Requisito previo: conjunto de listas de enlaces dobles 1 | Introducción e Inserción
Escriba una función para eliminar un Node dado en una lista doblemente enlazada.
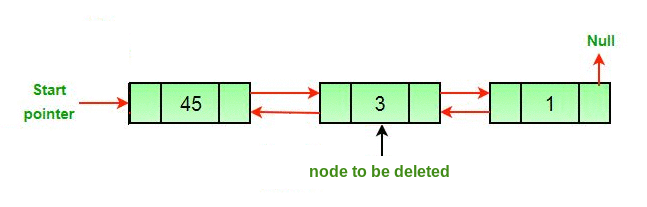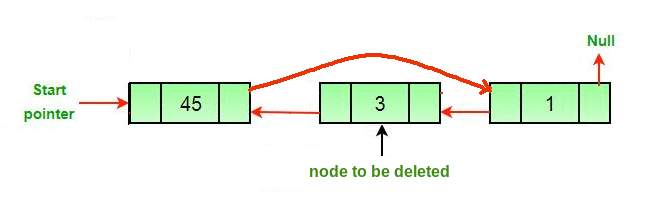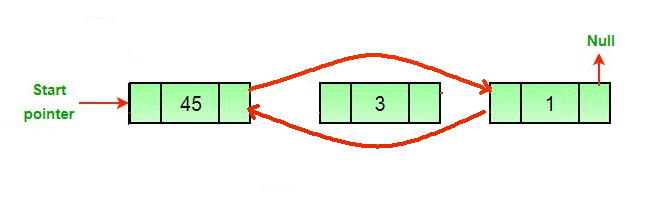
Lista original doblemente enlazada
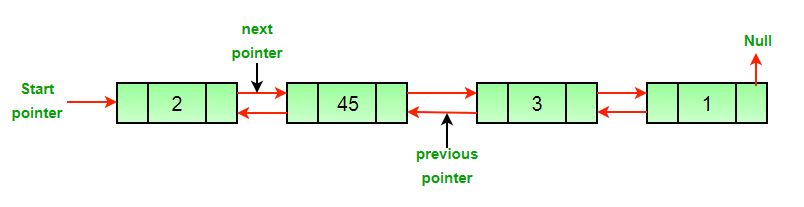
Enfoque: La eliminación de un Node en una lista doblemente enlazada se puede dividir en tres categorías principales:
- Después de la eliminación del Node principal.
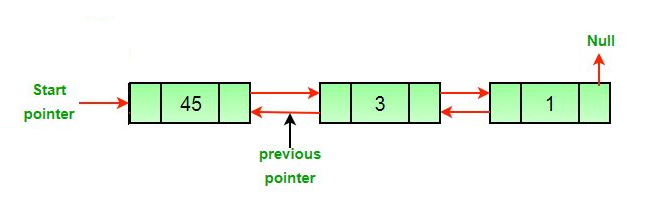
- Después de la eliminación del Node medio.
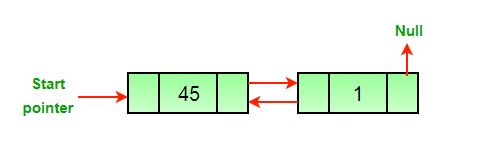
- Después de la eliminación del último Node.
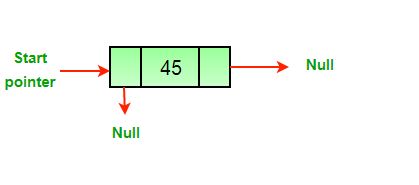
Los tres casos mencionados se pueden manejar en dos pasos si se conocen el puntero del Node a eliminar y el puntero principal.
- Si el Node que se eliminará es el Node principal, haga que el siguiente Node sea principal.
- Si se elimina un Node, conecte el Node siguiente y anterior del Node eliminado.
Algoritmo
- Deje que el Node a eliminar sea del .
- Si el Node que se eliminará es el Node principal, cambie el puntero principal al siguiente encabezado actual.
if headnode == del then
headnode = del.nextNode
- Establezca siguiente de anterior a del , si existe anterior a del .
if del.nextNode != none
del.nextNode.previousNode = del.previousNode
- Establecer prev de next to del , si existe next to del .
if del.previousNode != none
del.previousNode.nextNode = del.next
C
// C program to implement
// the above approach
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// A node of the doubly linked list
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};
/* Function to delete a node in a Doubly
Linked List. head_ref --> pointer to
head node pointer. del --> pointer
to node to be deleted. */
void deleteNode(struct Node** head_ref,
struct Node* del)
{
// Base case
if (*head_ref == NULL || del == NULL)
return;
// If node to be deleted is head node
if (*head_ref == del)
*head_ref = del->next;
/* Change next only if node to be deleted
is NOT the last node */
if (del->next != NULL)
del->next->prev = del->prev;
/* Change prev only if node to be deleted
is NOT the first node */
if (del->prev != NULL)
del->prev->next = del->next;
// Finally, free the memory occupied by del
free(del);
return;
}
// UTILITY FUNCTIONS
/* Function to insert a node at the
beginning of the Doubly Linked List */
void push(struct Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
/* Since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node->prev = NULL;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// Change prev of head node to new node
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
// Move the head to point to the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly
linked list. This function is same as
printList() of singly linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Start with the empty list
struct Node* head = NULL;
/* Let us create the doubly
linked list 10<->8<->4<->2 */
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 10);
printf(
"Original Linked list ");
printList(head);
/* Delete nodes from the doubly
linked list */
// Delete first node
deleteNode(&head, head);
// Delete middle node
deleteNode(&head, head->next);
// Delete last node
deleteNode(&head, head->next);
/* Modified linked list will be
NULL<-8->NULL */
printf(
"Modified Linked list ");
printList(head);
getchar();
}
Producción:
Original Linked list 10 8 4 2 Modified Linked list 8
Análisis de Complejidad:
- Complejidad Temporal: O(1).
Dado que no se requiere atravesar la lista enlazada, la complejidad del tiempo es constante. - Complejidad espacial: O(1).
Como no se requiere espacio adicional, la complejidad del espacio es constante.
¡Consulte el artículo completo sobre Eliminar un Node en una lista doblemente vinculada para obtener más detalles!
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA