Dados dos números representados por dos listas enlazadas, escribe una función que devuelva la lista de suma. La lista de suma es una representación de lista enlazada de la suma de dos números de entrada. No está permitido modificar las listas. Además, no está permitido usar espacio adicional explícito (Sugerencia: use recursividad).
Ejemplo :
Input: First List: 5->6->3 Second List: 8->4->2 Output: Resultant list: 1->4->0->5
Hemos discutido una solución aquí que es para listas enlazadas donde un dígito menos significativo es el primer Node de las listas y el dígito más significativo es el último Node. En este problema, el Node más significativo es el primer Node y el dígito menos significativo es el último Node y no se nos permite modificar las listas. La recursividad se usa aquí para calcular la suma de derecha a izquierda.
Los siguientes son los pasos.
- Calcular tamaños de dos listas enlazadas dadas.
- Si los tamaños son iguales, calcule la suma usando la recursividad. Mantenga todos los Nodes en la pila de llamadas recursivas hasta el Node más a la derecha, calcule la suma de los Nodes más a la derecha y avance hacia el lado izquierdo.
- Si el tamaño no es el mismo, siga los pasos a continuación:
- Calcular la diferencia de tamaños de dos listas enlazadas. Deje que la diferencia sea dif.
- Mueva los Nodes diff adelante en la lista enlazada más grande. Ahora use el paso 2 para calcular la suma de la lista más pequeña y la sublista derecha (del mismo tamaño) de una lista más grande. Además, almacene el acarreo de esta suma.
- Calcule la suma del acarreo (calculado en el paso anterior) con la sublista izquierda restante de una lista más grande. Los Nodes de esta suma se agregan al principio de la lista de suma obtenida en el paso anterior.
A continuación se muestra una ejecución en seco del enfoque anterior:
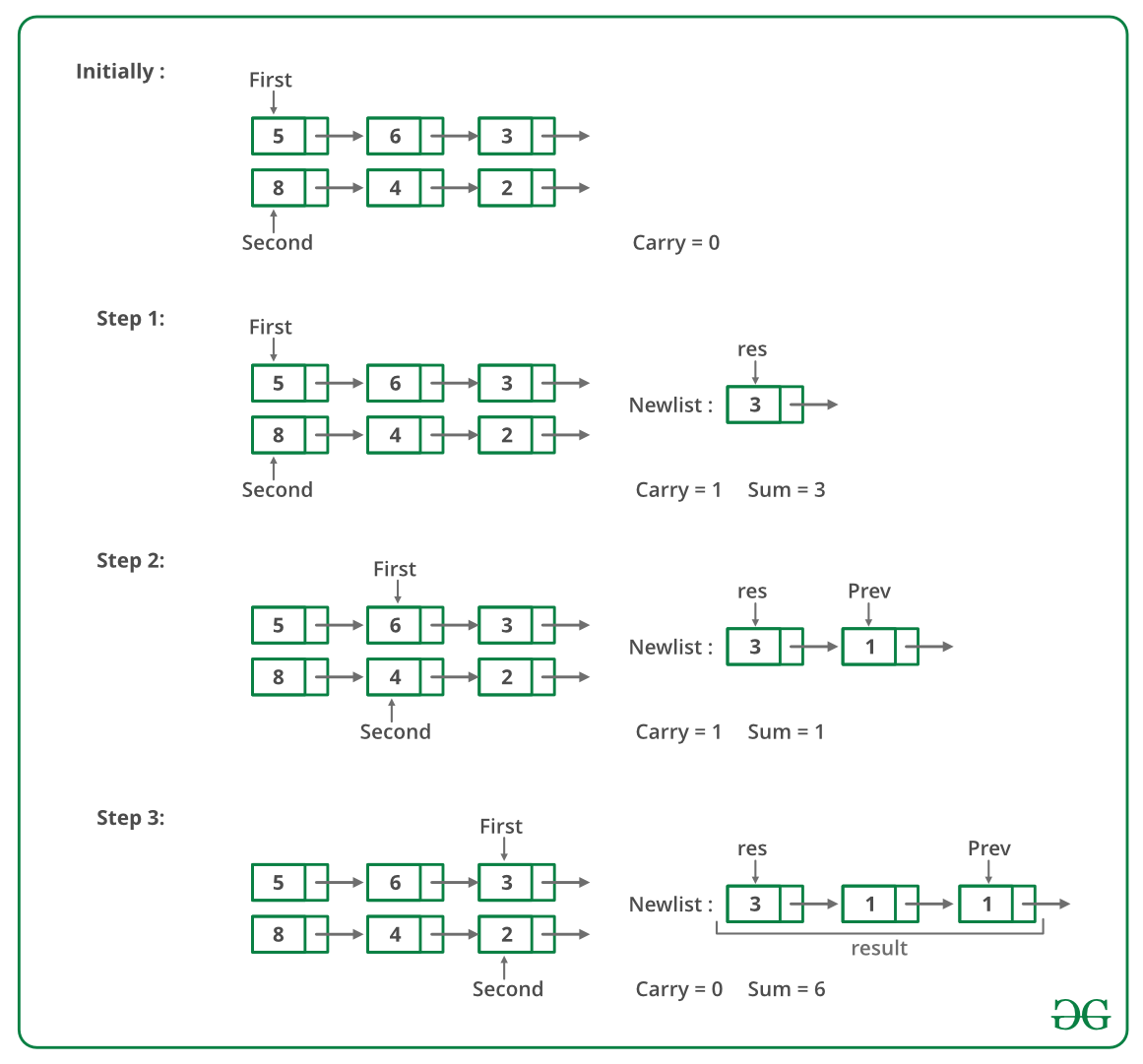
La imagen de abajo es la implementación del enfoque anterior.
C++
// A C++ recursive program to add two
// linked lists
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A linked List Node
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
typedef Node node;
/* A utility function to insert
a node at the beginning of
linked list */
void push(Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node* new_node =
new Node[(sizeof(Node))];
// Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the
// new node
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// Move the head to point to the
// new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// A utility function to print
// linked list
void printList(Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// A utility function to swap
// two pointers
void swapPointer(Node** a,
Node** b)
{
node* t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
/* A utility function to get size
of linked list */
int getSize(Node* node)
{
int size = 0;
while (node != NULL)
{
node = node->next;
size++;
}
return size;
}
// Adds two linked lists of same size
// represented by head1 and head2 and
// returns head of the resultant
// linked list. Carry is propagated
// while returning from the recursion
node* addSameSize(Node* head1,
Node* head2,
int* carry)
{
// Since the function assumes
// linked lists are of same size,
// check any of the two head pointers
if (head1 == NULL)
return NULL;
int sum;
// Allocate memory for sum node
// of current two nodes
Node* result = new Node[(sizeof(Node))];
// Recursively add remaining nodes
// and get the carry
result->next = addSameSize(head1->next,
head2->next,
carry);
// Add digits of current nodes and
// propagated carry
sum = head1->data + head2->data + *carry;
*carry = sum / 10;
sum = sum % 10;
// Assigne the sum to current node of
// resultant list
result->data = sum;
return result;
}
// This function is called after the
// smaller list is added to the bigger
// lists's sublist of same size. Once the
// right sublist is added, the carry
// must be added toe left side of larger
// list to get the final result.
void addCarryToRemaining(Node* head1,
Node* cur,
int* carry,
Node** result)
{
int sum;
// If diff. number of nodes are not
// traversed, add carry
if (head1 != cur)
{
addCarryToRemaining(head1->next, cur,
carry, result);
sum = head1->data + *carry;
*carry = sum / 10;
sum %= 10;
// Add this node to the front of
// the result
push(result, sum);
}
}
// The main function that adds two
// linked lists represented by head1
// and head2. The sum of two lists is
// stored in a list referred by result
void addList(Node* head1,
Node* head2,
Node** result)
{
Node* cur;
// First list is empty
if (head1 == NULL)
{
*result = head2;
return;
}
// Second list is empty
else if (head2 == NULL)
{
*result = head1;
return;
}
int size1 = getSize(head1);
int size2 = getSize(head2);
int carry = 0;
// Add same size lists
if (size1 == size2)
*result = addSameSize(head1,
head2,
&carry);
else
{
int diff = abs(size1 - size2);
// First list should always be larger
// than second list. If not, swap
// pointers
if (size1 < size2)
swapPointer(&head1, &head2);
// Move diff. number of nodes
// in first list
for (cur = head1; diff--;
cur = cur->next);
// Get addition of same size lists
*result = addSameSize(cur, head2,
&carry);
// Get addition of remaining first
// list and carry
addCarryToRemaining(head1, cur,
&carry, result);
}
// If some carry is still there, add a
// new node to the front of the result
// list. e.g. 999 and 87
if (carry)
push(result, carry);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node *head1 = NULL,
*head2 = NULL,
*result = NULL;
int arr1[] = {9, 9, 9};
int arr2[] = {1, 8};
int size1 = (sizeof(arr1) /
sizeof(arr1[0]));
int size2 = (sizeof(arr2) /
sizeof(arr2[0]));
// Create first list as 9->9->9
int i;
for (i = size1 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
push(&head1, arr1[i]);
// Create second list as 1->8
for (i = size2 - 1; i >= 0; --i)
push(&head2, arr2[i]);
addList(head1, head2, &result);
printList(result);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
Producción:
1 0 1 7
Complejidad de tiempo:
O(m+n) donde m y n son los tamaños de dos listas enlazadas dadas.
Enfoque iterativo:
esta implementación no tiene ninguna sobrecarga de llamadas recursivas, lo que significa que es una solución iterativa.
Dado que necesitamos comenzar a agregar números de la última de las dos listas vinculadas. Entonces, aquí usaremos la estructura de datos de pila para implementar esto.
- Primero haremos dos pilas de las dos listas enlazadas dadas.
- Luego, ejecutaremos un bucle hasta que ambas pilas queden vacías.
- en cada iteración, mantenemos la pista del acarreo.
- Al final, si carry>0, eso significa que necesitamos un Node adicional al comienzo de la lista resultante para acomodar este carry.
C++
// C++ Iterative program to add two
// linked lists
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A linked List Node
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
// To push a new node to
// linked list
void push(Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
Node* new_node =
new Node[(sizeof(Node))];
// Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the
// new node
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// To add two new numbers
Node* addTwoNumList(Node* l1,
Node* l2)
{
stack<int> s1,s2;
while(l1 != NULL)
{
s1.push(l1->data);
l1 = l1->next;
}
while(l2 != NULL)
{
s2.push(l2->data);
l2 = l2->next;
}
int carry = 0;
Node* result = NULL;
while(s1.empty() == false ||
s2.empty() == false)
{
int a = 0,b = 0;
if(s1.empty() == false)
{
a = s1.top();
s1.pop();
}
if(s2.empty() == false)
{
b = s2.top();
s2.pop();
}
int total = a + b + carry;
Node* temp = new Node();
temp->data = total % 10;
carry = total / 10;
if(result == NULL)
{
result = temp;
}
else
{
temp->next = result;
result = temp;
}
}
if(carry != 0)
{
Node* temp = new Node();
temp->data = carry;
temp->next = result;
result = temp;
}
return result;
}
// To print a linked list
void printList(Node *node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node *head1 = NULL,
*head2 = NULL;
int arr1[] = {5, 6, 7};
int arr2[] = {1, 8};
int size1 = (sizeof(arr1) /
sizeof(arr1[0]));
int size2 = (sizeof(arr2) /
sizeof(arr2[0]));
// Create first list as 5->6->7
int i;
for (i = size1-1; i >= 0; --i)
push(&head1, arr1[i]);
// Create second list as 1->8
for (i = size2-1; i >= 0; --i)
push(&head2, arr2[i]);
Node* result =
addTwoNumList(head1, head2);
printList(result);
return 0;
}
Producción:
5 8 5
Complejidad de tiempo: O(m + n) donde m y n son el número de Nodes en las dos listas enlazadas dadas.
Espacio auxiliar: O(n) donde n es el número de elementos en la pila
Artículo relacionado: Suma dos números representados por listas enlazadas | Conjunto 1
Consulte el artículo completo sobre Agregar dos números representados por listas enlazadas | Set 2 para más detalles!
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA