Escriba una función detectAndCountLoop() que verifique si una lista enlazada dada contiene un bucle y, si el bucle está presente, devuelve el recuento de Nodes en el bucle. Por ejemplo, el bucle está presente en la lista de enlaces a continuación y la longitud del bucle es 4. Si el bucle no está presente, la función debería devolver 0.
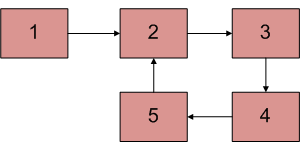
Enfoque:
Se sabe que el algoritmo de detección del ciclo de Floyd termina cuando los punteros rápido y lento se encuentran en un punto común. También se sabe que este punto común es uno de los Nodes del bucle. Almacene la dirección de este punto común en una variable de puntero, digamos (ptr). Luego inicialice un contador con 1 y comience desde el punto común y continúe visitando el siguiente Node y aumentando el contador hasta que se alcance nuevamente el puntero común.
En ese punto, el valor del contador será igual a la longitud del bucle.
Algoritmo:
- Encuentre el punto común en el bucle utilizando el algoritmo de detección del ciclo de Floyd
- Almacene el puntero en una variable temporal y mantenga un conteo = 0
- Recorra la lista enlazada hasta que se vuelva a alcanzar el mismo Node y aumente el conteo mientras pasa al siguiente Node.
- Imprimir el conteo como longitud de bucle
Python3
# Python program to detect a loop and
# find the length of the loop
# Node defining class
class Node:
# Function to make a node
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.next = None
# Linked List defining and loop
# length finding class
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize the
# head of the linked list
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to insert a new
# node at the end
def AddNode(self, val):
if self.head is None:
self.head = Node(val)
else:
curr = self.head
while(curr.next):
curr = curr.next
curr.next = Node(val)
# Function to create a loop in the
# Linked List. This function creates
# a loop by connecting the last node
# to n^th node of the linked list,
# (counting first node as 1)
def CreateLoop(self, n):
# LoopNode is the connecting node to
# the last node of linked list
LoopNode = self.head
for _ in range(1, n):
LoopNode = LoopNode.next
# end is the last node of the
# Linked List
end = self.head
while(end.next):
end = end.next
# Creating the loop
end.next = LoopNode
# Function to detect the loop and return
# the length of the loop if the returned
# value is zero, which means that either
# the linked list is empty or the linked
# list doesn't have any loop
def detectLoop(self):
# If linked list is empty then there
# is no loop, so return 0
if self.head is None:
return 0
# Using Floyd’s Cycle-Finding
# Algorithm/ Slow-Fast Pointer Method
slow = self.head
fast = self.head
# To show that both slow and fast
# are at start of the Linked List
flag = 0
while(slow and slow.next and fast and
fast.next and fast.next.next):
if slow == fast and flag != 0:
# Means loop is confirmed in the
# Linked List. Now slow and fast
# are both at the same node which
# is part of the loop
count = 1
slow = slow.next
while(slow != fast):
slow = slow.next
count += 1
return count
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
flag = 1
return 0 # No loop
# Setting up the code
# Making a Linked List and
# adding the nodes
myLL = LinkedList()
myLL.AddNode(1)
myLL.AddNode(2)
myLL.AddNode(3)
myLL.AddNode(4)
myLL.AddNode(5)
# Creating a loop in the linked List
# Loop is created by connecting the
# last node of linked list to n^th node
# 1<= n <= len(LinkedList)
myLL.CreateLoop(2)
# Checking for Loop in the Linked List
# and printing the length of the loop
loopLength = myLL.detectLoop()
if myLL.head is None:
print("Linked list is empty")
else:
print(str(loopLength))
# This code is contributed by _Ashutosh
Producción:
4
Análisis de Complejidad:
- Complejidad temporal: O(n).
Solo se necesita un recorrido de la lista enlazada. - Espacio Auxiliar: O(1).
Como no se requiere espacio adicional.
¡ Consulte el artículo completo sobre Encontrar la longitud del bucle en la lista vinculada para obtener más detalles!
Publicación traducida automáticamente
Artículo escrito por GeeksforGeeks-1 y traducido por Barcelona Geeks. The original can be accessed here. Licence: CCBY-SA