Dada una lista enlazada individualmente, escriba una función para intercambiar elementos por pares.
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->6->NULL
Output: 2->1->4->3->6->5->NULL Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output: 2->1->4->3->5->NULL Input: 1->NULL
Output: 1->NULL
Por ejemplo, si la lista enlazada es 1->2->3->4->5 entonces la función debería cambiarla a 2->1->4->3->5, y si la lista enlazada es entonces el la función debería cambiarlo a.
MÉTODO 1 (Iterativo):
Comience desde el Node principal y recorra la lista. Al atravesar los datos de intercambio de cada Node con los datos de su siguiente Node.
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C#
// C# program to pairwise swap elements
// of a linked list
using System;
class LinkedList
{
// Head of list
Node head;
// Linked list Node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
void pairWiseSwap()
{
Node temp = head;
/* Traverse only till there are
atleast 2 nodes left */
while (temp != null &&
temp.next != null)
{
// Swap the data
int k = temp.data;
temp.data = temp.next.data;
temp.next.data = k;
temp = temp.next.next;
}
}
// Utility functions
/* Inserts a new Node at front
of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make next of new Node as head
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to
new Node */
head = new_node;
}
// Function to print linked list
void printList()
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null)
{
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
/* Created Linked List
1->2->3->4->5 */
llist.push(5);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
Console.WriteLine(
"Linked List before calling pairWiseSwap() ");
llist.printList();
llist.pairWiseSwap();
Console.WriteLine(
"Linked List after calling pairWiseSwap() ");
llist.printList();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu
Producción:
Linked list before calling pairWiseSwap() 1 2 3 4 5 Linked list after calling pairWiseSwap() 2 1 4 3 5
Complejidad temporal: O(n)
MÉTODO 2 (recursivo):
si hay 2 o más de 2 Nodes en la lista enlazada, intercambie los dos primeros Nodes y llame recursivamente al resto de la lista.
La imagen de abajo es una ejecución en seco del enfoque anterior:
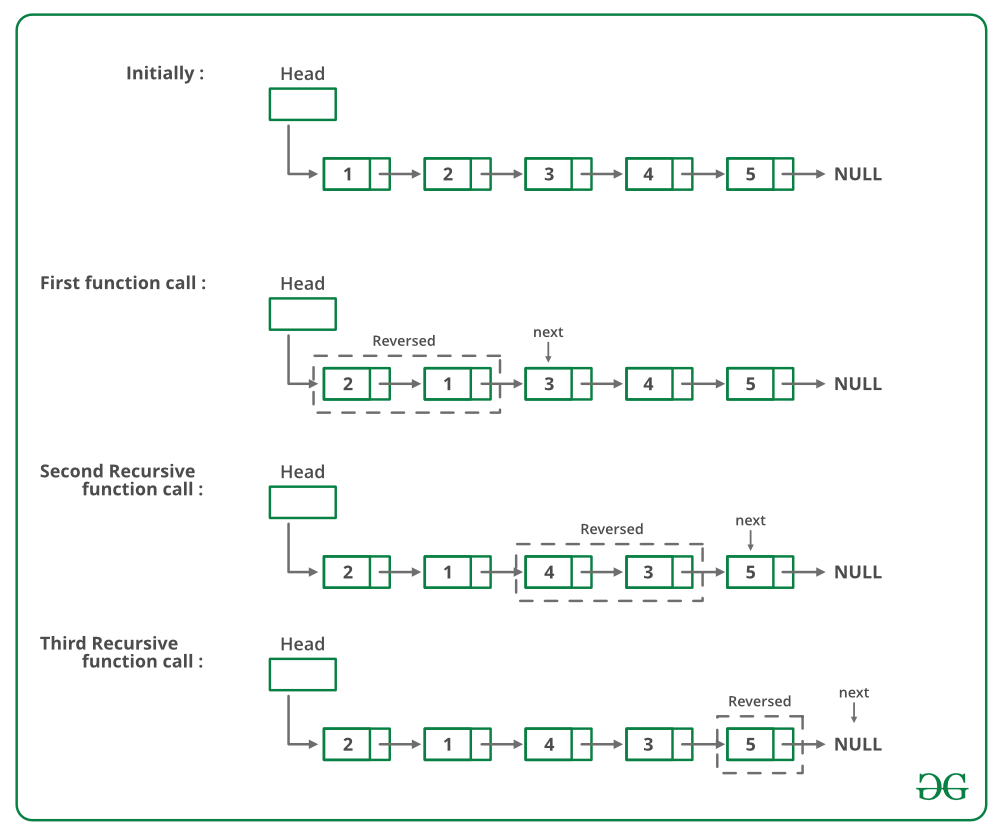
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C#
/* Recursive function to pairwise swap
elements of a linked list */
static void pairWiseSwap(node head)
{
/* There must be at-least two nodes
in the list */
if (head != null &&
head.next != null)
{
/* Swap the node's data with data
of next node */
swap(head.data, head.next.data);
/* Call pairWiseSwap() for rest
of the list */
pairWiseSwap(head.next.next);
}
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995
Complejidad de tiempo: O(n)
La solución provista allí intercambia datos de Nodes. Si los datos contienen muchos campos, habrá muchas operaciones de intercambio. Vea esto para una implementación que cambia enlaces en lugar de intercambiar datos.
¡ Consulte el artículo completo sobre los elementos de intercambio por pares de una lista vinculada dada para obtener más detalles!
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA