El siguiente artículo es una extensión del artículo discutido aquí .
En la inserción del árbol AVL , usamos la rotación como una herramienta para equilibrar después de que la inserción causara un desequilibrio. En Red-Black tree, usamos dos herramientas para equilibrar.
- Recolorear
- Rotación
Intentamos volver a colorear primero, si el cambio de color no funciona, entonces hacemos la rotación. A continuación se detalla el algoritmo. Los algoritmos tienen principalmente dos casos dependiendo del color del tío. Si el tío es rojo, hacemos recoloring. Si el tío es negro, hacemos rotaciones y/o recoloreados.
El color de un Node NULO se considera NEGRO.
Sea x el Node recién insertado.
- Realice la inserción BST estándar y haga que el color de los Nodes recién insertados sea ROJO.
- Si x es raíz, cambie el color de x a NEGRO (la altura negra del árbol completo aumenta en 1).
- Haga lo siguiente si el color del padre de x no es NEGRO o x no es raíz.
- Si el tío de f x es (los abuelos deben haber sido negros de la propiedad 4 )
- Cambia el color de padre y tío a NEGRO.
- color del abuelo como ROJO.
- 3. Cambie el abuelo de x = x, repita los pasos 2 y 3 para el nuevo x.
- Si el tío de f x es (los abuelos deben haber sido negros de la propiedad 4 )

2. Si el tío de x es NEGRO, entonces puede haber cuatro configuraciones para x, el padre de x ( p ) y el abuelo de x ( g ) (Esto es similar al Árbol AVL )
- Determinar la configuración:
- Caso izquierdo (p es el hijo izquierdo de g y x es el hijo izquierdo de p).
- Caso izquierdo derecho (p es hijo izquierdo de g y x es hijo derecho de p).
- Caso Derecho Derecho (Espejo del caso a).
- Caso Derecho Izquierdo (Espejo del caso c).
- Cambie el padre de x = x, repita los pasos 2 y 3 para la nueva x.
Las siguientes son operaciones a realizar en cuatro subcasos cuando el tío es NEGRO.
Los cuatro casos cuando el tío es NEGRO
Caja Izquierda Izquierda (Ver g, p y x)
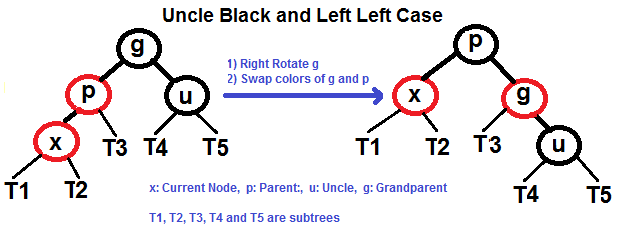
Caja Izquierda Derecha (Ver g, p y x)
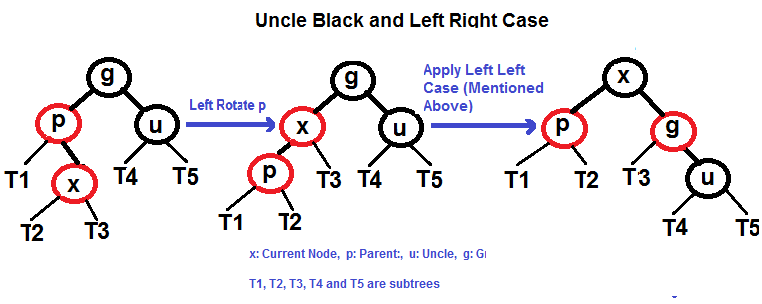
Derecha Derecha Caso (Ver g, p y x)

Caja derecha izquierda (Ver g, p y x)

Ejemplos de inserción

Implementación:
C++
/** C++ implementation for
Red-Black Tree Insertion
This code is adopted from
the code provided by
Dinesh Khandelwal in comments **/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
enum Color {RED, BLACK};
struct Node
{
int data;
bool color;
Node *left, *right, *parent;
// Constructor
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
left = right = parent = NULL;
this->color = RED;
}
};
// Class to represent Red-Black Tree
class RBTree
{
private:
Node *root;
protected:
void rotateLeft(Node *&, Node *&);
void rotateRight(Node *&, Node *&);
void fixViolation(Node *&, Node *&);
public:
// Constructor
RBTree() { root = NULL; }
void insert(const int &n);
void inorder();
void levelOrder();
};
// A recursive function to do inorder traversal
void inorderHelper(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
inorderHelper(root->left);
cout << root->data << " ";
inorderHelper(root->right);
}
/* A utility function to insert
a new node with given key
in BST */
Node* BSTInsert(Node* root, Node *pt)
{
/* If the tree is empty, return a new node */
if (root == NULL)
return pt;
/* Otherwise, recur down the tree */
if (pt->data < root->data)
{
root->left = BSTInsert(root->left, pt);
root->left->parent = root;
}
else if (pt->data > root->data)
{
root->right = BSTInsert(root->right, pt);
root->right->parent = root;
}
/* return the (unchanged) node pointer */
return root;
}
// Utility function to do level order traversal
void levelOrderHelper(Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
std::queue<Node *> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty())
{
Node *temp = q.front();
cout << temp->data << " ";
q.pop();
if (temp->left != NULL)
q.push(temp->left);
if (temp->right != NULL)
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
void RBTree::rotateLeft(Node *&root, Node *&pt)
{
Node *pt_right = pt->right;
pt->right = pt_right->left;
if (pt->right != NULL)
pt->right->parent = pt;
pt_right->parent = pt->parent;
if (pt->parent == NULL)
root = pt_right;
else if (pt == pt->parent->left)
pt->parent->left = pt_right;
else
pt->parent->right = pt_right;
pt_right->left = pt;
pt->parent = pt_right;
}
void RBTree::rotateRight(Node *&root, Node *&pt)
{
Node *pt_left = pt->left;
pt->left = pt_left->right;
if (pt->left != NULL)
pt->left->parent = pt;
pt_left->parent = pt->parent;
if (pt->parent == NULL)
root = pt_left;
else if (pt == pt->parent->left)
pt->parent->left = pt_left;
else
pt->parent->right = pt_left;
pt_left->right = pt;
pt->parent = pt_left;
}
// This function fixes violations
// caused by BST insertion
void RBTree::fixViolation(Node *&root, Node *&pt)
{
Node *parent_pt = NULL;
Node *grand_parent_pt = NULL;
while ((pt != root) && (pt->color != BLACK) &&
(pt->parent->color == RED))
{
parent_pt = pt->parent;
grand_parent_pt = pt->parent->parent;
/* Case : A
Parent of pt is left child
of Grand-parent of pt */
if (parent_pt == grand_parent_pt->left)
{
Node *uncle_pt = grand_parent_pt->right;
/* Case : 1
The uncle of pt is also red
Only Recoloring required */
if (uncle_pt != NULL && uncle_pt->color ==
RED)
{
grand_parent_pt->color = RED;
parent_pt->color = BLACK;
uncle_pt->color = BLACK;
pt = grand_parent_pt;
}
else
{
/* Case : 2
pt is right child of its parent
Left-rotation required */
if (pt == parent_pt->right)
{
rotateLeft(root, parent_pt);
pt = parent_pt;
parent_pt = pt->parent;
}
/* Case : 3
pt is left child of its parent
Right-rotation required */
rotateRight(root, grand_parent_pt);
swap(parent_pt->color,
grand_parent_pt->color);
pt = parent_pt;
}
}
/* Case : B
Parent of pt is right child
of Grand-parent of pt */
else
{
Node *uncle_pt = grand_parent_pt->left;
/* Case : 1
The uncle of pt is also red
Only Recoloring required */
if ((uncle_pt != NULL) && (uncle_pt->color ==
RED))
{
grand_parent_pt->color = RED;
parent_pt->color = BLACK;
uncle_pt->color = BLACK;
pt = grand_parent_pt;
}
else
{
/* Case : 2
pt is left child of its parent
Right-rotation required */
if (pt == parent_pt->left)
{
rotateRight(root, parent_pt);
pt = parent_pt;
parent_pt = pt->parent;
}
/* Case : 3
pt is right child of its parent
Left-rotation required */
rotateLeft(root, grand_parent_pt);
swap(parent_pt->color,
grand_parent_pt->color);
pt = parent_pt;
}
}
}
root->color = BLACK;
}
// Function to insert a new node with given data
void RBTree::insert(const int &data)
{
Node *pt = new Node(data);
// Do a normal BST insert
root = BSTInsert(root, pt);
// fix Red Black Tree violations
fixViolation(root, pt);
}
// Function to do inorder and level order traversals
void RBTree::inorder() { inorderHelper(root);}
void RBTree::levelOrder() { levelOrderHelper(root); }
// Driver Code
int main()
{
RBTree tree;
tree.insert(7);
tree.insert(6);
tree.insert(5);
tree.insert(4);
tree.insert(3);
tree.insert(2);
tree.insert(1);
cout << "Inorder Traversal of Created Tree\n";
tree.inorder();
cout << "\n\nLevel Order Traversal of Created Tree\n";
tree.levelOrder();
return 0;
}
C
/** C implementation for
Red-Black Tree Insertion
This code is provided by
costheta_z **/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure to represent each
// node in a red-black tree
struct node {
int d; // data
int c; // 1-red, 0-black
struct node* p; // parent
struct node* r; // right-child
struct node* l; // left child
};
// global root for the entire tree
struct node* root = NULL;
// function to perform BST insertion of a node
struct node* bst(struct node* trav,
struct node* temp)
{
// If the tree is empty,
// return a new node
if (trav == NULL)
return temp;
// Otherwise recur down the tree
if (temp->d < trav->d)
{
trav->l = bst(trav->l, temp);
trav->l->p = trav;
}
else if (temp->d > trav->d)
{
trav->r = bst(trav->r, temp);
trav->r->p = trav;
}
// Return the (unchanged) node pointer
return trav;
}
// Function performing right rotation
// of the passed node
void rightrotate(struct node* temp)
{
struct node* left = temp->l;
temp->l = left->r;
if (temp->l)
temp->l->p = temp;
left->p = temp->p;
if (!temp->p)
root = left;
else if (temp == temp->p->l)
temp->p->l = left;
else
temp->p->r = left;
left->r = temp;
temp->p = left;
}
// Function performing left rotation
// of the passed node
void leftrotate(struct node* temp)
{
struct node* right = temp->r;
temp->r = right->l;
if (temp->r)
temp->r->p = temp;
right->p = temp->p;
if (!temp->p)
root = right;
else if (temp == temp->p->l)
temp->p->l = right;
else
temp->p->r = right;
right->l = temp;
temp->p = right;
}
// This function fixes violations
// caused by BST insertion
void fixup(struct node* root, struct node* pt)
{
struct node* parent_pt = NULL;
struct node* grand_parent_pt = NULL;
while ((pt != root) && (pt->c != 0)
&& (pt->p->c == 1))
{
parent_pt = pt->p;
grand_parent_pt = pt->p->p;
/* Case : A
Parent of pt is left child
of Grand-parent of
pt */
if (parent_pt == grand_parent_pt->l)
{
struct node* uncle_pt = grand_parent_pt->r;
/* Case : 1
The uncle of pt is also red
Only Recoloring required */
if (uncle_pt != NULL && uncle_pt->c == 1)
{
grand_parent_pt->c = 1;
parent_pt->c = 0;
uncle_pt->c = 0;
pt = grand_parent_pt;
}
else {
/* Case : 2
pt is right child of its parent
Left-rotation required */
if (pt == parent_pt->r) {
leftrotate(parent_pt);
pt = parent_pt;
parent_pt = pt->p;
}
/* Case : 3
pt is left child of its parent
Right-rotation required */
rightrotate(grand_parent_pt);
int t = parent_pt->c;
parent_pt->c = grand_parent_pt->c;
grand_parent_pt->c = t;
pt = parent_pt;
}
}
/* Case : B
Parent of pt is right
child of Grand-parent of
pt */
else {
struct node* uncle_pt = grand_parent_pt->l;
/* Case : 1
The uncle of pt is also red
Only Recoloring required */
if ((uncle_pt != NULL) && (uncle_pt->c == 1))
{
grand_parent_pt->c = 1;
parent_pt->c = 0;
uncle_pt->c = 0;
pt = grand_parent_pt;
}
else {
/* Case : 2
pt is left child of its parent
Right-rotation required */
if (pt == parent_pt->l) {
rightrotate(parent_pt);
pt = parent_pt;
parent_pt = pt->p;
}
/* Case : 3
pt is right child of its parent
Left-rotation required */
leftrotate(grand_parent_pt);
int t = parent_pt->c;
parent_pt->c = grand_parent_pt->c;
grand_parent_pt->c = t;
pt = parent_pt;
}
}
}
root->c = 0;
}
// Function to print inorder traversal
// of the fixated tree
void inorder(struct node* trav)
{
if (trav == NULL)
return;
inorder(trav->l);
printf("%d ", trav->d);
inorder(trav->r);
}
// driver code
int main()
{
int n = 7;
int a[7] = { 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 };
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// allocating memory to the node and initializing:
// 1. color as red
// 2. parent, left and right pointers as NULL
// 3. data as i-th value in the array
struct node* temp
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->r = NULL;
temp->l = NULL;
temp->p = NULL;
temp->d = a[i];
temp->c = 1;
// calling function that performs bst insertion of
// this newly created node
root = bst(root, temp);
// calling function to preserve properties of rb
// tree
fixup(root, temp);
}
printf("Inorder Traversal of Created Tree\n");
inorder(root);
return 0;
}
Inorder Traversal of Created Tree 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Level Order Traversal of Created Tree 6 4 7 2 5 1 3
Complejidad de tiempo: O (log n), ya que la altura del árbol rojo-negro es O (log n) como máximo, y la complejidad de la rotación es constante.
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA