("ilikesamsung")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("iiiiiiii")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmango")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmangok")? cout <<"Yes\n": cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
Java
// A Dynamic Programming based program to test whether a given String can
// be segmented into space separated words in dictionary
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
/* A utility function to check whether a word is present in dictionary or not.
An array of Strings is used for dictionary. Using array of Strings for
dictionary is definitely not a good idea. We have used for simplicity of
the program*/
static boolean dictionaryContains(String word)
{
String dictionary[] = {"mobile","samsung","sam","sung","man","mango",
"icecream","and","go","i","like","ice","cream"};
int size = dictionary.length;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (dictionary[i].compareTo(word) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// Returns true if String can be segmented into space separated
// words, otherwise returns false
static boolean wordBreak(String str)
{
int size = str.length();
if (size == 0) return true;
// Create the DP table to store results of subproblems. The value wb[i]
// will be true if str[0..i-1] can be segmented into dictionary words,
// otherwise false.
boolean []wb = new boolean[size+1];
for (int i=1; i<=size; i++)
{
// if wb[i] is false, then check if current prefix can make it true.
// Current prefix is "str.substring(0, i)"
if (wb[i] == false && dictionaryContains( str.substring(0, i) ))
wb[i] = true;
// wb[i] is true, then check for all subStrings starting from
// (i+1)th character and store their results.
if (wb[i] == true)
{
// If we reached the last prefix
if (i == size)
return true;
for (int j = i+1; j <= size; j++)
{
// Update wb[j] if it is false and can be updated
// Note the parameter passed to dictionaryContains() is
// subString starting from index 'i' and length 'j-i'
if (wb[j] == false && dictionaryContains( str.substring(i, j) ))
wb[j] = true;
// If we reached the last character
if (j == size && wb[j] == true)
return true;
}
}
}
/* Uncomment these lines to print DP table "wb[]"
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++)
System.out.print(" " + wb[i]; */
// If we have tried all prefixes and none of them worked
return false;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
if(wordBreak("ilikesamsung"))
System.out.print("Yes\n");
else
System.out.print("No\n");
if(wordBreak("iiiiiiii"))
System.out.print("Yes\n");
else
System.out.print("No\n");
if(wordBreak(""))
System.out.print("Yes\n");
else
System.out.print("No\n");
if(wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii"))
System.out.print("Yes\n");
else
System.out.print("No\n");
if(wordBreak("samsungandmango"))
System.out.print("Yes\n");
else
System.out.print("No\n");
if(wordBreak("samsungandmangok"))
System.out.print("Yes\n");
else
System.out.print("No\n");
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Python3
# A Dynamic Programming based program to test whether a given String can
# be segmented into space separated words in dictionary
# A utility function to check whether a word is present in dictionary or not.
# An array of Strings is used for dictionary. Using array of Strings for
# dictionary is definitely not a good idea. We have used for simplicity of the
# program
def dictionaryContains(word):
dictionary = [ "mobile", "samsung", "sam", "sung", "man", "mango", "icecream", "and", "go", "i",
"like", "ice", "cream" ]
size = len(dictionary)
for i in range(size):
if (dictionary[i]== word):
return True
return False
# Returns True if String can be segmented into space separated
# words, otherwise returns False
def wordBreak(Str):
size = len(Str)
if (size == 0):
return True
# Create the DP table to store results of subproblems. The value wb[i]
# will be True if str[0..i-1] can be segmented into dictionary words,
# otherwise False.
wb = [False for i in range(size + 1)]
for i in range(1,size + 1):
# if wb[i] is False, then check if current prefix can make it True.
# Current prefix is "str.substring(0, i)"
if (wb[i] == False and dictionaryContains(Str[0: i])):
wb[i] = True
# wb[i] is True, then check for all subStrings starting from
# (i+1)th character and store their results.
if (wb[i] == True):
# If we reached the last prefix
if (i == size):
return True
for j in range(i + 1,size + 1):
# Update wb[j] if it is False and can be updated
# Note the parameter passed to dictionaryContains() is
# subString starting from index 'i' and length 'j-i'
if (wb[j] == False and dictionaryContains(Str[i: j])):
wb[j] = True
# If we reached the last character
if (j == size and wb[j] == True):
return True
# If we have tried all prefixes and none of them worked
return False
# Driver program to test above functions
if (wordBreak("ilikesamsung")):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
if (wordBreak("iiiiiiii")):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
if (wordBreak("")):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
if (wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii")):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
if (wordBreak("samsungandmango")):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
if (wordBreak("samsungandmangok")):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
# This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
C#
// A Dynamic Programming based program to test whether a given String can
// be segmented into space separated words in dictionary
// Include namespace system
using System;
public class GFG
{
// A utility function to check whether a word is present in dictionary or not.
// An array of Strings is used for dictionary. Using array of Strings for
// dictionary is definitely not a good idea. We have used for simplicity of
// the program
public static bool dictionaryContains(String word)
{
String[] dictionary = {"mobile", "samsung", "sam", "sung", "man", "mango", "icecream", "and", "go", "i", "like", "ice", "cream"};
var size = dictionary.Length;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
if (string.CompareOrdinal(dictionary[i],word) == 0)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// Returns true if String can be segmented into space separated
// words, otherwise returns false
public static bool wordBreak(String str)
{
var size = str.Length;
if (size == 0)
{
return true;
}
// Create the DP table to store results of subproblems. The value wb[i]
// will be true if str[0..i-1] can be segmented into dictionary words,
// otherwise false.
bool[] wb = new bool[size + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++)
{
// if wb[i] is false, then check if current prefix can make it true.
// Current prefix is "str.substring(0, i)"
if (wb[i] == false && GFG.dictionaryContains(str.Substring(0,i-0)))
{
wb[i] = true;
}
// wb[i] is true, then check for all subStrings starting from
// (i+1)th character and store their results.
if (wb[i] == true)
{
// If we reached the last prefix
if (i == size)
{
return true;
}
for (int j = i + 1; j <= size; j++)
{
// Update wb[j] if it is false and can be updated
// Note the parameter passed to dictionaryContains() is
// subString starting from index 'i' and length 'j-i'
if (wb[j] == false && GFG.dictionaryContains(str.Substring(i,j-i)))
{
wb[j] = true;
}
// If we reached the last character
if (j == size && wb[j] == true)
{
return true;
}
}
}
}
// Uncomment these lines to print DP table "wb[]"
// for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++)
// System.out.print(" " + wb[i];
// If we have tried all prefixes and none of them worked
return false;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
if (GFG.wordBreak("ilikesamsung"))
{
Console.Write("Yes\n");
}
else
{
Console.Write("No\n");
}
if (GFG.wordBreak("iiiiiiii"))
{
Console.Write("Yes\n");
}
else
{
Console.Write("No\n");
}
if (GFG.wordBreak(""))
{
Console.Write("Yes\n");
}
else
{
Console.Write("No\n");
}
if (GFG.wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii"))
{
Console.Write("Yes\n");
}
else
{
Console.Write("No\n");
}
if (GFG.wordBreak("samsungandmango"))
{
Console.Write("Yes\n");
}
else
{
Console.Write("No\n");
}
if (GFG.wordBreak("samsungandmangok"))
{
Console.Write("Yes\n");
}
else
{
Console.Write("No\n");
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by mukulsomukesh
Javascript
<script>
// A Dynamic Programming based program to test whether a given String can
// be segmented into space separated words in dictionary
/*
* A utility function to check whether a word is present in dictionary or not.
* An array of Strings is used for dictionary. Using array of Strings for
* dictionary is definitely not a good idea. We have used for simplicity of the
* program
*/
function dictionaryContains( word) {
var dictionary = [ "mobile", "samsung", "sam", "sung", "man", "mango", "icecream", "and", "go", "i",
"like", "ice", "cream" ];
var size = dictionary.length;
for (var i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (dictionary[i]===(word))
return true;
return false;
}
// Returns true if String can be segmented into space separated
// words, otherwise returns false
function wordBreak( str) {
var size = str.length;
if (size == 0)
return true;
// Create the DP table to store results of subproblems. The value wb[i]
// will be true if str[0..i-1] can be segmented into dictionary words,
// otherwise false.
var wb = Array(size + 1).fill(false);
for (var i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
// if wb[i] is false, then check if current prefix can make it true.
// Current prefix is "str.substring(0, i)"
if (wb[i] == false && dictionaryContains(str.substring(0, i)))
wb[i] = true;
// wb[i] is true, then check for all subStrings starting from
// (i+1)th character and store their results.
if (wb[i] == true) {
// If we reached the last prefix
if (i == size)
return true;
for (j = i + 1; j <= size; j++) {
// Update wb[j] if it is false and can be updated
// Note the parameter passed to dictionaryContains() is
// subString starting from index 'i' and length 'j-i'
if (wb[j] == false && dictionaryContains(str.substring(i, j)))
wb[j] = true;
// If we reached the last character
if (j == size && wb[j] == true)
return true;
}
}
}
/*
* Uncomment these lines to print DP table "wb" for (i = 1; i <= size;
* i++) document.write(" " + wb[i];
*/
// If we have tried all prefixes and none of them worked
return false;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
if (wordBreak("ilikesamsung"))
document.write("Yes<br/>");
else
document.write("No<br/>");
if (wordBreak("iiiiiiii"))
document.write("Yes<br/>");
else
document.write("No<br/>");
if (wordBreak(""))
document.write("Yes<br/>");
else
document.write("No<br/>");
if (wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii"))
document.write("Yes<br/>");
else
document.write("No<br/>");
if (wordBreak("samsungandmango"))
document.write("Yes<br/>");
else
document.write("No<br/>");
if (wordBreak("samsungandmangok"))
document.write("Yes<br/>");
else
document.write("No<br/>");
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Programación dinámica optimizada :
en este enfoque, además de la tabla dp, también mantenemos todos los índices que coincidieron anteriormente. Luego verificaremos las substrings de esos índices al índice actual. Si alguno de ellos coincide, podemos dividir la string hasta ese índice.
En este programa, estamos usando algo de espacio extra. Sin embargo, su complejidad temporal es O(n*s) donde s es la longitud de la string más grande del diccionario y n es la longitud de la string dada.
CPP
// A Dynamic Programming based program to test
// whether a given string can be segmented into
// space separated words in dictionary
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* A utility function to check whether a word
is present in dictionary or not. An array of
strings is used for dictionary. Using array
of strings for dictionary is definitely not
a good idea. We have used for simplicity of
the program*/
int dictionaryContains(string word)
{
string dictionary[]
= { "mobile", "samsung", "sam", "sung", "man",
"mango", "icecream", "and", "go", "i",
"like", "ice", "cream" };
int size = sizeof(dictionary) / sizeof(dictionary[0]);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
if (dictionary[i].compare(word) == 0)
return true;
return false;
}
// Returns true if string can be segmented into space
// separated words, otherwise returns false
bool wordBreak(string s)
{
int n = s.size();
if (n == 0)
return true;
// Create the DP table to store results of subproblems.
// The value dp[i] will be true if str[0..i] can be
// segmented into dictionary words, otherwise false.
vector<bool> dp(n + 1, 0); // Initialize all values
// as false.
// matched_index array represents the indexes for which
// dp[i] is true. Initially only -1 element is present
// in this array.
vector<int> matched_index;
matched_index.push_back(-1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int msize = matched_index.size();
// Flag value which tells that a substring matches
// with given words or not.
int f = 0;
// Check all the substring from the indexes matched
// earlier. If any of that substring matches than
// make flag value = 1;
for (int j = msize - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
// sb is substring starting from
// matched_index[j]
// + 1 and of length i - matched_index[j]
string sb = s.substr(matched_index[j] + 1,
i - matched_index[j]);
if (dictionaryContains(sb)) {
f = 1;
break;
}
}
// If substring matches than do dp[i] = 1 and
// push that index in matched_index array.
if (f == 1) {
dp[i] = 1;
matched_index.push_back(i);
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
wordBreak("ilikesamsung") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("iiiiiiii") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("") ? cout << "Yes\n" : cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("ilikelikeimangoiii") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmango") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
wordBreak("samsungandmangok") ? cout << "Yes\n"
: cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static boolean wordBreak(String s, List<String> dictionary) {
// create a dp table to store results of subproblems
// value of dp[i] will be true if string s can be segmented
// into dictionary words from 0 to i.
boolean[] dp = new boolean[s.length() + 1];
// dp[0] is true because an empty string can always be segmented.
dp[0] = true;
for(int i = 0; i <= s.length(); i++){
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++){
if(dp[j] && dictionary.contains(s.substring(j, i))){
dp[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return dp[s.length()];
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
String[] dictionary = { "mobile", "samsung", "sam", "sung", "man",
"mango", "icecream", "and", "go", "i",
"like", "ice", "cream" };
List<String> dict = new ArrayList<>();
for(String s : dictionary){
dict.add(s);
}
if (wordBreak("ilikesamsung", dict)) {
System.out.println("Yes");
} else {
System.out.println("No");
}
if (wordBreak("iiiiiiii", dict)) {
System.out.println("Yes");
} else {
System.out.println("No");
}
if (wordBreak("", dict)) {
System.out.println("Yes");
} else {
System.out.println("No");
}
if (wordBreak("samsungandmango", dict)) {
System.out.println("Yes");
} else {
System.out.println("No");
}
if (wordBreak("ilikesamsung", dict)) {
System.out.println("Yes");
} else {
System.out.println("No");
}
if (wordBreak("samsungandmangok", dict)) {
System.out.println("Yes");
} else {
System.out.println("No");
}
}
}
Python3
def wordBreak(s, dictionary):
# create a dp table to store results of subproblems
# value of dp[i] will be true if string s can be segmented
# into dictionary words from 0 to i.
dp = [False for i in range(len(s) + 1)]
# dp[0] is true because an empty string can always be segmented.
dp[0] = True
for i in range(len(s) + 1):
for j in range(i):
if dp[j] and s[j: i] in dictionary:
dp[i] = True
break
return dp[len(s)]
# driver code
dictionary = [ "mobile", "samsung", "sam", "sung", "man", "mango", "icecream", "and", "go", "i", "like", "ice", "cream" ]
dict = set()
for s in dictionary:
dict.add(s)
if (wordBreak("ilikesamsung", dict)):
print("Yes")
else :
print("No")
if (wordBreak("iiiiiiii", dict)):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
if (wordBreak("", dict)):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
if (wordBreak("samsungandmango", dict)):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
if (wordBreak("ilikesamsung", dict)):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
if (wordBreak("samsungandmangok", dict)):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
# This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
Javascript
<script>
function wordBreak( s, dictionary)
{
// create a dp table to store results of subproblems
// value of dp[i] will be true if string s can be segmented
// into dictionary words from 0 to i.
var dp = Array(s.length + 1).fill(false);
// dp[0] is true because an empty string can always be segmented.
dp[0] = true;
for (var i = 0; i <= s.length; i++) {
for (var j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (dp[j] && dictionary.has(s.substring(j, i))) {
dp[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return dp[s.length];
}
var dictionary = [ "mobile", "samsung", "sam", "sung", "man", "mango", "icecream", "and", "go", "i",
"like", "ice", "cream" ];
var dict = new Set();
for (var s of dictionary) {
dict.add(s);
}
if (wordBreak("ilikesamsung", dict)) {
document.write("<br/>Yes");
} else {
document.write("<br/>No");
}
if (wordBreak("iiiiiiii", dict)) {
document.write("<br/>Yes");
} else {
document.write("<br/>No");
}
if (wordBreak("", dict)) {
document.write("<br/>Yes");
} else {
document.write("<br/>No");
}
if (wordBreak("samsungandmango", dict)) {
document.write("<br/>Yes");
} else {
document.write("<br/>No");
}
if (wordBreak("ilikesamsung", dict)) {
document.write("<br/>Yes");
} else {
document.write("<br/>No");
}
if (wordBreak("samsungandmangok", dict)) {
document.write("<br/>Yes");
} else {
document.write("<br/>No");
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No
Problema de separación de palabras | (Solución Trie)
Ejercicio:
Las soluciones anteriores solo averiguan si una string determinada se puede segmentar o no. Extienda la solución de programación dinámica anterior para imprimir todas las particiones posibles de la string de entrada.
Ejemplos:
Input: ilikeicecreamandmango Output: i like ice cream and man go i like ice cream and mango i like icecream and man go i like icecream and mango Input: ilikesamsungmobile Output: i like sam sung mobile i like samsung mobile
Problema de separación de palabras | (Solución hashmap):
En este enfoque primero, estamos almacenando todas las palabras en un Hashmap. después de eso, recorremos la string de entrada y verificamos si hay una coincidencia o no.
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool CanParseUtil(unordered_map<string, bool>mp, string word)
{
// if the size id zero that means we completed the word. so we can return true
int size = word.size();
if(size == 0)
{
return true;
}
string temp = "";
for(int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++)
{
temp += word[i];
// if the temp exist in hashmap and the parsing operation of the remaining word is true, we can return true.
if(mp.find(temp) != mp.end() && CanParseUtil(mp, word.substr(i+1)))
{
return true;
}
}
// if there is a mismatch in the dictionary, we can return false.
return false;
}
string CanParse(vector<string>words, string word)
{
int start = 0;
// store the words in the hashmap
unordered_map<string, bool>mp;
for(auto it : words)
{
mp[it] = true;
}
return CanParseUtil(mp,word ) == true ? "YES" : "NO";
}
int main() {
vector<string>words{"mobile","samsung","sam","sung",
"man","mango","icecream","and",
"go","i","like","ice","cream"};
string word = "samsungandmangok";
cout << CanParse(words, word) << endl;
}
Python3
def CanParseUtil(mp,word):
# if the size id zero that means we completed the word. so we can return True
size = len(word)
if(size == 0):
return True
temp = ""
for i in range(len(word)):
temp += word[i]
# if the temp exist in hashmap and the parsing operation of the remaining word is True, we can return True.
if(temp in mp and CanParseUtil(mp, word[i+1:])):
return True
# if there is a mismatch in the dictionary, we can return false.
return False
def CanParse(words,word):
start = 0
# store the words in the hashmap
mp = {}
for it in words:
mp[it] = True
return "YES" if CanParseUtil(mp,word ) == True else "NO"
# driver code
words = ["mobile","samsung","sam","sung",
"man","mango","icecream","and",
"go","i","like","ice","cream"]
word = "samsungandmangok"
print(CanParse(words, word))
# This code is contributed by shinjanpatra
Javascript
<script>
function CanParseUtil(mp,word)
{
// if the size id zero that means we completed the word. so we can return true
let size = word.length;
if(size == 0)
{
return true;
}
let temp = "";
for(let i = 0; i < word.length; i++)
{
temp += word[i];
// if the temp exist in hashmap and the parsing operation of the remaining word is true, we can return true.
if(mp.has(temp) === true && CanParseUtil(mp, word.substring(i+1)))
{
return true;
}
}
// if there is a mismatch in the dictionary, we can return false.
return false;
}
function CanParse(words,word)
{
let start = 0;
// store the words in the hashmap
let mp = new Map();
for(let it of words)
{
mp.set(it , true);
}
return CanParseUtil(mp,word ) == true ? "YES" : "NO";
}
// driver code
let words = ["mobile","samsung","sam","sung",
"man","mango","icecream","and",
"go","i","like","ice","cream"];
let word = "samsungandmangok";
document.write(CanParse(words, word),"</br>");
// code is contributed by shinjanpatra
</script>
NO
Consulte la publicación a continuación para ver la solución del ejercicio.
Problema de salto de palabra al usar el retroceso
. Escriba comentarios si encuentra algo incorrecto o si desea compartir más información sobre el tema tratado anteriormente.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA