Dada una lista enlazada, escribe una función para invertir cada k Node (donde k es una entrada a la función).
Ejemplo:
Entrada : 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->NULL, K = 3
Salida : 3->2->1->6->5->4- >8->7->NULO
Entrada : 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->NULO, K = 5
Salida : 5->4->3-> 2->1->8->7->6->NULO
Algoritmo: inverso (cabeza, k)
- Invierta la primera sublista de tamaño k. Mientras retrocede, realice un seguimiento del siguiente Node y del Node anterior. Deje que el puntero al siguiente Node sea next y el puntero al Node anterior sea prev . Consulte esta publicación para invertir una lista vinculada.
- head->next = reverse(next, k) (Llama recursivamente al resto de la lista y vincula las dos sublistas)
- Return prev ( prev se convierte en el nuevo encabezado de la lista (ver los diagramas de un método iterativo de esta publicación )
La siguiente imagen muestra cómo funciona la función inversa:
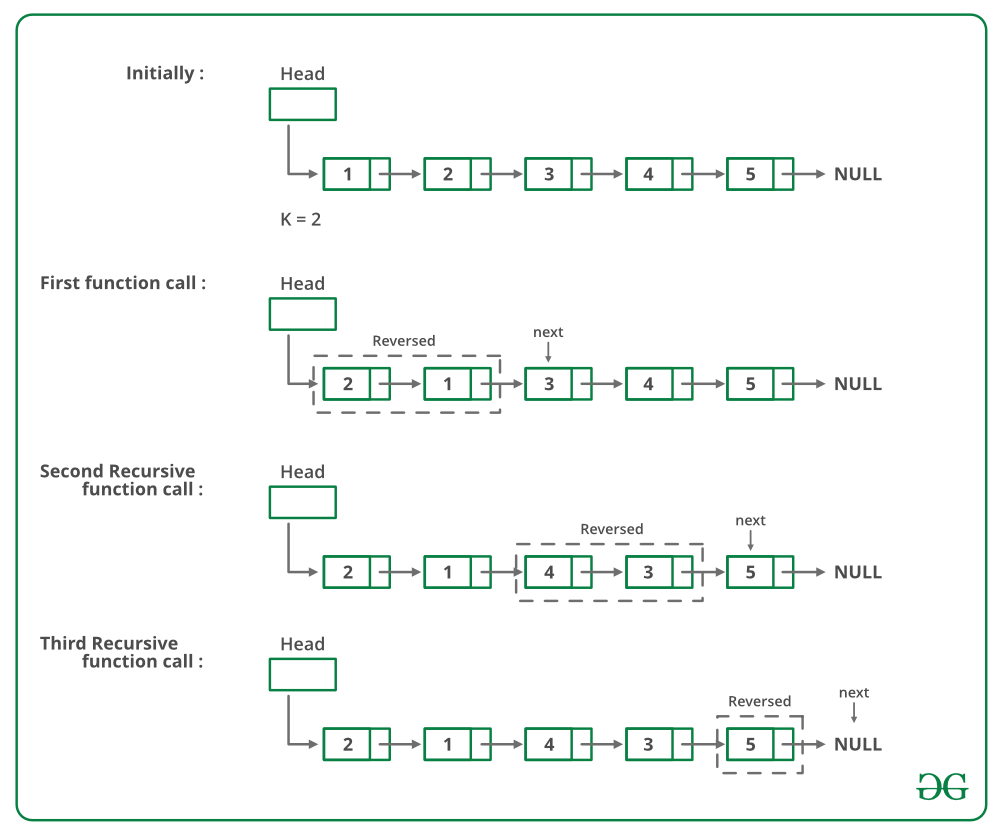
A continuación se muestra la implementación del enfoque anterior:
C++
// C++ program to reverse a linked list
// in groups of given size
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Link list node
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
/* Reverses the linked list in groups
of size k and returns the pointer
to the new head node. */
Node* reverse(Node* head, int k)
{
// Base case
if (!head)
return NULL;
Node* current = head;
Node* next = NULL;
Node* prev = NULL;
int count = 0;
// Reverse first k nodes of the
// linked list
while (current != NULL &&
count < k)
{
next = current->next;
current->next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
count++;
}
/* next is now a pointer to (k+1)th node
Recursively call for the list starting
from current. And make rest of the list
as next of first node */
if (next != NULL)
head->next = reverse(next, k);
// prev is new head of the input list
return prev;
}
// UTILITY FUNCTIONS
// Function to push a node
void push(Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node* new_node = new Node();
// Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the
// new node
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Function to print linked list
void printList(Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Start with the empty list
Node* head = NULL;
/* Create Linked list
1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->9 */
push(&head, 9);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 7);
push(&head, 6);
push(&head, 5);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 1);
cout << "Given linked list ";
printList(head);
head = reverse(head, 3);
cout << "Reversed Linked list ";
printList(head);
return (0);
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
Producción:
Given Linked List 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Reversed list 3 2 1 6 5 4 9 8 7
Análisis de Complejidad:
- Complejidad temporal: O(n).
El recorrido de la lista se realiza solo una vez y tiene ‘n’ elementos. - Espacio Auxiliar: O(n/k).
Para cada Lista Enlazada de tamaño n, n/k o (n/k)+1 se realizarán llamadas durante la recursividad.
Consulte el artículo completo sobre Invertir una lista vinculada en grupos de tamaño determinado | ¡ Establezca 1 para más detalles!
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA