Dada una lista enlazada individualmente con cada Node que tiene un puntero «arbitrario» adicional que actualmente apunta a NULL. Necesitamos hacer el puntero «arbitrario» al Node de mayor valor en una lista enlazada en su lado derecho.
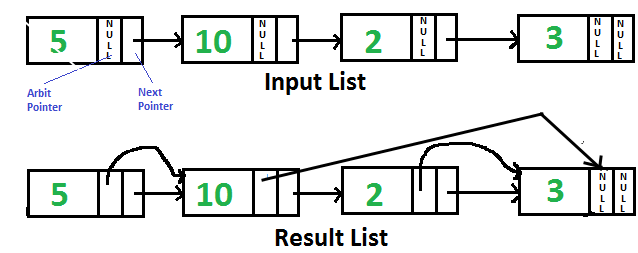
Una solución simple es atravesar todos los Nodes uno por uno. Para cada Node, busque el Node que tiene el mayor valor en el lado derecho y cambie el siguiente puntero. La complejidad temporal de esta solución es O(n 2 ).
Una Solución Eficiente puede funcionar en tiempo O(n). A continuación se muestran los pasos.
- Invierta la lista enlazada dada.
- Comience a recorrer la lista vinculada y almacene el Node de valor máximo encontrado hasta el momento. Haga un arbitraje de cada Node para que apunte al máximo. Si los datos en el Node actual son más que el Node máximo hasta el momento, actualice max.
- Invierta la lista enlazada modificada y devuelva el encabezado.
A continuación se muestra la implementación de los pasos anteriores.
C++
// C++ program to point arbit pointers
// to highest value on its right
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Link list node
struct Node
{
int data;
Node* next, *arbit;
};
/* Function to reverse the
linked list */
Node* reverse(Node *head)
{
Node *prev = NULL,
*current = head, *next;
while (current != NULL)
{
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
return prev;
}
// This function populates arbit pointer
// in every node to the greatest value
// to its right.
Node* populateArbit(Node *head)
{
// Reverse given linked list
head = reverse(head);
// Initialize pointer to maximum
// value node
Node *max = head;
// Traverse the reversed list
Node *temp = head->next;
while (temp != NULL)
{
// Connect max through arbit
// pointer
temp->arbit = max;
// Update max if required
if (max->data < temp->data)
max = temp;
// Move ahead in reversed list
temp = temp->next;
}
// Reverse modified linked list
// and return head.
return reverse(head);
}
// Utility function to print result
// linked list
void printNextArbitPointers(Node *node)
{
printf("Node Next Pointer Arbit Pointer");
while (node!=NULL)
{
cout << node->data <<
" ";
if (node->next)
cout << node->next->data <<
" ";
else cout << "NULL" << " ";
if (node->arbit)
cout << node->arbit->data;
else cout << "NULL";
cout << endl;
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Function to create a new node with
given data */
Node *newNode(int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
return new_node;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node *head = newNode(5);
head->next = newNode(10);
head->next->next = newNode(2);
head->next->next->next = newNode(3);
head = populateArbit(head);
printf("Resultant Linked List is: ");
printNextArbitPointers(head);
return 0;
}
Producción:
Resultant Linked List is: Node Next Pointer Arbit Pointer 5 10 10 10 2 3 2 3 3 3 NULL NULL
Solución recursiva:
podemos llegar recursivamente al último Node y recorrer la lista enlazada desde el final. La solución recursiva no requiere invertir la lista enlazada. También podemos usar una pila en lugar de recursividad para contener Nodes temporalmente. Gracias a Santosh Kumar Mishra por proporcionar esta solución.
C++
// C++ program to point arbit pointers
// to highest value on its right
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Link list node
struct Node
{
int data;
Node* next, *arbit;
};
// This function populates arbit pointer
// in every node to the greatest value
// to its right.
void populateArbit(Node *head)
{
// using static maxNode to keep track
// of maximum orbit node address on
// right side
static Node *maxNode;
// if head is null simply return
// the list
if (head == NULL)
return;
/* if head->next is null it means we
reached at the last node just update
the max and maxNode */
if (head->next == NULL)
{
maxNode = head;
return;
}
/* Calling the populateArbit to the
next node */
populateArbit(head->next);
/* Updating the arbit node of the
current node with the maximum
value on the right side */
head->arbit = maxNode;
/* If current Node value id greater
then the previous right node then
update it */
if (head->data > maxNode->data)
maxNode = head;
return;
}
// Utility function to print result
// linked list
void printNextArbitPointers(Node *node)
{
printf("Node Next Pointer Arbit Pointer");
while (node!=NULL)
{
cout << node->data <<
" ";
if(node->next)
cout << node->next->data <<
" ";
else cout << "NULL" <<
" ";
if(node->arbit)
cout << node->arbit->data;
else cout << "NULL";
cout << endl;
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Function to create a new node
with given data */
Node *newNode(int data)
{
Node *new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
return new_node;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node *head = newNode(5);
head->next = newNode(10);
head->next->next = newNode(2);
head->next->next->next = newNode(3);
populateArbit(head);
printf("Resultant Linked List is: ");
printNextArbitPointers(head);
return 0;
}
Producción:
Resultant Linked List is: Node Next Pointer Arbit Pointer 5 10 10 10 2 3 2 3 3 3 NULL NULL
¡ Consulte el artículo completo sobre el puntero de arbitraje de punto al Node del lado derecho de mayor valor en una lista vinculada para obtener más detalles!
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA